Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Practice Question Answers - Heredity and Evolution
Q1. The basic unit of heredity is called a _______.
Ans: The basic unit of heredity is called a gene. A gene is a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for producing specific proteins. Genes determine the inherited traits of an organism, such as eye colour or height.
Q2. The process by which favorable traits are passed on to the next generation is called _______.
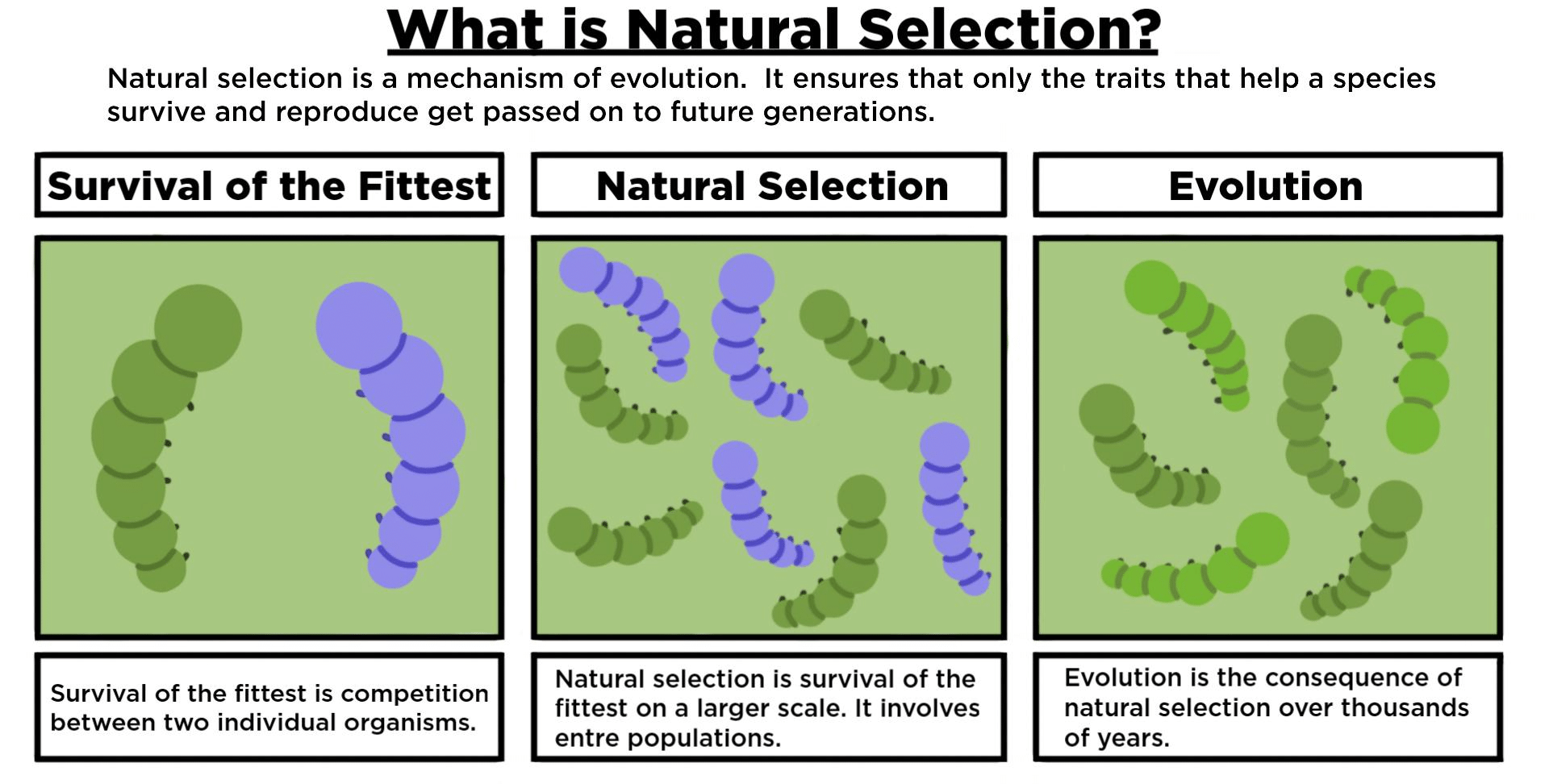
Ans: The process by which favourable traits are passed on to the next generation is called natural selection. Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution where organisms with advantageous traits survive and reproduce. This allows them to pass those traits to the next generation, thereby increasing the prevalence of these traits in the population over time.
