Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Question Answers - Democratic Politics - I
Q1. How can you say that the forms of government ruling in countries like Myanmar, Chile, Nepal and Saudi Arabia are not Democratic?
Ans: Democracy is a form of government where rulers are elected by the people. This definition helps us identify governments that are not democratic, such as those in Myanmar, Chile, Nepal, and Saudi Arabia. Here’s why these countries do not qualify as democratic:
- Myanmar: The country is ruled by military leaders who are not elected. The army controls the government, and the people have no influence over this.
- Chile: Under Pinochet, the government was not elected by the people, making it undemocratic.
- Nepal and Saudi Arabia: The kings in these countries rule by virtue of their birthright, not through a democratic election by the populace.
Q2. ‘The elections held in China and Mexico are not fair elections.’ Explain.
Ans: Elections are held in both China and Mexico, but they are not fair. The electoral processes in these countries do not provide genuine choices for voters.
- In China, citizens can only vote for candidates approved by the ruling party, limiting their options.
- In Mexico, while it appears that voters have choices, the ruling party has historically maintained power, making it nearly impossible for opposition parties to win.
For a system to be considered a true democracy, elections must allow for a real chance of change in leadership. This means:
- Voters should have the ability to choose from multiple political alternatives.
- Those currently in power must have a fair possibility of losing.
Q3. How are elections in India different from those of Mexico?
Ans: India and Mexico both have a multi-party system, but their election processes differ significantly:
- Free and Fair Elections: In India, elections are generally considered free and fair, allowing for a real chance of losing. In contrast, from 1930 to 2000, the PRI (Institutional Revolutionary Party) in Mexico won every election.
- Election Oversight: During elections, Indian government officials operate under the authority of the Election Commission, not the government. This is not the case in Mexico.
- Election Frequency: Elections in India occur every five years, while Mexico holds elections every six years.
Q4. “Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.” Explain.
Ans: Democracy provides a method to deal with differences and conflicts.
In any society, differences in opinions and interests are inevitable, especially in a diverse country like ours. Here are some key points:
- People come from various regions, speak different languages, practise different religions, and belong to different castes.
- These differences can lead to clashes between groups, making peaceful coexistence challenging.
Democracy offers a peaceful way to manage these conflicts:
- In a democracy, there are no permanent winners or losers.
- It allows different groups to coexist peacefully, promoting unity in a diverse nation like India.
Additionally, democracy enhances the dignity of citizens by involving them in decision-making processes. This approach:
- Encourages careful consideration of important decisions.
- Reduces the likelihood of rash or irresponsible choices.
Q5. ‘A democratic government rules within limits set by constitutional law and citizens’ right’. Explain.
Ans: A democratic government cannot act without limits, even after winning an election. It must adhere to certain fundamental rules, particularly those that protect minority rights. Major decisions require thorough consultations.
- Each office holder has specific rights and responsibilities defined by the Constitution and the law.
- They are accountable to both the public and independent officials.
- All individuals should be treated equally under the law.
- Citizens must have the freedom to think, express opinions, form associations, protest, and engage in political activities.
Q6. What steps did president Robert Mugabe of Zimbabwe take to remain in power?
Ans: Robert Mugabe ruled Zimbabwe from its independence in 1980 until he was ousted in 2017. His government employed several tactics to maintain power:
- Regular Elections: Elections were consistently held, with ZANU-PF winning each time. While Mugabe enjoyed some popularity, he also engaged in unfair practices to secure victories.
- Constitutional Changes: The government altered the Constitution multiple times to enhance presidential powers and reduce accountability.
- Suppression of Opposition: Opposition party members faced harassment, and their meetings were often disrupted. Public protests were declared illegal, and laws restricted criticism of the President.
- Media Control: The government controlled television and radio, promoting only its narrative. Independent newspapers faced harassment, and journalists critical of the government were targeted.
- Judicial Pressure: The government ignored court rulings against it and pressured judges to comply with its demands.
Q7. What is representative democracy? Why is it criticised?
Ans: Representative democracy is a system of government where elected representatives make decisions on behalf of the people. This approach is necessary because it is impractical for everyone to participate in decision-making directly. Despite its widespread acceptance and praise, representative democracy faces several criticisms:
- Political competition: The focus on power struggles often overshadows ethical considerations.
- Decision-making delays: The need to consult multiple leaders can slow down important decisions.
- Misguided leaders: Elected officials may not always act in the best interest of their constituents, resulting in poor choices.
- Corruption: The competitive nature of elections can foster corrupt practices.
- Lack of knowledge: Many citizens may not be well-informed enough to make significant decisions.
While democracy is not a perfect solution to all societal issues, it provides a framework for governance that allows for public participation and accountability. However, it is essential to critically evaluate its effectiveness and the arguments against it.
Q8. Is it right to criticise democracy? Give your opinion.
Ans: Arguments against democracy
- Leaders frequently change, leading to instability.
- Democracy often revolves around political competition, which can lack moral considerations.
- Consulting many people can result in delays in decision-making.
- Elected leaders may not always act in the best interest of the public, leading to poor decisions.
