Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Practice Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The property of a substance to attract or repel another substance is known as
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Magnetism.
Explanation: Magnetism is the property of materials like iron or nickel to attract or repel other materials due to their magnetic fields, caused by moving electric charges.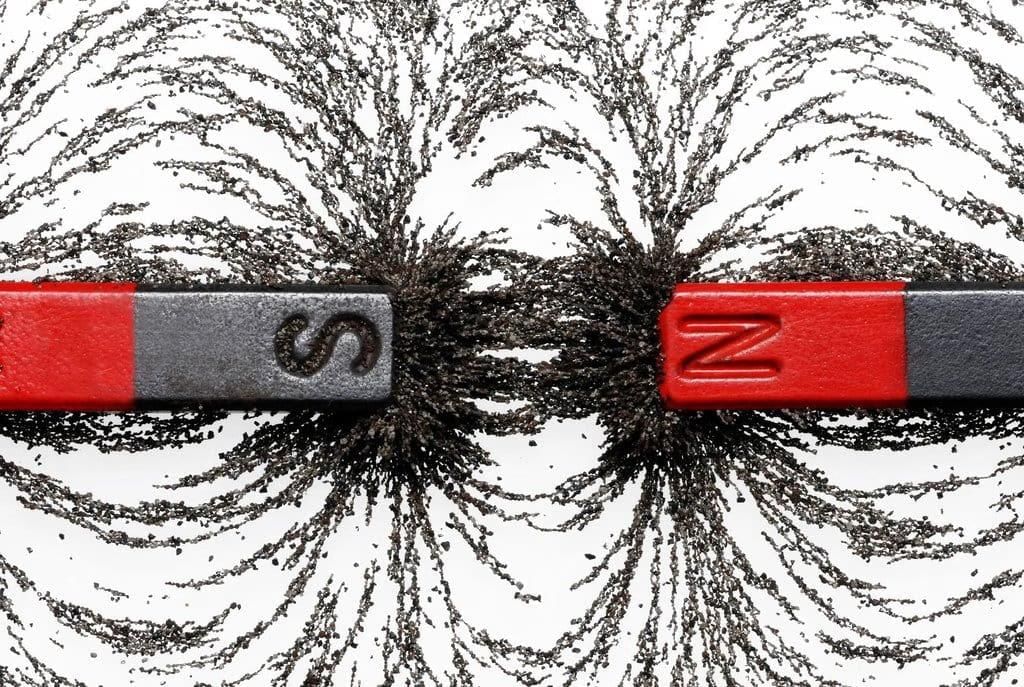
Q2: The current-carrying conductor is surrounded by a magnetic field, which is in the form of ___________ lines.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Magnetic field lines.
Explanation: Magnetic field lines are invisible lines that represent the direction and strength of a magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor. They form concentric circles around the wire.
Q3: The SI unit of magnetic field strength is ___________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Tesla (T).
Explanation: Tesla (T) is the SI unit of magnetic field strength, measuring the intensity of the magnetic field at a given point.
Q4: The magnetic field inside a current-carrying solenoid is ___________ and uniform.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Strong.
