Class 5 EVS Chapter 3 HOTS Questions - From Tasting to Digesting
Q1: What will happen if mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
(a) Erosion of stomach wall
(b) Erosion of intestinal wall
(c) Indigestion of food
(d) Enlargement of stomach
Ans: (a) Erosion of stomach wall
 View Answer
View AnswerExplanation:
- Mucus is a protective layer inside the stomach.
- It prevents the stomach lining from being harmed by strong stomach acids.
- If there is no mucus, the stomach walls would get damaged or eroded.
- So, the correct answer is that the stomach wall would erode.
Q2: The inner layer of the stomach releases
(a) Water
(b) Blood
(c) Minerals
(d) Digestive juices
Ans: (d) Digestive juices
 View Answer
View AnswerExplanation:
- The stomach has layers, and the innermost layer releases special juices.
- These juices help break down the food we eat.
- These juices include things like acids and enzymes.
- So, the inner layer releases digestive juices.
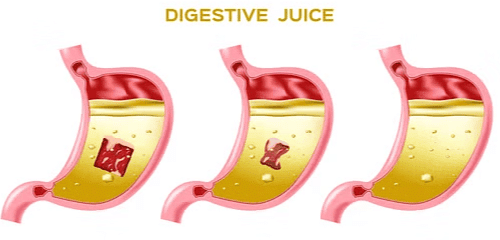 Q3: Stomach secretes
Q3: Stomach secretes
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid
(b) Dilute sulphuric acid
(c) Dilute citric acid
(d) Dilute nitric acid
Ans: (a) Dilute hydrochloric acid
 View Answer
View Answer- The stomach produces about 2 liters of a liquid called gastric juice every day.
- This juice contains water, mucus, and hydrochloric acid.
- Hydrochloric acid helps kill germs and make food easier to digest.
- The correct answer is dilute hydrochloric acid.
So, the answer is A.
Q4: __________ can be used to treat acidity.
(a) Sodium bicarbonate
(b) Hydrochloric acid
(c) Amylase
(d) Pepsin
Ans: (a) Sodium bicarbonate
 View Answer
View Answer- Sometimes, the stomach makes too much acid, which causes a burning feeling (acidity).
- Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) can neutralize this acid.
- Mixing it with water helps to calm the stomach.
- So, sodium bicarbonate treats acidity.

Q5: Taste buds are mainly located in ______ surface of the tongue.
(a) Upper
(b) Lower
(c) Both A and B
(d) Margins
Ans: (a) Upper
 View Answer
View Answer- Taste buds help us taste food and are mostly found on the upper surface of the tongue.
- Some taste buds are also in the mouth and throat, but most are on the tongue.
- So, the correct answer is 'upper' surface.
Q6: Which of the following activities improves digestion?
(a) Swallowing
(b) Chewing
(c) Dehydration
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b) Chewing
 View Answer
View Answer- Chewing breaks down food into smaller pieces.
- This makes it easier for our saliva and stomach juices to digest the food.
- So, chewing helps improve digestion.
Q7: Which of the following act as a receptor on the tongue to taste?
(a) Taste buds
(b) Salivary gland
(c) Sensation
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Taste buds
 View Answer
View Answer- Taste buds are special parts on our tongue that sense flavors.
- They help us taste sweet, sour, salty, and bitter foods.
- So, taste buds help us taste food.
 Taste Buds
Taste Buds
Q8: _____ helps in digesting the food.
(a) Swallowing of food
(b) Chewing of food
(c) Tasting the food
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b) Chewing of food
Option (A):
 View Answer
View Answer- Chewing breaks food into small pieces.
- This helps saliva mix with the food to start the digestion process.
- So, chewing helps digest food.
Q9: A piece of bread should be chewed .......... times and then swallowed.
(a) 2
(b) 10
(c) 20
(d) 5
Ans: (c) 20
 View Answer
View Answer- It is important to chew food well before swallowing.
- Chewing food about 20 times helps break it down properly for better digestion.
- So, the food should be chewed 20 times before swallowing.
Q10: Rita put small piece imli on her tongue. Which of the following taste did she feel?
(a) Sweet
(b) Sour
(c) Bitter
(d) Salty
Ans: (b) Sour
 View Answer
View Answer- Imli (tamarind) has a sour taste.
- The taste buds on the tongue can detect sweet, sour, salty, and bitter tastes.
- So, when Rita tasted imli, she felt the sour taste.
Q11: The path taken by food material after ingestion is represented by
(a) Mouth → Oesophagus → Stomach → Pharynx
(b) Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Small Intestine → Stomach
(c) Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Stomach
(d) Oesophagus → Mouth → Pharynx → Stomach
Ans: (c) Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Stomach
 View Answer
View Answer- When we eat food, it first goes into the mouth.
- Then it passes through the pharynx, a part at the back of the throat.
- From there, food moves through the oesophagus (food pipe) and reaches the stomach.
- So, this is the correct sequence of food movement.
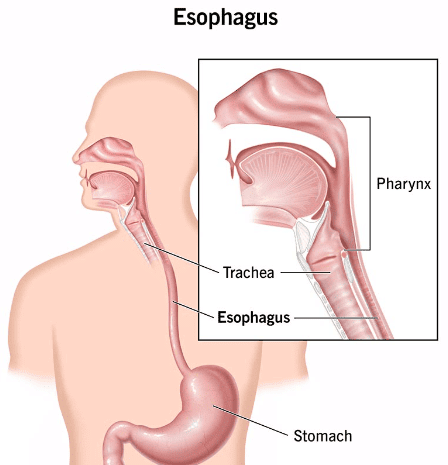
Q12: How is shape of stomach?
