UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Prime Ministers' Museum and Library (PMML) Society
Subject: History, Art and Culture

Why in News?
The Nehru Memorial Museum and Library (NMML) has officially been renamed the Prime Ministers' Museum and Library Society recently.
About Prime Ministers' Museum and Library (PMML) Society:
- Status: It is an autonomous institution under the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- Location: It is housed in the historic Teen Murti campus located south of Rashtrapati Bhavan in New Delhi.
- PMML is dedicated to the objective of promoting advanced research on Modern and Contemporary India.
- History:
- Designed by Robert Tor Russel and built in 1929-30 as part of Edwin Lutyens' imperial capital, Teen Murti House was the official residence of the Commander-in-Chief in India.
- In August 1948, after the departure of the last British Commander-in-Chief, Teen Murti House became the official residence of independent India's first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, who lived here for sixteen years until his death on May 27, 1964.
- On Jawaharlal Nehru's 75th birth anniversary on November 14, 1964 Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan, President of India, formally dedicated the Teen Murti House to the nation and inaugurated the Nehru Memorial Museum.
- On 1 April 1966, the Government set up the Prime Ministers Museum and Library (PMML) Society to manage the institution.
- PMML has four major constituents, namely-
- Memorial Museum;
- Library on modern India;
- Centre for Contemporary Studies;
- Nehru Planetarium;
- Administration: The General Council and the President and the Vice-President of the PMML Society are nominated by the Central Government.
Source: The Hindu
Murmansk Port
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
India’s engagement with Russia’s Arctic region has been strengthening with India-bound goods constituting the maximum share of cargo handled this year by Murmansk Port.
About Murmansk Port:
- The seaport of Murmansk is one of the largest ice-free ports in Russia.
- It is located on the Kola Peninsula at the coast of Barents Sea.
- It is about 2,000 km northwest of Moscow.
- The port is navigated all year round. The dimensions of vessels calling at the port of Murmansk are not limited.
- The main port capabilities are located on the western coast of Kola Bay, among them the mooring berths of the commercial port (including passenger area), fishing port, ship-repair yard, shipyard, oil terminal, and FSUE Atomflot premises.
- On the eastern coast of Kola Bay there is a number of small fish and fleet maintenance terminals.
Key facts about Kola Peninsula
- It is situated in northwest Russia which is one of the most important economic regions in the circumpolar North.
- The region contains valuable natural resources, including a wide variety of mineral and fish resources, and is proximate to the large gas fields of the Barents Sea.
- A large population, industrial complexes, and military infrastructure are also characteristic of the region.
Source: The Hindu
Himachal Cloudburst
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Over 50 people have died within 24 hours in incidents related to heavy rains in Himachal Pradesh.
- Chief Minister Sukhvinder Singh Sukhu said that along with landslides, reports of cloudbursts have also emerged in the state.
Cloudbursts
- A cloudburst is a localised but intense rainfall activity. Short spells of very heavy rainfall over a small geographical area can cause widespread destruction.
- Not all instances of very heavy rainfall, however, are cloudbursts. A cloudburst has a very specific definition.
- Rainfall of 10 cm or more in an hour over a roughly 10 km x 10-km area is classified as a cloudburst event.
- By this definition, 5 cm of rainfall in a half-hour period over the same area would also be categorized as a cloudburst.
How common are cloudbursts?
- Cloudbursts are not uncommon events, particularly during the monsoon months.
- Most of these happen in the Himalayan states where the local topology, wind systems, and temperature gradients between the lower and upper atmosphere facilitate the occurrence of such events.
Consequence of cloudburst
- Because of the nature of terrain, the heavy rainfall events often trigger landslides and flash floods, causing extensive destruction downstream.
- Although these events take place in very small areas which are often devoid of rainfall measuring instruments. The consequences of these events, however, are not confined to the small areas.
Forecasting of cloudbursts
- The India Meteorological Department forecasts rainfall events well in advance, but it does not predict the quantum of rainfall — in fact, no meteorological agency does.
- The forecasts can be about light, heavy, or very heavy rainfall, but weather scientists do not predict exactly how much rain is likely to fall at any given place.
- Also, the forecasts are for a relatively large geographical area, usually a region, a state, a meteorological sub-division, or at best a district.
- The forecasts get more and more uncertain for smaller areas.
- Theoretically, it is not impossible to forecast rainfall over a very small area as well.
- It requires a very dense network of weather instruments, and computing capabilities that seem unfeasible with current technologies.
- As a result, specific cloudburst events cannot be forecast.
Are cloudburst incidents increasing?