Explanation: Inside a solenoid, the magnetic field is strong and uniform due to the alignment of magnetic field lines in the same direction, creating a powerful magnetic effect.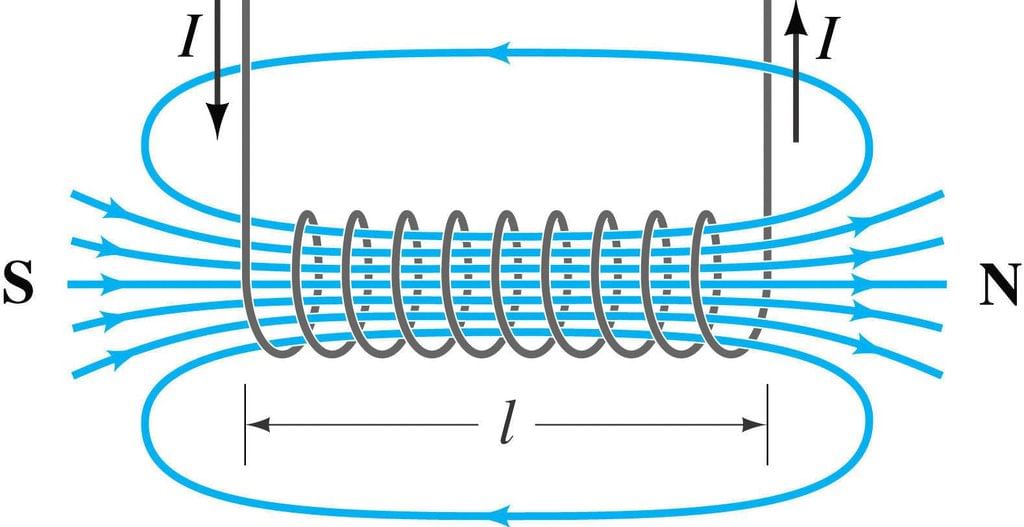
Q5: The device used to detect the presence of current in a circuit is called a ___________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Galvanometer.
Explanation: A galvanometer is a sensitive instrument used to detect and measure small electric currents in a circuit by showing deflection on its scale.
Short Answer Questions
Q6: How does the strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying conductor change when the current is increased?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The strength of the magnetic field increases with an increase in current.
Q7: Explain why the North pole of a magnet gets attracted to the South pole of another magnet.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: This attraction occurs due to the alignment of magnetic domains in opposite directions, creating a stronger combined magnetic field.
Q8: State Ampere's law.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ampere's law states that the magnetic field around a closed loop is directly proportional to the electric current passing through the loop.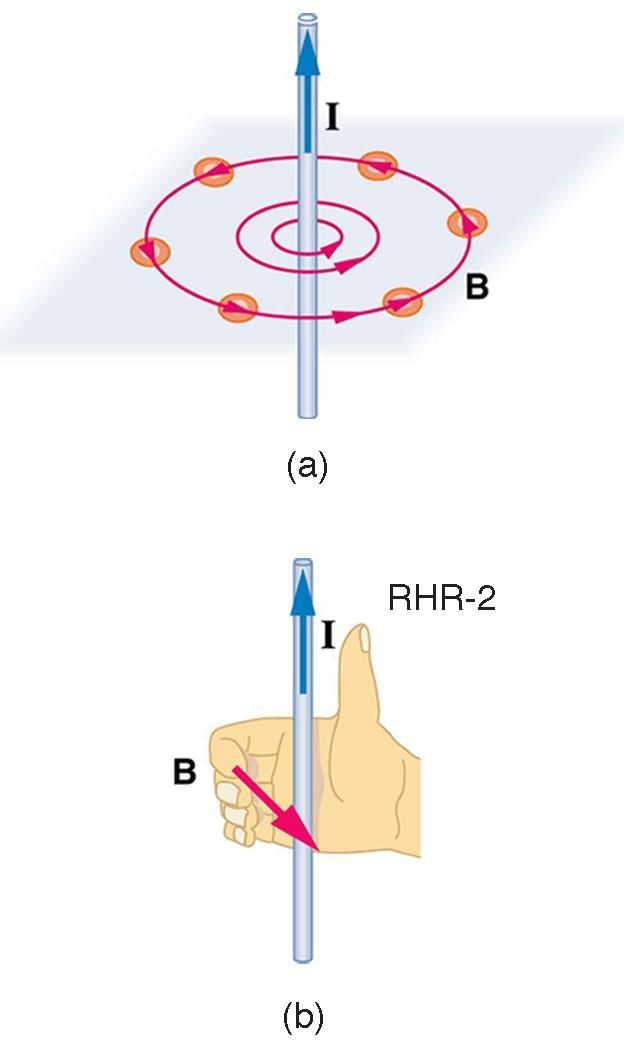
Q9: What is the purpose of using a soft iron core in an electromagnet?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A soft iron core enhances the magnetic field strength in an electromagnet by providing a path for the magnetic lines of force to concentrate.