Q3. The scientific study of heredity and variation is known as _______.
Ans: Genetics is the scientific study of heredity and variation. It is a branch of biology that explores how traits are inherited from one generation to the next and examines the genetic variation that occurs among individuals.
Q4. The sex determination in humans is based on the presence of _______ chromosome in the individual.
Ans: The sex determination in humans is based on the presence of the Y chromosome in the individual. In humans, the Y chromosome determines male sex. Individuals with an XY chromosome pair are male, while those with an XX pair are female.
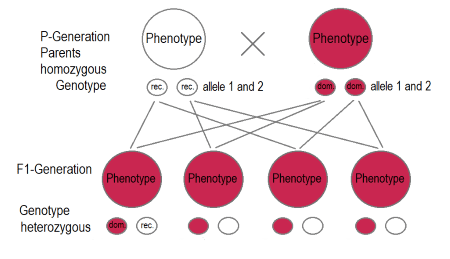
Q5. The first filial generation obtained in a cross is represented as _______.
Ans: The F1 generation is the first generation of offspring resulting from a cross between two genetically distinct parent organisms. This generation is important in genetics because it shows the traits inherited from each parent. The F1 generation can exhibit a combination of characteristics that may differ from both parents, providing insight into how traits are passed down.
Q6. Define Mendel's Law of Segregation.
Ans: Mendel's Law of Segregation states that during the formation of gametes, the alleles (which are alternate forms of a gene) segregate from one another. This means that each gamete carries only one allele for a specific trait.
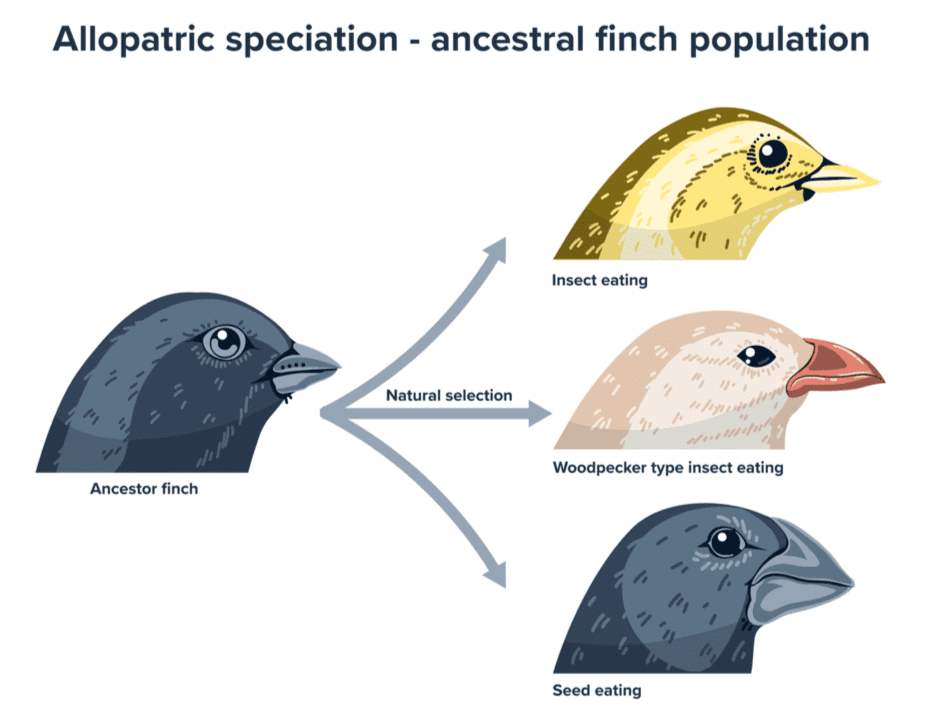
Q7. How does a new species arise according to Darwin's theory of natural selection?