- There is no long-term trend that suggests that cloudbursts, as defined by the IMD, are rising.
- However, incidents of extreme rainfall, as also other extreme weather events, are increasing — not just in India but across the world.
- While the overall amount of rainfall in India has not changed substantially, an increasing proportion of rainfall is happening in a short span of time.
- That means that the wet spells are very wet, and are interspersed with prolonged dry spells even in the rainy season.
- This kind of pattern, attributed to climate change, does suggest that cloudburst events might also be on the rise.
What is a Landslide and what causes one?
- A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope.
- Landslides are a type of "mass wasting," which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
- Landslides occur mainly in mountainous terrains where there are conducive conditions of soil, rock, geology and slope.
- Natural Causes that trigger it include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, snow melting and undercutting of slopes due to flooding.
- Landslides can also be caused by Anthropogenic Activities such as excavation, cutting of hills and trees, excessive infrastructure development, and overgrazing by cattle.
- In India, rainfall-induced landslide events are more common.
How Prone is India to Landslides?
- India is considered among the top five landslide-prone countries in the world.
- In India, at least one death per 100 sq. km is reported in a year due to a landslide event.
- Rainfall variability pattern is the single biggest cause for landslides in the country, with the Himalayas and the Western Ghats remaining highly vulnerable.
- Excluding snow covered areas, approximately 12.6% of the country’s geographical land area (0.42 million sq. km) is prone to landslides.
- As many as 66.5% of the landslides are reported from the North-western Himalayas,
- About 18.8% from the North-eastern Himalayas, and
- About 14.7% from the Western Ghats.
What’s causing heavy rains in Himachal, Uttarakhand?
- The northward movement of the monsoon trough, and its interaction with a weak western disturbance are responsible for the heavy rains in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- The monsoon trough is an elongated low-pressure area which extends from a so-called “heat low” (a low pressure over the seas) over Pakistan to the head of the Bay of Bengal region (parts of Odisha, West Bengal, and Bangladesh).
- This is one of semi-permanent features of monsoon circulation according to the India Meteorological Department.
- Currently, the monsoon trough is north of its normal position and it is over the Himalayan foothills.
- The monsoon trough will gradually shift southward now temporarily which will lead to reduction of rainfall over the hills and increase in rainfall over east-central India.
Source: Live Mint
GS-II
Annapurna Food Packet Scheme in Rajasthan
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
Rajasthan’s government launched the Annapurna food packet scheme as part of its welfare initiatives, aiming to support 1.10 crore people, especially those hit hard by the pandemic.
Annapurna Food Packet Scheme
- The scheme primarily benefits families identified through the National Food Security Act (NFSA) survey, encompassing poor and destitute families.
- It also extends beyond NFSA beneficiaries to encompass families that received ₹5,500 pandemic assistance, totalling around 1.05 crore beneficiaries.
Benefits and Contents
- Monthly Distribution: Eligible beneficiaries can collect Annapurna food packets monthly from fair price shops (FPS) at no cost.
- Content Details: Each packet contains essential items – 1 kg gram pulses, sugar, and iodized salt, 1 litre soybean refined edible oil, 100 grams each of chilli powder and coriander powder, and 50 grams of turmeric powder.
- Commission to FPS: FPS will receive a ₹10 commission per packet distributed, incentivizing their participation.
National Food Security Act (NFSA)
- The NFS Act was enacted on 12th September 2013, with retrospective effect from 5th July 2013.
- It integrates legal entitlements for prevailing food security initiatives of the GoI, encompassing the Midday Meal Scheme, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), and the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- The NFSA enshrines a legal right for individuals belonging to “eligible households” to acquire food grains at subsidized rates.
Features
- Recognizing Maternity: The NFS Act acknowledges the importance of maternal health by incorporating maternity entitlements within its provisions.
- Coverage Spectrum: While the Midday Meal Scheme and ICDS are accessible to all, the PDS caters to about two-thirds of the population (75% in rural areas and 50% in urban areas).
- Special Benefits: Pregnant women, lactating mothers, and specific categories of children enjoy the privilege of daily free cereals, enhancing their nutritional security.
- Subsidized Rates: The act establishes central issue prices (CIPs) for food grains, offering rice at Rs 3/kg, wheat at Rs 2/kg, and coarse grains at Rs 1/kg through the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
Source: The Hindu
Cauvery Water Dispute
Subject: Polity
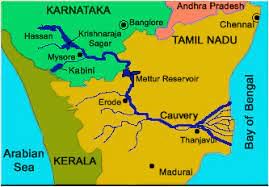
Why in News?
Tamil Nadu has urged the Supreme Court to compel Karnataka to release 24,000 cusecs of water immediately.
