Weather and Climate - 2 Class 5 Worksheet SST
| Table of contents |

|
| True or False |

|
| Find the Odd One Out and Give Reason |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Real-Life Application-Based Questions |

|
True or False
(i) Weather refers to the long-term atmospheric conditions of a place.
(ii) The Sun’s rays fall more directly at the Equator than at the poles.
(iii) Altitude does not affect the climate of a place.
(iv) The monsoon is a type of rainfall pattern that affects India.
(v) All coastal areas experience extreme climates.
(vi) Humidity is the amount of moisture present in the air.
(vii) Frigid zones receive the most sunlight and have the highest temperatures.
(viii) Chennai and Mumbai have extreme climates like deserts.
(ix) Distance from the sea does not affect the climate of a place.

Find the Odd One Out and Give Reason
(i) Equator, Frigid Zone, Monsoon, Temperate Zone
(ii)Temperature, Rainfall, Wind Speed, Earthquake
(iii) Latitude, Altitude, Distance from the Sea, Rain Gauge
(iv) Tropical Zone, Desert Climate, Frigid Zone, Temperate Zone
(v) Sunlight, Humidity, Glacier, Air Pressure
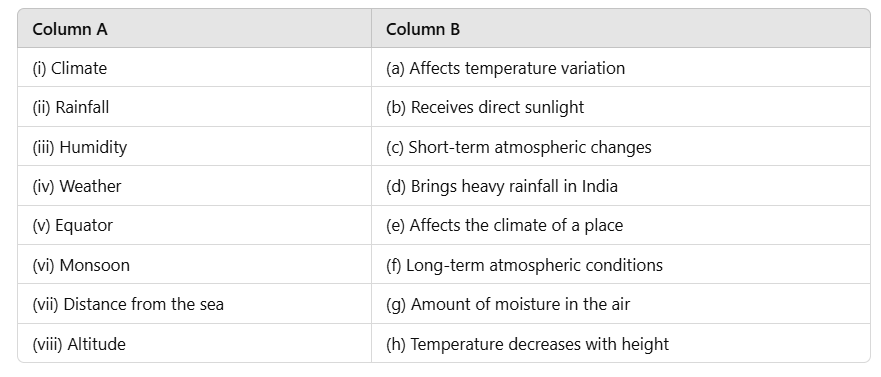
Match the Following
 |
Download the notes
Worksheet: Weather and Climate - 2
|
Download as PDF |
Real-Life Application-Based Questions
(i) Why do people living near coastal areas experience less temperature variation than those living in deserts or inland areas?
(ii) Why is the Equator hotter than the Polar regions?
(iii) Why do farmers check the weather forecast before sowing their crops?
(iv) Why does Chennai experience a more moderate climate than Delhi, even though both are in India?
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
32 videos|228 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Weather and Climate - 2 Class 5 Worksheet SST
| 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? |  |
| 2. How do meteorologists predict the weather? |  |
| 3. What are the main factors that influence climate? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding climate change important? |  |
| 5. How do seasons change in different parts of the world? |  |















