Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Practice Question Answers - Metals and Non-metals
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires is called _______________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: ductility
Q2: Non-metals generally have _______________ lustre.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: no
Q3: The element that is an essential constituent of chlorophyll is _______________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: magnesium
Q4: The process of applying a thin layer of zinc on iron to prevent rusting is called _______________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: galvanization
Q5: _______________ is a soft metal used in making electric wires and cables.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Copper
Short Answer Questions
Q6: Differentiate between metals and non-metals based on their physical properties.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity, have a metallic lustre, and are malleable and ductile. Non-metals are poor conductors, lack lustre, and are brittle.
Q7: Why do ionic compounds generally have high melting and boiling points?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ionic compounds consist of positive and negative ions held together by strong electrostatic forces. It requires a considerable amount of energy to overcome these forces, leading to high melting and boiling points.
Q8: Explain the process of rusting of iron with the help of a chemical reaction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Rusting is the oxidation of iron in the presence of moisture and air, forming iron oxide.
The chemical equation is: 4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O → 4Fe(OH)3. This process weakens the iron structure over time.
Q9: How does the reactivity of metals change as we move down the reactivity series?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The reactivity of metals increases as we move down the reactivity series. Metals at the top are less reactive and lose electrons easily, while those at the bottom are highly reactive and tend to gain electrons.
Q10: Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sodium is highly reactive and reacts vigorously with air and moisture. Keeping it immersed in kerosene oil prevents its contact with air and moisture, thus preventing rapid oxidation.
Long Answer Questions
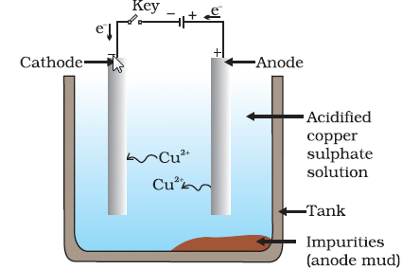
Q11: Explain the process of electrolytic refining of copper.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The process of electrolytic refining of copper is as follows:
- Electrolytic refining is a method used to clean impure copper.
- In this process, the impure copper serves as the anode, while a thin sheet of pure copper acts as the cathode.
- The electrolytic cell is filled with a solution of copper sulfate.
- When electricity flows through the cell:
- Copper from the anode dissolves.
- This dissolved copper is then deposited onto the cathode as pure copper.
- The impurities that do not dissolve settle at the bottom and form what is known as anode mud.
Q12: Compare the properties of metals and non-metals in terms of their chemical reactivity.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Metals:
- Readily lose electrons to form positive ions (cations).
- Good reducing agents.
- React with acids to liberate hydrogen gas.
- Non-Metals:
- Tend to gain electrons to form negative ions (anions).
- Good oxidizing agents.
- Do not react with acids to liberate hydrogen gas.
Q13: Describe the extraction of iron from its ore, haematite, using a blast furnace.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- In a blast furnace, haematite (iron ore) is mixed with coke (carbon) and limestone (flux).
- The mixture is heated at high temperatures, and carbon monoxide reduces haematite to iron.
- The iron melts and collects at the bottom, forming pig iron.
- The impurities react with limestone to form slag, which floats on top and is removed.
Q14: Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state or aqueous solutions but not in solid state?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- In the solid state, ions in ionic compounds are held in a fixed position and cannot move.
- However, in the molten state or in aqueous solutions, the ions are free to move and can carry an electric current.
- This is because the movement of ions is necessary for electrical conduction.
Q15: Discuss the uses of metals and non-metals in daily life with suitable examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Metals like iron are used in construction, aluminum in making utensils, and copper in electrical wiring.
- Non-metals like sulfur are used in making matches, carbon in pencils, and oxygen in respiration.
- Non-metalhelium is used in filling balloons due to its low density.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Practice Question Answers - Metals and Non-metals
| 1. What are the physical properties that distinguish metals from non-metals? |  |
| 2. How do metals and non-metals react with oxygen? |  |
| 3. Can you give examples of common metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the reactivity series in understanding metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. What are the methods of extraction for metals and how do they differ from non-metals? |  |





















