Important Diagrams: Metals & Non-Metals | Science Class 10 PDF Download
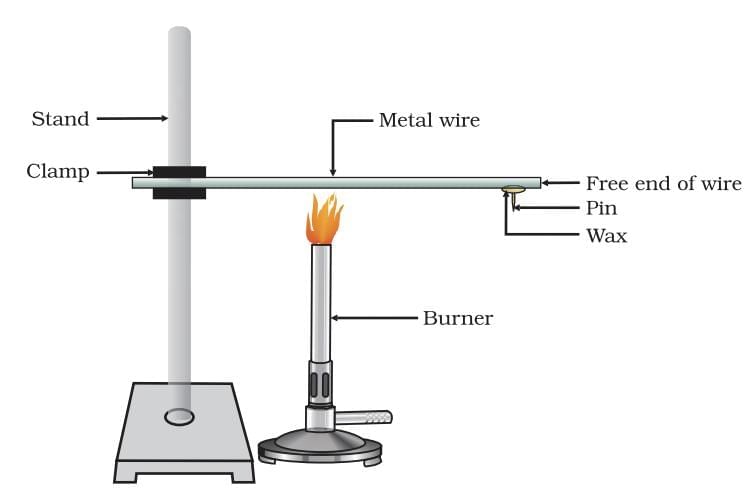
Heat conductance or metal
Heat conductance is the ability of a material to allow heat to pass through it. Metals are good conductor of heat
Order of conductivity: Silver > Copper > Gold > Aluminium > Iron
Electricity conductance of metals
Electrical conductance is the ability of a material to allow electric current to pass through it.
Conductivity order (high to low): Silver > Copper > Gold > Aluminium > Iron > Lead
Reaction of metals with water
Metals react with water and produce a metal oxide and hydrogen gas. However all metals do not react with water.
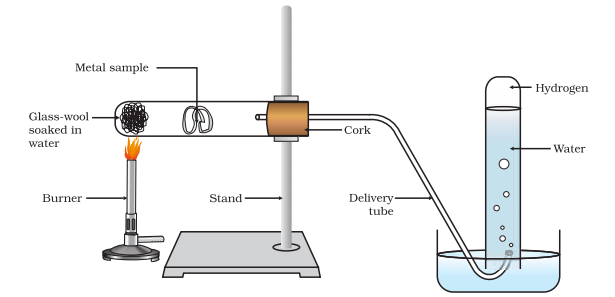 Action of steam on a metal
Action of steam on a metal
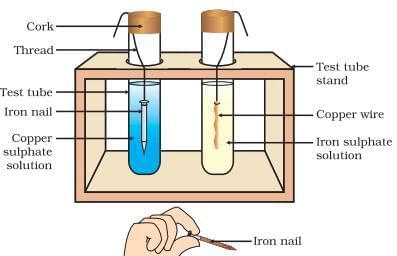
Reaction of Metals with Solutions of other Metal Salts
Metal A + Salt solution B → Salt solution A + Metal B
Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution form.
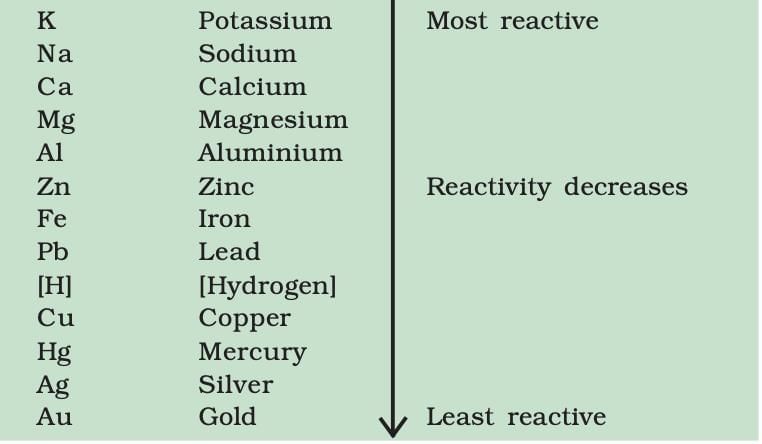
The Reactivity Series
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities.
