Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Practice Question Answers - Light Reflection and Refraction
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: When light passes from a rarer to a denser medium, it bends _______ the normal.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: towards
Explanation: When light travels from a rarer medium (e.g., air) to a denser medium (e.g., glass), it slows down and bends towards the normal due to the change in speed.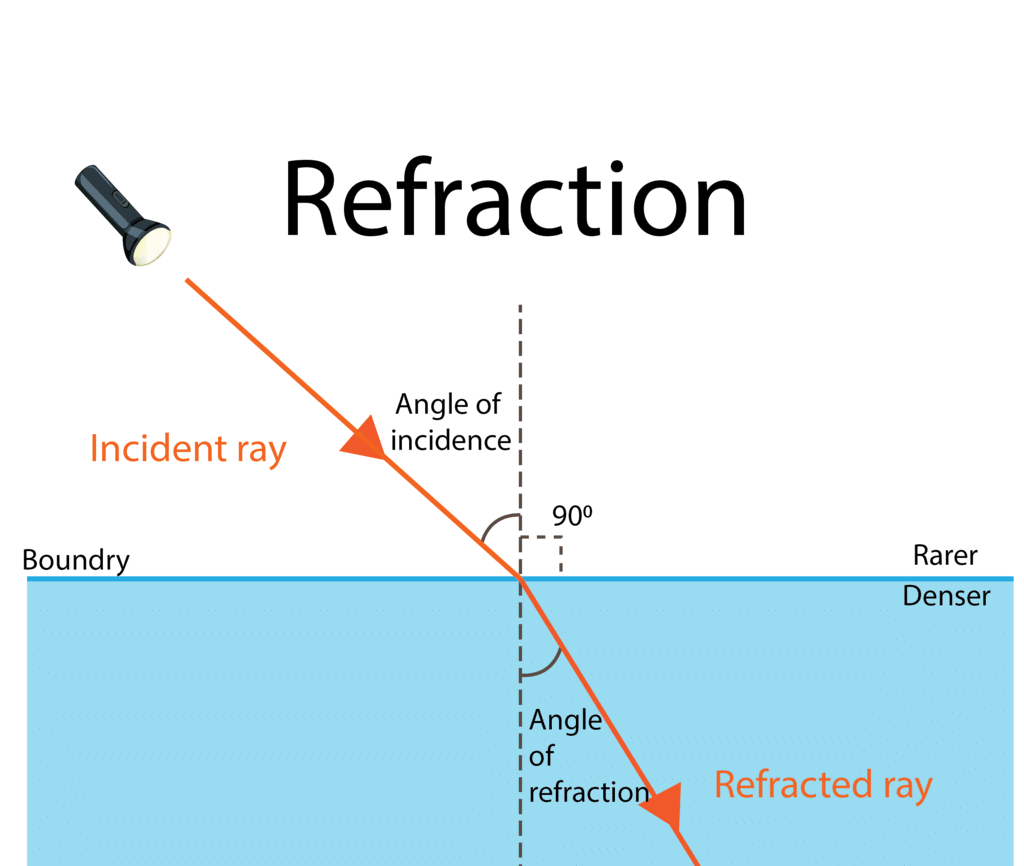
Q2: The point at which the incident ray meets the mirror is called the _______ point.Ans: incident
 View Answer
View AnswerExplanation: The incident point is where the incoming ray of light touches the mirror's surface before reflection occurs.
Q3: The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as the angle of _______.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: incidence
Explanation: The angle of incidence is the angle formed by the incident ray and the perpendicular line (normal) at the point of incidence.
Q4: The type of mirror used in a magnifying glass is a _______ mirror.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: convex
Explanation: A convex mirror is curved outward and is used in magnifying glasses because it allows light rays to diverge, creating a larger virtual image.
Q5: The phenomenon responsible for the dispersion of white light into its component colors is called _______.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: dispersion
Explanation: Dispersion occurs when white light splits into its spectrum of colors (e.g., in a prism) due to different wavelengths of light bending by different amounts.
Short Answer Questions
Q6: Define the term 'refraction' of light.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another, due to a change in its speed.
