Long Questions: Electricity and Circuits | NCERT Summary: UPSC PDF Download
Q1: In the following diagram explain whether the bulb will glow in each of the cases.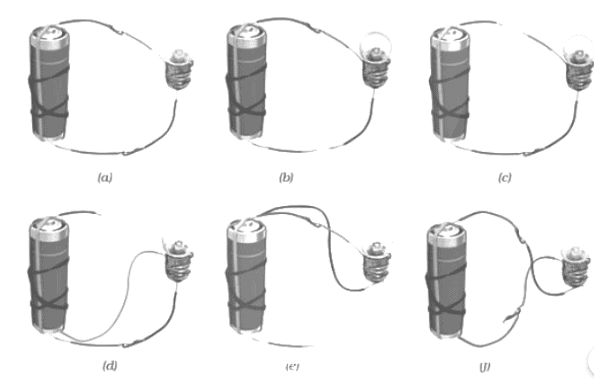 Ans: a) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
Ans: a) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
b) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
c) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
d) The bulb will not glow as both wires are connected only to the negative terminal of the cell.
e) The bulb will not glow as both wires from the bulb are connected only to the positive terminal of the cell.
f) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
Q2: Differentiate between conductors and insulators.
Ans: The differences between conductors and insulators are as follows:
Q3: Explain the concept of electricity and its importance in our daily lives. Provide examples of devices that use electricity and discuss their significance in various activities.
Ans: Electricity is a form of energy produced by the movement of electrons. It plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Various devices use electricity, such as bulbs, fans, refrigerators, and TVs.
Importance of Electricity:
- Lighting: Bulbs provide light in homes, streets, and buildings, enhancing visibility.
- Comfort: Fans and air conditioners regulate temperatures for comfort.
- Food Preservation: Refrigerators keep food fresh by maintaining low temperatures.
- Communication: Devices like phones and computers rely on electricity for communication and information access.
Electricity has transformed modern living by enabling convenient and efficient operations of devices that are essential for comfort, productivity, and communication.
Q4: Describe the components of an electric circuit. Explain the roles of a cell/battery, switch, and bulb in a simple circuit. Provide examples to illustrate each component's function.
Ans: An electric circuit consists of various components that work together to allow the flow of electricity.
The main components include:
- Cell/Battery: It provides the energy source needed to move electrons in the circuit.
- Switch: It controls the flow of electricity by either completing or interrupting the circuit.
- Bulb: It is a device that converts electrical energy into light energy when the circuit is complete.
Function of Components:
- Cell/Battery: The battery provides the necessary voltage that pushes electrons through the circuit.
- Switch: When the switch is closed (turned on), the circuit is complete, and electricity flows. When it's open (turned off), the circuit is interrupted.
- Bulb: When the circuit is complete, electricity flows through the bulb's filament, heating it and producing light.
- Example: In a flashlight, the battery provides energy, the switch turns the light on or off, and the bulb emits light when the circuit is complete.
Q5: Explain the terms 'conductor' and 'insulator'. Provide examples of materials that are good conductors and insulators of electricity.
Ans:
- Conductor: A conductor is a material that allows electricity to flow through it easily. Metals like copper, aluminum, and iron are good conductors as they have free electrons that can move freely, facilitating the flow of electric current.
- Insulator: An insulator is a material that does not allow electricity to flow through it. Rubber, plastic, glass, and wood are good insulators. They have tightly bound electrons, making it difficult for electricity to pass through.
- Example: Copper wires are used in electrical circuits as conductors, while plastic or rubber covering the wires prevents electric shocks and acts as an insulator.
Q6: Explain the concept of an open and closed circuit. Describe the role of a switch in controlling the flow of electricity in a circuit. Provide examples to illustrate each type of circuit.
Ans:
- An open circuit is a circuit where there is a break or interruption, preventing the flow of electricity. A closed circuit is a circuit where there is a complete path for electricity to flow.
- Switch's Role: A switch controls the flow of electricity in a circuit. When the switch is closed, the circuit is complete, and electricity flows. When the switch is open, the circuit is interrupted, and electricity stops flowing.
- Example: In an open circuit, the switch is off, and a bulb won't light up. In a closed circuit, when the switch is on, the bulb lights up because the circuit is complete and electricity flows.
Q7: Describe the concept of a series and parallel circuit. Explain how devices are connected in each type of circuit and discuss the impact on brightness and functioning. Provide examples to illustrate each type.
Ans:
- Series Circuit: In a series circuit, devices are connected in a single path. The same current flows through all devices. If one device fails or is disconnected, the entire circuit is interrupted. Devices in a series circuit are dimmer because the same current passes through each.
- Parallel Circuit: In a parallel circuit, devices are connected in multiple paths. Each device gets the full voltage, and if one device fails, others continue to function. Devices in a parallel circuit are brighter because they each get the full voltage.
- Example: In a series circuit of bulbs, if one bulb goes out, all bulbs go out. In a parallel circuit of bulbs, if one bulb goes out, the others remain lit.
Q8: Explain the role of conductors in electricity flow. Describe the importance of using appropriate materials for wires in electrical circuits. Provide examples of good conductor materials used for electrical wiring.
Ans:
- Conductors facilitate the flow of electric current. In electrical circuits, conductors like copper and aluminum wires are used to allow electricity to flow from the source to the devices.
- Importance of Appropriate Materials: Using appropriate materials for wires is essential for safety and efficiency. Good conductors like copper offer low resistance, reducing energy loss as heat. They are also ductile and malleable, making them suitable for wiring.
- Example: Copper wires are commonly used for electrical wiring due to their excellent conductivity, flexibility, and safety features.
Q9: Describe the concept of a fuse and its role in electrical safety. Explain how a fuse works to prevent electrical overloading. Provide examples of situations where fuses are used.
Ans:
- A fuse is a safety device in electrical circuits designed to protect devices from overloading. It consists of a thin wire with a low melting point.
- Fuse's Role: If the current exceeds safe levels due to a malfunction or short circuit, the fuse wire melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage or fire.
- Example: Fuses are used in electrical appliances like irons, refrigerators, and computers. If a malfunction occurs, the fuse breaks the circuit, preventing further damage.
Q10: Explain the concept of an electric cell. Describe the structure and working of a simple electric cell. Provide examples of devices that use electric cells and discuss their importance.
Ans:
- An electric cell is a device that produces electricity using chemical reactions. It has two terminals: positive (+) and negative (-).
- Structure and Working: An electric cell consists of two electrodes (one positive and one negative) immersed in an electrolyte solution. Chemical reactions between the electrodes and the electrolyte produce electrons, generating electric current.
- Examples: Devices like torches, remote controls, and watches use electric cells as power sources. Electric cells provide portable and reliable energy for various daily applications.
|
666 docs
|