Ans: According to Darwin's theory, a new species arises through the process of natural selection. This occurs when individuals with favourable traits that enhance their survival and reproduction are more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation. Over time, these accumulated changes can lead to the emergence of a new species.
Q8. Differentiate between homologous and analogous structures.
Ans: Homologous structures are similar in structure but may serve different functions, indicating a common evolutionary origin. An example is the bones in the forelimbs of mammals, which share a similar arrangement despite differing functions. In contrast, analogous structures have similar functions but differ in structure, arising from separate evolutionary paths. For instance, the wings of birds and insects serve the same purpose of flight but have different structural designs.
Q9. How is the sex of a newborn determined in humans?
Ans: In humans, the sex of a newborn is determined by the combination of sex chromosomes inherited from the parents. If the child inherits an X chromosome from both parents, the child will be female (XX). Conversely, if the child inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father, the child will be male (XY).
Long Answer Questions
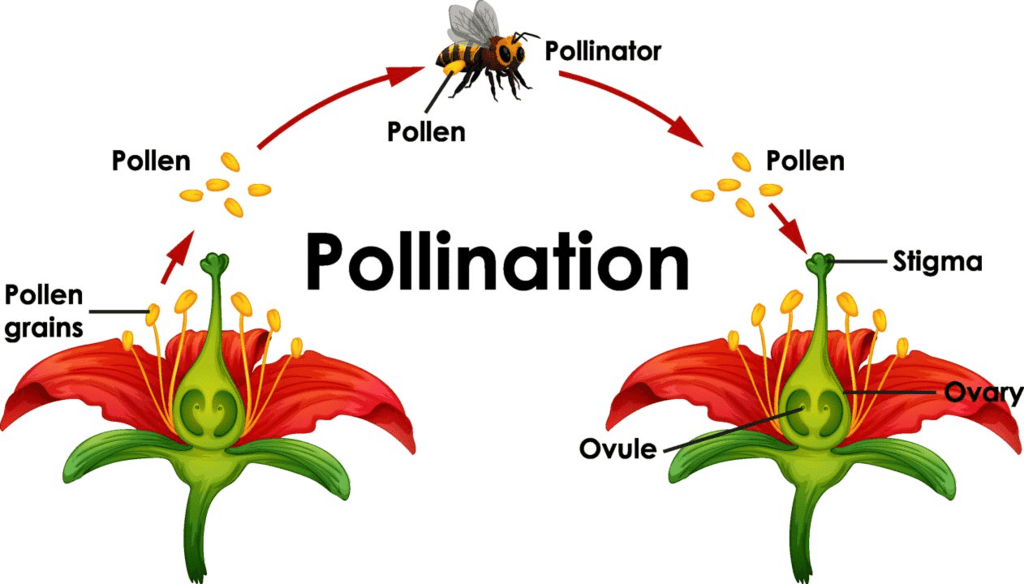
Q1. Describe the process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants.Ans: In flowering plants, sexual reproduction involves the formation of male and female gametes. The process begins with pollination, where pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma. Following this, the pollen tube grows through the style to reach the ovary. Fertilization occurs when the male gamete fuses with the female gamete (ovule), resulting in the formation of a zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo, while the ovule transforms into a seed. Eventually, the seed germinates to form a new plant.
Q2. Explain the inheritance of traits with the help of a Punnett square.