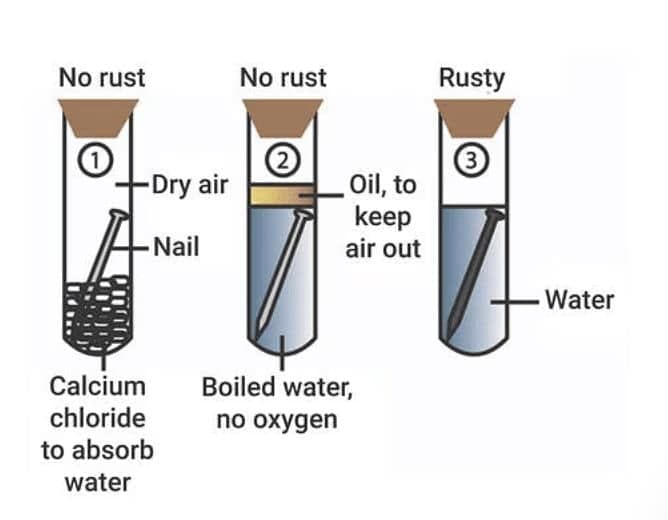
Corrosion
The surface of some metals gets corroded when they are exposed to moist air for a long period. This is called corrosion.
Ionic Bonding in NaCl
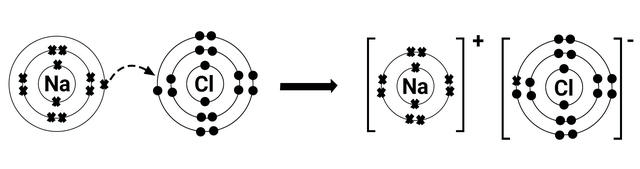
Sodium (Na): Atomic number 11 → Electron configuration: 2, 8, 1
Chlorine (Cl): Atomic number 17 → Electron configuration: 2, 8, 7
Atoms aim to achieve a stable octet by transferring electrons.
Sodium (Na) wants to lose 1 electron → forms Na⁺
Chlorine (Cl) wants to gain 1 electron → forms Cl⁻
Electron Transfer:
Na → Na⁺ + 1e⁻
Cl + 1e⁻ → Cl⁻
This gain and loss of electrons results in ionic bond formation.
Ionic Bonding in MgCl2
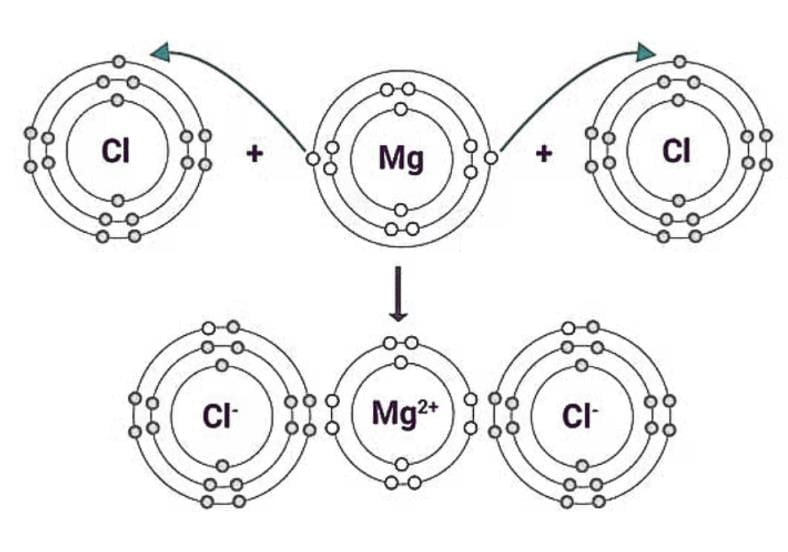
Magnesium (Mg): Atomic number 12 → Electron configuration: 2, 8, 2
Chlorine (Cl): Atomic number 17 → Electron configuration: 2, 8, 7
Atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable octet (like noble gases).
Magnesium wants to lose 2 electrons → forms Mg²⁺ ion.
Each Chlorine atom wants to gain 1 electron → forms Cl⁻ ion.
Atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable octet (like noble gases).
Magnesium wants to lose 2 electrons → forms Mg²⁺ ion.
Each Chlorine atom wants to gain 1 electron → forms Cl⁻ ion.
This gain and loss of electrons results in ionic bond formation.