(a) As V
(b) As J
(c) As O
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b) As J
 View Answer
View Answer- The stomach is shaped like the letter "J."
- It is a hollow organ between the oesophagus and the small intestine.
- So, the correct answer is 'J-shaped.'
Q13: Which among the following protects the lining of the stomach from hydrochloric acid?
(a) Pepsin
(b) Mucus
(c) Salivary amylase
(d) Bile
Ans: (b) Muscus
 View Answer
View Answer- Mucus forms a protective layer inside the stomach.
- It stops the acid in the stomach from hurting the stomach wall.
- So, mucus protects the stomach lining.
Q14: Raju got stomach ache. Which of the following could be a reason?
(a) He ate food at seven in the evening.
(b) He drank water after eating food.
(c) He did not chew the food properly.
(d) He did not wash his hands properly after eating food.
Ans: (c)
 View Answer
View Answer- Chewing food helps break it down into small pieces, making digestion easier.
- If food is not chewed well, it can cause stomach pain.
- So, Raju's stomach ache may be because he didn’t chew the food properly.
Q15: What is the role of acid in our stomach?
(a) Acidify the food for proper action of pepsin
(b) Conversion of pepsinogen and prorenin into active forms of pepsin and renin
(c) Killing of microorganisms present in food
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
 View Answer
View Answer- Acid in the stomach helps digest food.
- It kills harmful germs that might be in the food.
- It also helps activate enzymes that break down food.
- So, all the given options are correct.
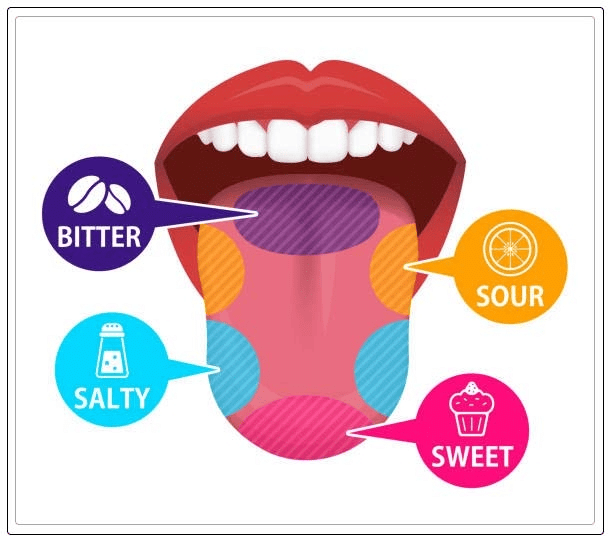
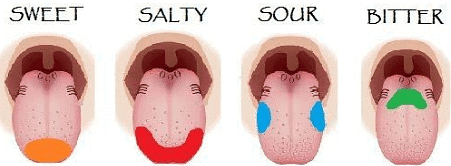
Q16: Salty taste is perceived by the taste buds located on _______.
(a) Tip of the tongue
(b) Sides of the tongue
(c) Back side of the tongue
(d) Both A and B
Ans: (a)
 View Answer
View Answer- The four basic kinds of tastes are: sweet, salty, sour, and bitter.
- The salty/sweet taste buds are located near the front of the tongue, the sour taste buds line the sides of the tongue, and the bitter taste buds are found at the back of the tongue.
- The centre of the tongue has few taste buds.
 Thus, the correct answer is option A.
Thus, the correct answer is option A.
Q17: Digestion of starch starts in the stomach.
(a) True
(b) False
Ans: (b)
 View Answer
View Answer- Digestion of starch starts from the mouth.
- The salivary gland in the mouth secretes saliva, which mixes with the food that is chewed.
- This is because to moisten the food.
- The saliva in the mouth contains the enzyme called amylase that is the starch-digesting enzyme.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Q18: Lowest pH is found in
(a) Small intestine
(b) Large intestine
(c) Stomach
(d) Esophagus
(e) Mouth
Ans: (c)
 View Answer
View Answer- The gastric glands of stomach produce gastric juice, which contains pepsinogen, HCl, and mucus.
- HCl imparts highly acidic pH to stomach which in turn supports conversion of inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- The proper acidic environment of stomach triggers the opening of one way pyrrolic sphincter which in turn allow the chyme to move into the small intestine for further digestive processes.
- Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Q19: Which of the following part of tongue detects the taste of jaggery?
(a) Front
(b) End
(c) Center
(d) Sides
Ans: (a)
 View Answer
View Answer- The taste buds for "sweet" are on the tip of the tongue;
- the "salt" taste buds are on either side of the front of the tongue;
- "sour" taste buds are behind this; and
- "bitter" taste buds are way in the back.
- As the jaggery is sweet in taste, the front part of the tongue detects the taste of jaggery.
- So, the correct answer is 'front'.
 Jaggery
Jaggery
Q20: Chief function of HCl is
(a) To maintain a low pH to prevent growth of microorganisms.
(b) To facilitate absorption.
(c) To maintain low pH to activate pepsinogen to form pepsin.
(d) To dissolve enzyme secreted in stomach.
Ans: (c)
 View Answer
View Answer- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach makes the environment acidic.
- This helps activate pepsinogen, which turns into pepsin and helps digest proteins.
- So, the main function of HCl is to activate pepsinogen
|
37 videos|242 docs|41 tests
|
