- The state seeks the release of 36.76 TMC for September 2023, as per the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal’s (CWDT) award.
Cauvery Water Dispute: Historical Background
- 1892 Onset: The water dispute dates back to 1892 between the British-ruled Madras Presidency and the princely state of Mysore (now Karnataka).
- 1924 Agreement: A 50-year agreement mediated by the British aimed to quell tensions but merely laid the groundwork for future disagreements.
- Post-Independence Battles: Karnataka’s dam constructions in the 1960s-80s sparked Tamil Nadu’s appeal to the Supreme Court. The Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT) followed.
- Interim Measures: The Cauvery River Authority (CRA) in 1998 implemented interim orders. Contentious issues persisted despite CWDT’s 2013 award.
- Final Award: The CWDT’s award in 2013 allocated water quantities for Tamil Nadu (419 TMC), Karnataka (270 TMC), Kerala (30 TMC), and Puducherry (7 TMC).
Water Sharing Criteria
- Monthly Schedule: Karnataka, the upper riparian state, is mandated to provide Tamil Nadu with a specified water quantity each month.
- Annual Allocation: In a “normal” year, Karnataka must provide 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu, of which 123.14 TMC is during the southwest monsoon.
- Challenges: The contentious period is the monsoon when disagreements often arise due to varying rainfall.
Constitutional Provisions for Water Sharing
- Article 262: Empowers Parliament to address inter-State river disputes; IRWD Act, 1956 enacted under this article.
- Seventh Schedule: Defines the legislative authority over water resources in Entry 17 (State List) and Entry 56 (Union List).
Resolving Cauvery Water Sharing
(A) Supreme Court’s 2018 Verdict
- Cauvery as National Asset: The Supreme Court declared Cauvery a “national asset” and upheld inter-State river water equality.
- Allocation Adjustments: The Court noted deficiencies in CWDT’s assessment, leading to Karnataka receiving marginal relief and Tamil Nadu’s allocation reduced to 177.25 TMC.
- Formation of CMB: The Court directed the establishment of the Cauvery Management Board (CMB) for effective implementation of orders.
(B) Cauvery Water Management Scheme
- CWMA Establishment: The Cauvery Water Management Authority (CWMA) was formed to regulate water releases with assistance from the Cauvery Water Regulation Committee (CWRC).
- Permanent and Technical Bodies: CWMA oversees water regulation, while CWRC ensures data collection and implementation of the final award.
Current Status and Future Implications:
- Ongoing Challenge: The Cauvery water dispute remains an ongoing challenge with historical and legal dimensions.
- Resource Management: The establishment of CWMA and CWRC aims to address the dispute through effective water management.
- Continued Struggle: The dispute underscores the complexity of water sharing in a federal system and the need for equitable solutions.
Tamil Nadu’s Contention
- CWMA’s Decision: The CWMA sought 10,000 cusecs for 15 days from Karnataka, but Karnataka proposed only 8,000 cusecs up to August 22.
- Previous Agreement: Karnataka’s refusal to adhere to the earlier agreement of 15,000 cusecs for 15 days at the CWRC meeting irked Tamil Nadu.
- Distress-sharing Formula: TN CM supports a distress-sharing formula, but Karnataka has not embraced it.
Karnataka’s Perspective
- Rainfall Deficit: Karnataka claims lower rainfall in Cauvery’s catchment areas, including Kerala, leading to reduced inflow into its reservoirs.
- Challenging Situation: Karnataka stated that it couldn’t release water as the reservoirs received less inflow this year.
- Lack of Consistency: Despite Karnataka’s endorsing distress-sharing, the state declined to accept the formula.
Future Scenario
- Tamil Nadu’s Concerns: The Mettur reservoir’s storage is critically low, impacting farmers and the upcoming kuruvai crop.
- Water Shortage: The current water availability may last only 10 days, considering dead storage and drinking water needs.
- Awaiting Supreme Court: The case’s outcome now rests with the Supreme Court’s interpretation and decision.
- Need for a Resolution: The pressing need for a mutually acceptable distress-sharing formula is evident.
Ongoing Challenges and Factors Prolonging the Dispute:
- Erratic Water Levels: Flood-drought cycles, pollution, and groundwater depletion have led to unpredictable water levels.
- Idealistic Calculations: SC’s verdict relies on favorable conditions that often do not align with reality.
- Dependency and Population: Both states rely heavily on the river, causing conflicting water needs for urban areas and agriculture.
- Inefficient Water Use: Inefficient irrigation methods lead to low crop productivity per unit of water used.