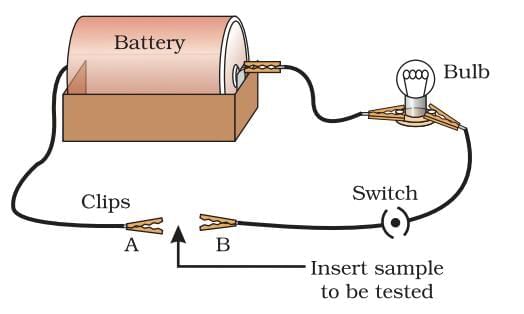
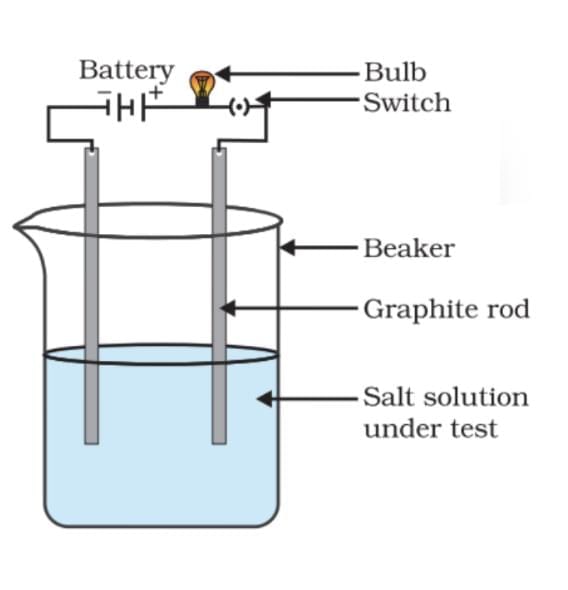
Salt Solution conductance
A salt solution conducts electricity because it contains ions.
These ions are charged particles that move and carry current in solution.
When voltage is applied, positive ions move to the negative electrode and negative ions move to the positive electrode.
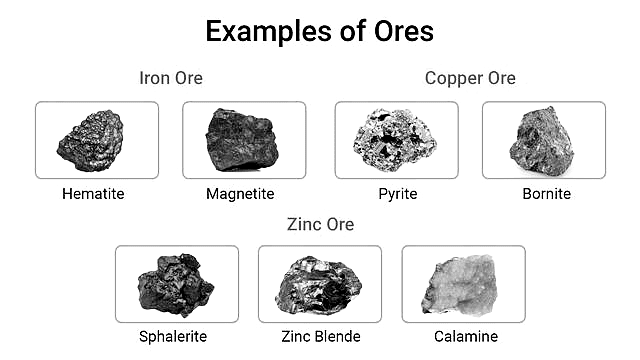
Occurrence of Ore
An ore is a naturally occurring rock or mineral from which a metal can be profitably extracted
Most metals occur in combined form
Reactivity of metal determines how it occurs (native or combined)
Extraction depends on the cost and feasibility.
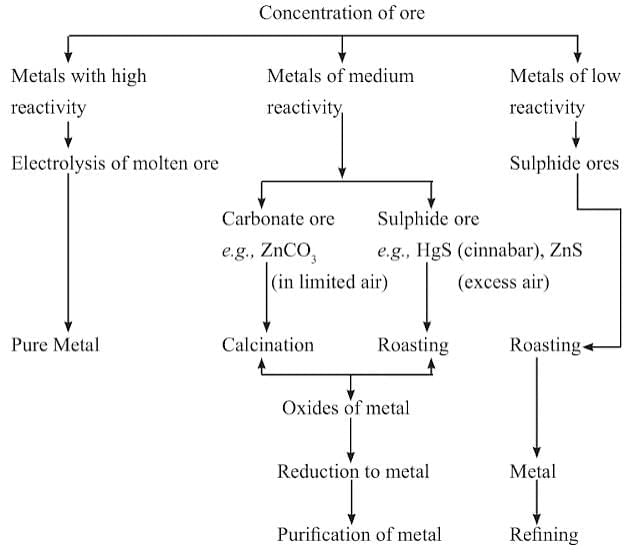
Extraction of Ore Steps
Electrolytic Refining of Copper
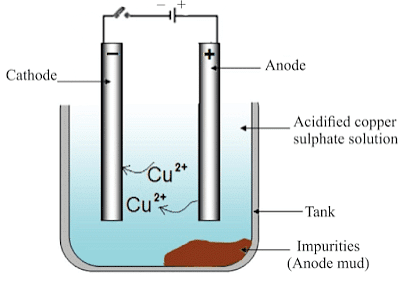
(i) Anode: Impure copper
(ii) Cathode: Strip of pure copper
(iii) Electrolyte: Solution of acidified copper sulphate
- On passing the current through the electrolyte, the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte.
- An equivalent amount of pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited at the cathode.
The insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode and are called anode mud.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Metals & Non-Metals - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the reactivity series and how does it help in predicting the reactions of metals with other metal salts? |  |
| 2. What are the main steps involved in the extraction of ores? |  |
| 3. How does corrosion occur in metals, and what are some methods to prevent it? |  |
| 4. How is ionic bonding demonstrated in sodium chloride (NaCl) and magnesium chloride (MgCl₂)? |  |
| 5. What is electrolytic refining of copper and why is it important? |  |
