Q7: State Snell's Law.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Snell's Law states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant when a ray of light passes from one medium to another. Mathematically, it can be written as: n1 sin α1 = n2 sin α2, where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media, and α1 and α2 are the angles of incidence and refraction, respectively. 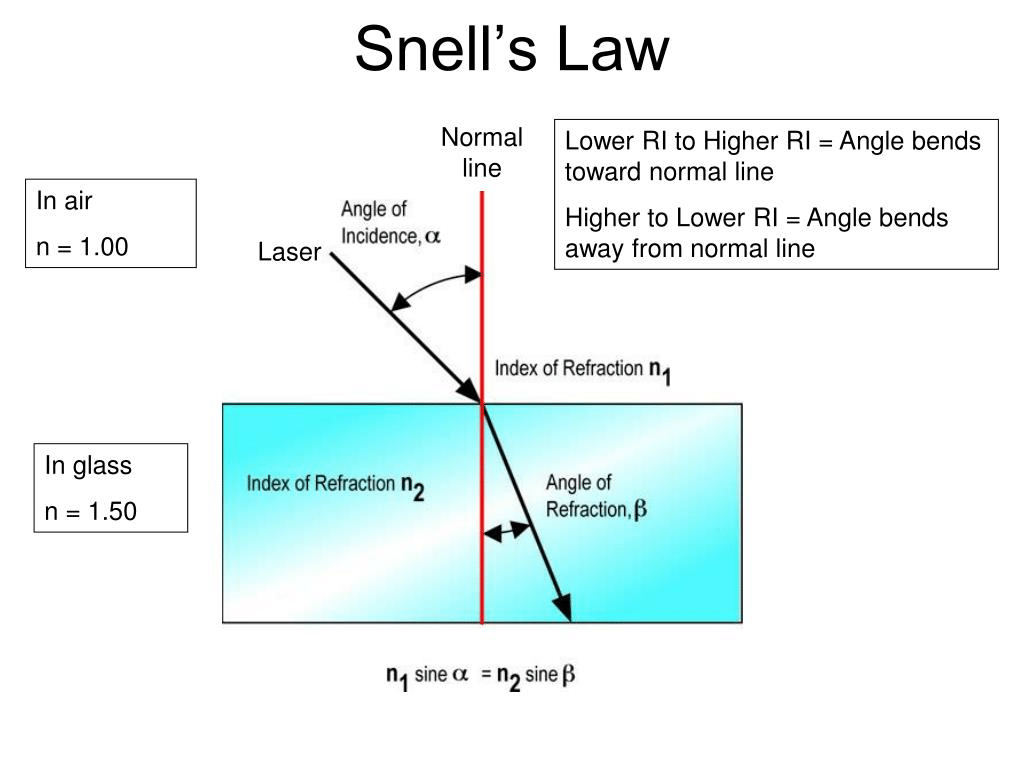
Q8: Explain the term 'total internal reflection' of light.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
- Total internal reflection occurs when a ray of light traveling in a denser medium strikes the boundary with a rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
- In such cases, the light is completely reflected back into the denser medium, and no refraction occurs.
Q9: Differentiate between a real image and a virtual image.
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: A real image is formed when actual light rays converge at a point after reflecting or refracting, and it can be captured on a screen. A virtual image, on the other hand, is formed when the apparent path of light rays appears to diverge from a point behind the mirror or lens, and it cannot be captured on a screen.
Q10: Why does a pencil appear to be bent when placed in a glass of water?
 View Answer
View AnswerLong Answer Questions
Q11: Explain how a convex lens forms an image of an object. View Answer
View Answer- A convex lens forms an image by refracting light rays that pass through it.
- When parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens, they converge at a point on the other side of the lens called the focus.
- This point is the principal focus of the lens.
- If an object is placed beyond twice the focal length, a real inverted image is formed.
- If the object is placed within the focal length, a virtual and erect image is formed

Q12: Describe the difference between regular and diffuse reflection.
 View Answer
View Answer- Regular reflection occurs when a smooth and polished surface reflects light rays in a specific direction, such as in a mirror.
- Diffuse reflection occurs when a rough and irregular surface scatters light rays in various directions, leading to the formation of non-distinct images.