- Corruption can arise due to the competitive nature of elections.
- Ordinary citizens may lack the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Despite these criticisms, it is important to note that democracy is not a perfect solution for all issues. It has not eradicated poverty in our country or globally.
Q9. How is Zimbabwe an example of non-democratic country?
Ans: Zimbabwe became independent in 1980 and has been ruled by the ZANU-PF party, led by Robert Mugabe, since then.
- Elections are held regularly, but ZANU-PF always wins. Although Mugabe was popular, he employed unfair practices during elections.
- The government has amended the Constitution multiple times to enhance presidential powers and reduce accountability.
- Opposition party members face harassment, and their meetings are often disrupted. Public protests are deemed illegal.
- A law restricts the right to criticise the President, limiting free speech.
- Media is government-controlled, promoting only the ruling party's perspective. Independent journalists face intimidation for opposing views.
Mugabe was ousted in 2017, illustrating that while popular support is crucial in a democracy, it does not guarantee democratic practices.
Q10. Give broader meaning of democracy.
Ans: Democracy is often viewed as a form of government, but its meaning extends beyond that. Here are some broader interpretations:
- A democratic family allows all members to participate in decision-making, ensuring everyone's opinion is valued.
- Democracy can also represent an ideal standard that societies strive for, where no one goes to bed hungry and all citizens have an equal role in decisions.
Understanding democracy as an ideal helps us evaluate existing systems and identify their weaknesses. It emphasises that:
- Democratic decisions involve consultation and consent from all affected individuals.
- Everyone, regardless of power, should have an equal say in decision-making.
This principle can apply to various aspects of life, not just government. For example, in a small community, decisions can be made collectively, reflecting true democratic practice.
Q11. “Democracy allows people to correct their own mistakes.” Explain.
Ans: Democracy does not guarantee that mistakes won't happen; no government can assure that. However, it offers significant advantages:
- Transparency: Mistakes in a democracy cannot be hidden for long.
- Public Discussion: There is space for open dialogue about errors.
- Correction Mechanism: Rulers can change their decisions or be replaced, which is not possible in non-democratic systems.
Thus, democracy provides a way to correct mistakes and enhances the dignity of all citizens. It acknowledges that every individual, regardless of their background, has equal status and responsibility in governance.
Q12. Which is the most common form of democracy? Why is it important in today’s world? Or why is direct democracy not possible in the present day world? Or why do we need a representative democracy in the present day world?
Ans: The most common form of democracy today is representative democracy. In democratic countries, not everyone rules directly; instead, a majority makes decisions through their elected representatives. This system is crucial for several reasons:
- Modern democracies involve a large number of people, making it impractical for everyone to gather and make decisions together.
- Most citizens lack the time or desire to participate in every decision, which is why representatives are essential.
- Representative democracy allows for efficient governance and better representation of diverse interests.
In smaller communities, direct decision-making can occur, but for larger populations, representative democracy is necessary.
Q13. Why do we need a representative democracy in the present day world?
Ans: The most common form of democracy today is representative democracy. In democratic countries, not everyone rules directly. Instead, a majority makes decisions through their elected representatives. This system is crucial for several reasons:
- Modern democracies involve a large number of people, making it physically impossible for everyone to gather and make decisions together.
- Even if they could meet, most citizens lack the time, desire, or skills to participate in every decision.
Q14. How can you say that Saudi Arabia, Estonia and Fiji are not democratic countries in true sense of the term?
Ans: Although the principle of Universal Adult Franchise is widely accepted, there are still significant instances of unequal voting rights:
- In Saudi Arabia, women were denied the right to vote until 2015.
- Estonia has citizenship rules that make it difficult for the Russian minority to obtain voting rights.
- In Fiji, the electoral system values the vote of an indigenous Fijian more than that of an Indian-Fijian.
These factors highlight the challenges to true democratic representation in these countries.
Q15. Explain how elections are held in China. Why is the government there always formed by the Communist Party only?
Ans: Elections in China occur every five years to elect the country's parliament, known as the National People's Congress (NPC).
The NPC has the authority to appoint the President of China and consists of nearly 3,000 members elected from across the nation, including some from the military.
Key points about the electoral process include:
- Candidates must receive approval from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) before running.
- Only members of the CCP or eight smaller allied parties can contest elections.
- This system ensures that the government is consistently formed by the Communist Party.
Q16. “Till 2000, Mexican people seem to have a choice to elect their leader, but practically they had no choice”. Support this statement with valid reasons.
Ans: The elections in Mexico until 2000 were largely undemocratic. Here are some key reasons:
- Every election was won by the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), with opposition parties failing to secure victories.
- The PRI employed various manipulative tactics to ensure its success, including requiring government employees to attend party meetings.
- Government school teachers pressured parents to vote for the PRI.
- The media predominantly ignored opposition parties, focusing mainly on their criticisms.
- Polling booths were sometimes relocated at the last minute, complicating the voting process.
- The PRI invested significant funds in its election campaigns.