Ans: A Punnett square is a useful tool for predicting the possible outcomes of a genetic cross. It visually represents the different combinations of alleles that can result from the mating of two individuals. To construct a Punnett square:
- Write each parent's alleles along the top and side of the square.
- The boxes inside the square represent the potential genotypes of the offspring.
- By combining the alleles from each parent, you can determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Q3. How do fossils provide evidence for evolution? Give an example.
Ans: Fossils are preserved remains or traces of organisms from the past. They provide a crucial record of the history of life on Earth and illustrate how organisms have changed over time. For example, the fossil record of horses demonstrates the evolution of their limb structure, transitioning from small, multi-toed ancestors to the single-toed modern horses. This change reflects an adaptive response to changing environments.
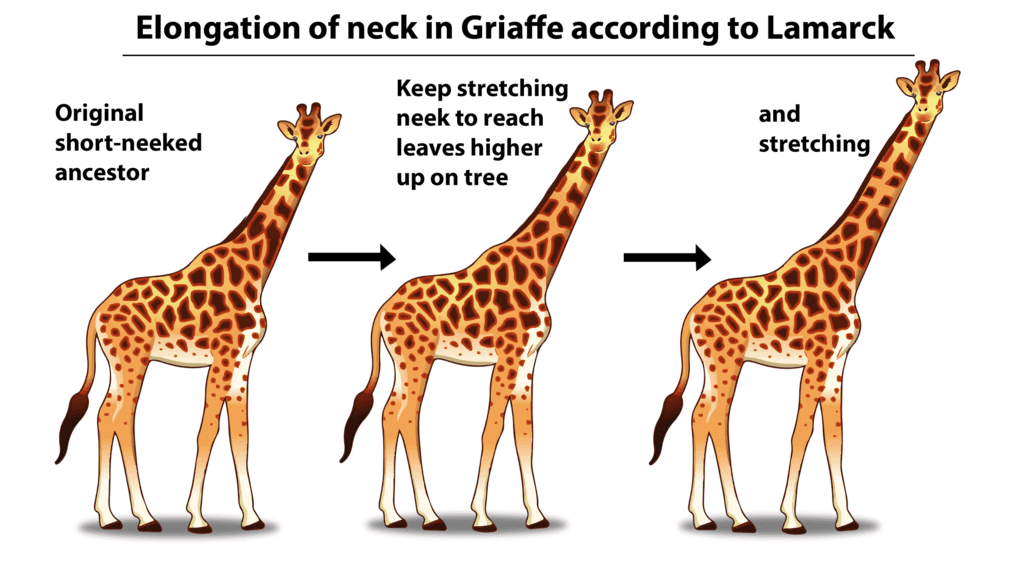
Q4. Discuss Lamarck's theory of evolution and its shortcomings.
Ans: Lamarck's theory of evolution proposed that organisms could acquire or lose traits during their lifetimes in response to environmental changes and pass these changes to their offspring. However, this theory has notable shortcomings:
- Lamarck's theory lacks a mechanism of inheritance, such as genes, which are crucial for passing on traits.
- It has been demonstrated that acquired traits are not inherited in the way Lamarck suggested.
- Modern genetics and the discovery of DNA have shown that traits are primarily inherited through genes, not through modifications made during an organism's lifetime.
Q5. How does natural selection lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria?
Ans: Natural selection occurs in bacterial populations when antibiotics are used. Some bacteria may possess mutations that render them resistant to antibiotics. When antibiotics are applied, susceptible bacteria die off, while the resistant ones survive and reproduce. Over time, the resistant bacteria become more prevalent, leading to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains. This process is a classic example of natural selection in action.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Practice Question Answers - Heredity and Evolution
| 1. What is heredity and how does it influence physical traits in organisms? |  |
| 2. How do dominant and recessive traits differ in heredity? |  |
| 3. What role do mutations play in evolution? |  |
| 4. How does natural selection contribute to the process of evolution? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of genetic variation and its importance in evolution? |  |
