Q10: Describe the rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field using the right-hand thumb rule.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Point your thumb in the direction of the current flow, and your curled fingers indicate the direction of the magnetic field around the conductor.
Long Answer Questions
Q11: Explain the working principle of an electric motor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: An electric motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When current flows through a coil (armature) placed in a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the coil due to the interaction between the magnetic field and the current. This force causes the coil to rotate, resulting in mechanical motion.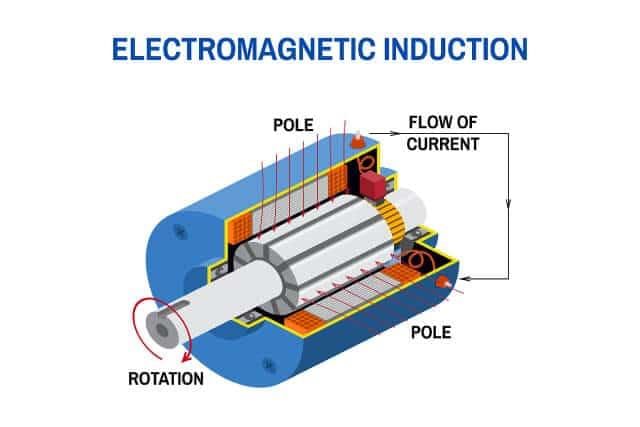
Q12: Compare the working of a direct current (DC) motor and an alternating current (AC) motor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A DC motor operates on direct current and uses a split-ring commutator to reverse the direction of current in the coil, causing continuous rotation. An AC motor operates on alternating current and doesn't require a commutator. The direction of current in the coil changes with each half-cycle, causing the rotor to turn.
Q13: How does an electric bell work?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: An electric bell consists of an electromagnet, a hammer, and a gong. When the current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the iron armature, causing the hammer to strike the gong. This interrupts the circuit, and the magnetic field collapses. The armature returns to its original position due to a spring, completing the circuit again. This cycle repeats, producing the bell's ringing sound.
Q14:State and explain Fleming's left-hand rule for the direction of the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: According to Fleming's left-hand rule, if the forefinger, thumb, and middle finger of the left hand are held perpendicular to each other, with the forefinger representing the magnetic field direction (B), the middle finger representing the current direction (I), then the thumb indicates the direction of the force (F) experienced by the conductor.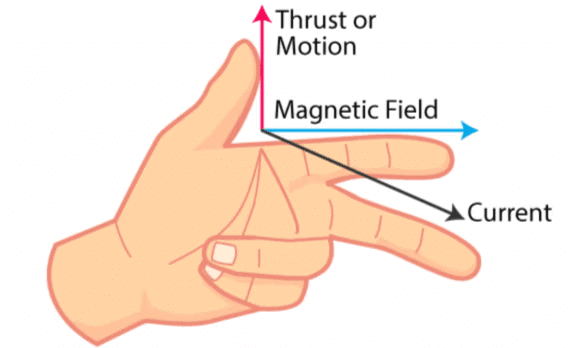
Q15: Describe the construction and working of a simple DC generator.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A simple DC generator consists of a rectangular coil of wire rotating between the poles of a permanent magnet. When the coil rotates, it cuts across the magnetic field lines, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the coil. This EMF causes current to flow through the external circuit when the coil is connected to a load. The split-ring commutator reverses the direction of current in the coil at each half-rotation, resulting in a unidirectional current output.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Practice Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
| 1. What is the principle behind the magnetic effects of current? |  |
| 2. How can we visualize the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of the magnetic effects of current? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of electromagnetic induction in the context of magnetic effects of current? |  |
| 5. How does the direction of current affect the magnetic field produced? |  |





