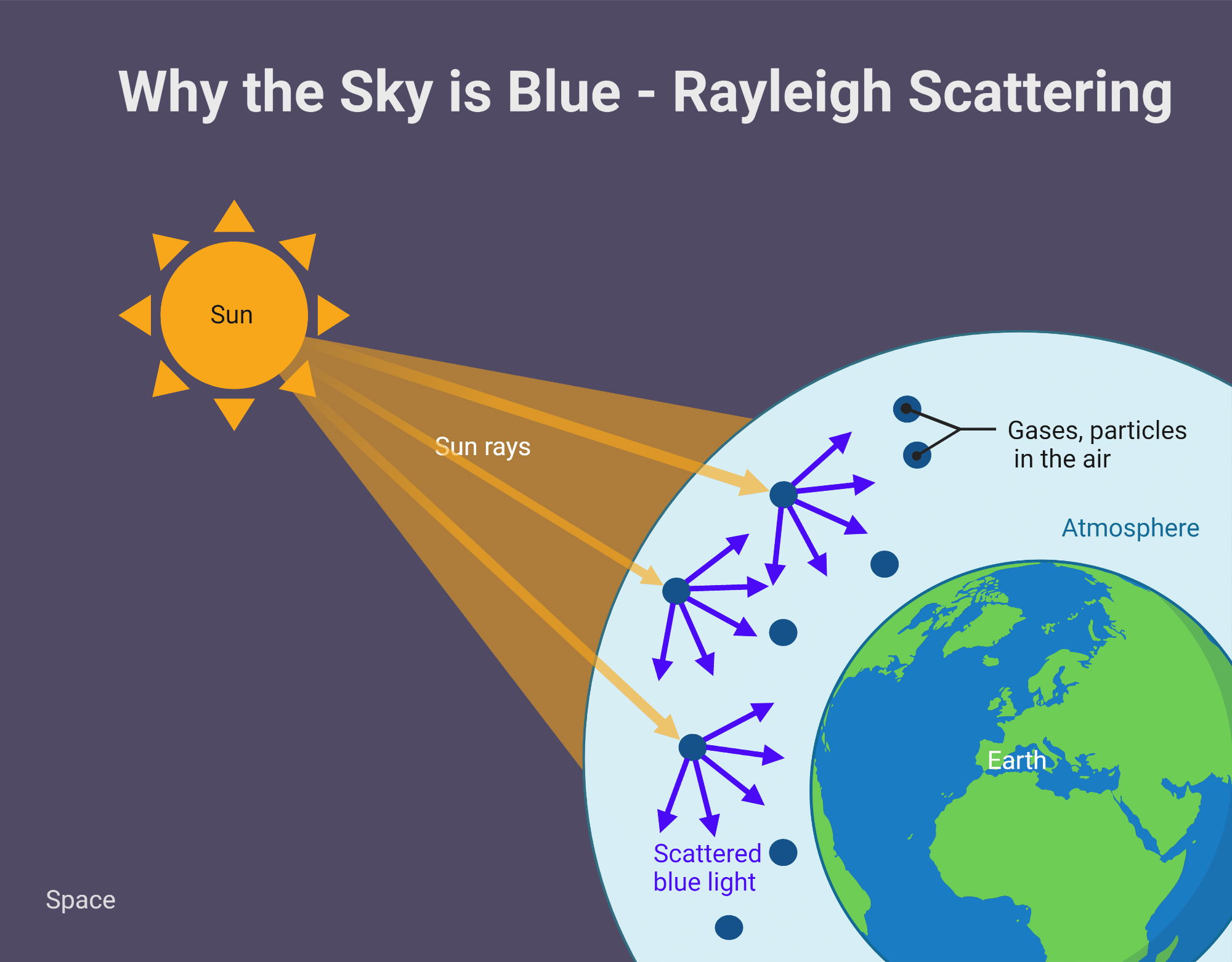
Q13: Why does the sky appear blue to us?
 View Answer
View Answer- The sky appears blue due to Rayleigh scattering.
- The Earth's atmosphere contains tiny particles and molecules that scatter sunlight.
- Blue light, being of shorter wavelength, scatters more than other colors, making the sky predominantly blue when viewed from all directions.
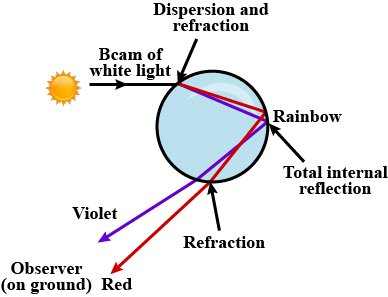
Q14: Explain the formation of a rainbow.
 View Answer
View Answer- Refraction: Light enters a raindrop and bends as it slows down, separating into its component colors.
- Internal Reflection: The light reflects off the inner surface of the raindrop.
- Refraction Again: As the light exits the raindrop, it bends again, further separating the colors.
- Dispersion: This separation of light into colors creates the spectrum, with red on the outer edge and violet on the inner edge.
- A rainbow is seen when the observer's back is to the sun and the light exits raindrops at a specific angle.
Q15: How does the human eye focus on near and distant objects?
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: The human eye adjusts its focus using a process called accommodation.
When focusing on a near object, the ciliary muscles contract, causing the lens to become more convex, which increases its refractive power. For distant objects, the ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to become flatter, reducing its refractive power. This adjustment ensures that clear images are formed on the retina for objects at varying distances.|
80 videos|512 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Practice Question Answers - Light Reflection and Refraction
| 1. What is the law of reflection in ray optics? |  |
| 2. What are the types of mirrors and their characteristics? |  |
| 3. How does refraction occur and what factors affect it? |  |
| 4. What is the critical angle and total internal reflection? |  |
| 5. How do lenses refract light and what are their types? |  |