Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
Q1: (i) Draw the sound waves for a low pitched and the high pitched sound.
(ii) Write one use of ultrasonography.
(iii) Which wave property determines pitch?
Ans:
(i) The diagram is as shown: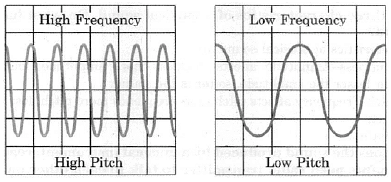 Frequency of sound wave(ii) Ultrasonography is used for examination of the fetus during pregnancy to detect congenital defects and growth abnormalities.
Frequency of sound wave(ii) Ultrasonography is used for examination of the fetus during pregnancy to detect congenital defects and growth abnormalities.
(iii) The pitch depends on frequency.
Q2: The stem of a tuning fork is pressed against a table top. Answer the following questions :
(i) Would the above action produce any audible sound?
(ii) Does the above action cause the table to set into vibrations?
(iii) If the answer above is yes, what type of vibrations are they?
(iv) Under what conditions does the above action lead to resonance?
Ans:
(i) Yes, there is an audible sound produced.
(ii) Yes, the table top is set into ‘forced vibrations’ by this.
(iii) The vibrations are forced vibrations.
(iv) P ressing the stem of a vibrating tuning fork against a table top, would lead to resonance if the frequency of the tuning fork equals the natural frequency of oscillations of the table top.
Q3: How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
Ans : When a vibrating object moves forward, it pushes and compresses the air in front of it creating a region of high pressure called compression. This compression starts to move away from the vibrating object. When vibrating object moves backwards, it creates a region of low pressure called refraction. As the object moves forth and back rapidly, a series of compressions and refractions are created in the air. These produce the sound wave that propagates through the medium. This continues until the sound wave reaches to the ear of the listener.
Q4: Write conditions for the production of an echo.
Ans: Conditions for the production of an echo are :
- Time gap: The echo is heard if the original sound reflected by an obstacle reaches our ears after at least 0.1 seconds.
- Distance: The minimum distance between the sound source and the obstacle must be 17.2 metres in air at 25°C for a clear echo.
- Nature of the obstacle: The reflecting surface must be rigid, such as a building, hill, or cliff.
- Size of the obstacle: The obstacle should be large enough to effectively reflect the sound.
Q5: With the help of a labelled diagram show that sound needs a material medium for its propagation.
Ans: A well labelled diagram is as shown :
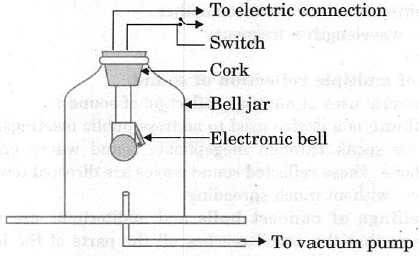 Bell jar experiment
Bell jar experiment
(i) Take an electric circuit which consists of a cell, a switch and an electric bell arranged inside a bell jar, which stands on the platform of an evacuating pump.
(ii) The switch of the bell is pressed to close the electric circuit. When there is air within the bell jar, sound is heard. Air is now pumped out of the bell jar. When the air is completely removed from the bell jar, no sound is heard as it is obvious from fig. because the medium of air which has to carry energy from the bell to the bell jar is removed. It shows that sound needs material medium for its propagation.
Q6: A particular transmitter of Aakashvani broadcasts at 420.5 m wavelength. (Given the speed of radio waves 3 × 108 ms–1) Calculate the frequency at which the radio station broadcasts its program. What is the direction of oscillations of the medium particles through which a :
(i) Transverse w ave is propagating?
(ii) Longitudinal wave is propagating?
Ans:
Given
λ = 420.5 m, v = 3 × 108 ms–1, n = ?
Using the expression v = nλ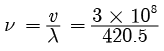
= 7 × 105 Hz
(i) The particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
(ii) The particles oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
Q7: (i) State two characteristics of wave motion.
(ii) W hat is the relation between frequency, wavelength and speed of a wave?
Ans:
(i) A wave motion is periodic in nature. The particles of the medium do not move from their mean position but execute vibration but only the energy is transmitted from one point to another.
(ii) Speed = wavelen gth × frequency
v = λ x v
Q8:Give uses of multiple reflection of sound.
Ans: There are several uses of multiple reflection of sound :
- Megaphone: This horn-shaped device is used to address public gatherings. When you speak into a megaphone, sound waves are reflected and directed towards the audience, minimising spreading.
- Concert Halls: The ceilings in concert halls and auditoriums are often curved. This design helps sound reflect evenly throughout the space, ensuring all areas receive sound. Additionally, these ceilings use sound-absorbing materials to reduce reverberation.
- Stethoscope: Doctors use this instrument to listen to sounds from the heart and lungs. The sounds produced by these organs reach the doctor's ears through multiple reflections.
- Sound Boards: These are curved surfaces (concave) placed in large halls to direct sound waves towards the audience. The speaker is positioned at the focus of the sound board, enhancing sound delivery.
- Hearing Aids: For individuals with hearing difficulties, hearing aids concentrate incoming sound waves into a narrow beam through reflection. This beam vibrates the ear's diaphragm with greater amplitude, improving hearing ability.
Q9: Give application of ultrasound (ultrasonic waves).
Ans: Ultrasonic waves have number of uses :
- Ultrasonic vibrations are used to homogenise milk, breaking down larger fat particles into smaller ones.
- In dishwashing machines, ultrasonic vibrations help clean utensils by agitating detergent particles.
- These vibrations can create a depression effect in pests like rats and cockroaches.
- Ultrasonic waves are essential for monitoring fetal growth during pregnancy.
- They are also effective in relieving pain in joints and muscles.
- In industry, ultrasonic vibrations detect flaws in metal products and measure their thickness.
Q10: A tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds. Calculate the frequency to the tuning fork.
Ans: The tuning fork produces 1024 waves in 4 seconds. To find the frequency:
- Frequency (v) is the number of vibrations per second.
- Calculate by dividing the total number of waves by the time:
- Frequency = 1024 waves / 4 seconds
- Thus, Frequency = 256 Hz.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
| 1. What is sound and how does it travel through different mediums? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of sound waves? |  |
| 3. How does sound affect human health and well-being? |  |
| 4. What are sound frequencies and how do they impact sound perception? |  |
| 5. How can sound be measured and what tools are used for this purpose? |  |

