These factors indicate that while it appeared people had a choice, in reality, they did not. The ruling party was virtually unstoppable, regardless of public sentiment. Therefore, these elections cannot be considered a true representation of democracy.
Q17. What arguments are given against democracy? Enlist any five.
Ans: Arguments against democracy often highlight its perceived flaws. Here are some common criticisms:
- Frequent leadership changes can create instability.
- Democracy often involves political competition, which may overshadow moral considerations.
- Consulting many leaders can lead to delays in decision-making.
- Elected leaders may not always understand the best interests of the people, resulting in poor choices.
- Electoral competition can foster corruption.
- Some argue that ordinary people lack the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Despite these criticisms, it's important to remember that democracy is not a perfect solution for all issues. It has not eradicated poverty in many regions, including our own.
Q18. Give some of the features of non-democratic government that are also applicable to Pakistan under Pervez Musharraf.
Ans: In Pakistan, General Pervez Musharraf led a military coup in October 1999, overthrowing the democratically elected government. He declared himself the 'Chief Executive' and later became President. In 2002, he held a controversial referendum that allegedly involved malpractices and fraud, granting him a five-year extension.
Key features of Musharraf's non-democratic government include:
- Amendment of the Constitution through a 'Legal Framework Order' in August 2002, allowing him to dismiss national and provincial assemblies.
- Supervision of the civilian cabinet by a National Security Council dominated by military officers.
- While elections were held for national and provincial assemblies, the real power remained with military officials and Musharraf.
Thus, Pakistan under Musharraf cannot be considered a democracy. The rulers were not truly elected by the people, and the final decision-making power rested with those not elected. This situation contradicts the fundamental principles of democratic governance.
Q19. What are the merits or benefits of democracy?
Ans: Democracy is rapidly gaining popularity worldwide as people seek it and fight for it. Many influential figures have praised this form of government, making it a preferred choice over other political systems. Supporters of democracy highlight several key benefits:
- Responsiveness to Needs: Democracy is more effective than non-democratic systems in addressing the needs of the people. While non-democratic governments may respond to public needs, their actions depend on the rulers' desires. In contrast, democratic leaders must consider the people's wishes, making them more accountable.
- Consultation and Discussion: Democratic decisions involve extensive consultation and discussion. This collaborative approach reduces the likelihood of hasty or irresponsible choices, thereby enhancing the quality of decision-making.
- Conflict Resolution: Democracy offers a framework for managing differences and conflicts. In diverse nations like India, it fosters cooperation and peaceful solutions between various groups, preventing clashes.
- Dignity of Citizens: Democracy is rooted in the principle of political equality, recognising that every individual, regardless of their background, holds the same status. Citizens are not subjects of a ruler; they are the rulers themselves, which enhances their dignity.
- Self-Correction: While mistakes can occur in any government, democracies have mechanisms for correcting errors. Public discussion allows for transparency and accountability, ensuring that mistakes are addressed and rectified.
Q20. Compare some of the major features of democratic and non-democratic governments.
Ans: A democratic government differs significantly from a non-democratic government in several ways: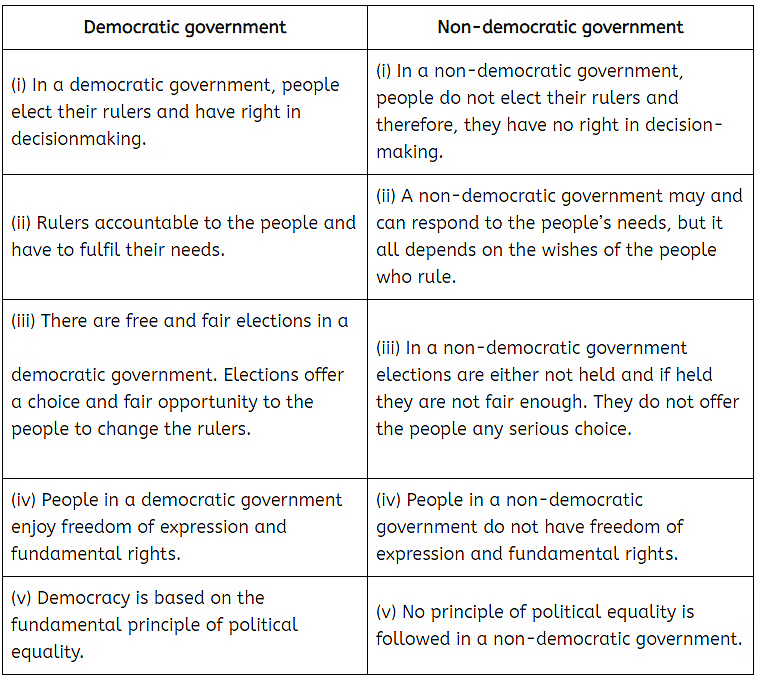
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Question Answers - Democratic Politics - I
| 1. What are the key features of democracy? |  |
| 2. Why is democracy important for society? |  |
| 3. How does democracy differ from other forms of government? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by democracies today? |  |
| 5. How can citizens contribute to strengthening democracy? |  |





