- Hydropolitics and Delays: Political parties capitalize on water disputes for mobilization. Prolonged tribunal adjudications contribute to delays.
Conclusion
- The Cauvery River dispute is a microcosm of water-related challenges in India.
- To address this century-old struggle, collaborative efforts, sustainable practices, and empowered community involvement are essential.
- By learning from global examples and innovating locally, a future of equitable water allocation, prosperity, and harmony can be envisioned.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Corbett Tiger Reserve
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
In the recent bird survey at Corbett Tiger Reserve about 275 bird species, including two critically endangered, four vulnerable ones and two endangered species, were counted.
Key findings of the survey:
- As per the report, two species, namely white-rumped vulture and red-headed vulture, considered critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) list, have been documented in the survey,
- Two endangered species — Pallas’s fish-eagle, Egyptian vulture were also counted by the researchers in the survey.
- Four vulnerable bird species — great hornbill, great slaty woodpecker, grey-crowned prinia and river tern — have also been counted in the survey.
About Corbett Tiger Reserve:
- It is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand which encompasses the Patli Dun valley.
- The Ramganga, Sonanadi, Palain and Mandal, and Kosi rivers form the prominent hydrological resource for the Corbett.
- The core area of the reserve contains the Corbett National Park and the Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary is part of its buffer area.
- Flora: The trees which contribute to the Flora of Corbett consist of evergreen Sal and its combined trees, the Sheesham, and the Kanju found extensively on the ridges.
- Fauna: Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Hog deer, spotted deer, Samber etc.
Source: The Hindu
ISRO gears up for Aditya-L1 Mission
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Although the mission launch date is yet to be announced, the Aditya-L1 satellite has arrived at the Satish Dhawan Space Center (SDSC) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, for integration with the launch vehicle, PSLV.
Aditya-L1 Mission
- Aditya-L1’s primary objective is to closely observe the Sun and gather insights into its corona, solar emissions, flares, solar winds, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- The satellite is equipped with seven advanced payloads for these scientific endeavors.
- The mission promises round-the-clock imaging of the Sun, enabling an unprecedented understanding of its behavior and impacts.
Significance of the mission
- Solar Influence: The evolution of every celestial body, including Earth and distant exoplanets, is intricately linked to its parent star. The Sun’s weather and environment have a profound impact on the entire solar system.
- Space Weather Impact: Variations in solar activity can disrupt satellite orbits, damage electronics, trigger power blackouts, and induce disturbances on Earth. Accurate knowledge of solar events is essential for comprehending and predicting space weather phenomena.
L1 Lagrange Point Advantage
- Continuous Solar Observations: Positioned at the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1) — about 1.5 million km from Earth — Aditya-L1 will be uniquely positioned to observe the Sun without the interference of occultation or eclipses. L1 is an orbital location where gravitational forces create stable regions of attraction and repulsion.
- L1’s Significance: The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO) is stationed at L1 and has facilitated groundbreaking solar research. Aditya-L1’s observations will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of solar behavior.
Comparison with International Missions
- Closer than Ever: While NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has ventured closer to the Sun, Aditya-L1 will focus on direct solar observations from a greater distance.
- Technical Challenges: Many instruments and components for Aditya-L1 are being developed in India for the first time, representing both a challenge and an opportunity for the nation’s scientific and engineering communities.
Source: The Hindu
Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit
Subject: Economy
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled a Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit to transform credit accessibility and lending efficiency.
About the Public Tech Platform
- It is developed by the RBI’s subsidiary Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH).
- It aims to streamline the credit delivery process by enabling seamless digital information flow to lenders.
- It intends to simplify the credit assessment by providing an end-to-end digital ecosystem that facilitates the smooth exchange of essential digital data among stakeholders.
Features of the Platform
- Open Architecture: The platform adopts an open architecture model, fostering interoperability and collaboration among various financial sector players.
- Plug and Play Model: The open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and standards enable seamless integration and interaction among participating entities.
- Efficiency and Scalability: The platform aims to enhance lending efficiency, reduce costs, expedite disbursement, and scale up lending operations.
Launch and Scope
- Calibrated Rollout: The platform is set to launch as a pilot project on August 17, 2023, with gradual access to information providers and use cases.
- Initial Focus: The pilot phase will focus on credit products like Kisan Credit Card loans, dairy loans, collateral-free MSME loans, personal loans, and home loans.
- Integration and Services: The platform will integrate services such as Aadhaar e-KYC, state government land records, satellite data, PAN validation, Aadhaar e-signing, account aggregation, and more.
Source: Money Control
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|





















