Delhi Sultanate - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The Delhi Sultanate, spanning from 1206 to 1526 AD, marked a significant era in the history of India. This article delves into the various dynasties that ruled during this period, shedding light on their administration, economic policies, cultural contributions, and architectural marvels.
I. Dynastic Succession
After the demise of Mohammed Ghori, multiple contenders vied for the throne of the Delhi Sultanate. Among them, Qutb-ud-din Aibak emerged as the victor and initiated the rule of the Slave Dynasty. Over the centuries, the Delhi Sultanate witnessed the reign of five distinct dynasties, each leaving a unique imprint on the Indian subcontinent: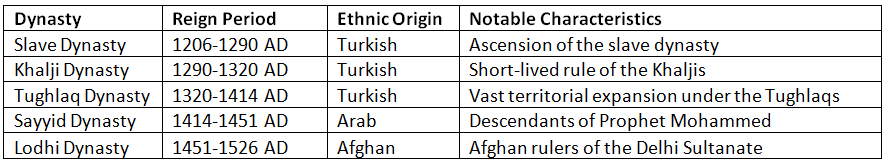
Notably, the first three dynasties were of Turkish descent, while the Sayyids traced their ancestry to Arab origins, proudly proclaiming their lineage from Prophet Mohammed. The Lodhis, on the other hand, were of Afghan heritage. An interesting observation is that the Slave Dynasty witnessed the most number of sultans, whereas the Lodhi Dynasty had the fewest.
II. Duration and Territory
The Tughlaq Dynasty stands out for its remarkably long reign, while the Khalji Dynasty had a relatively brief tenure. The Tughlaqs expanded their dominion across vast territories, whereas the Sayyids ruled over the smallest expanse during their rule.
III. Administrative Structure
The Delhi Sultanate implemented a structured administrative system to govern its vast territories.
Key aspects of the administration included:
- Iqta System: A land revenue system where military officials were granted control over specific regions in exchange for their services.
- Divisions: The empire was divided into provinces called 'iqtas,' each governed by an 'iqtadar.'
- Central Authority: The sultan held ultimate authority, while provincial governors managed day-to-day affairs.
- Military: The sultanate maintained a formidable army comprising cavalry, infantry, and elephants.
IV. Economic Policies
Economically, the Delhi Sultanate era witnessed significant developments:
- Agriculture: The economy was primarily agrarian, with the Iqta system playing a pivotal role in revenue collection.
- Trade: Trade flourished, with the sultanate serving as a key hub on the Silk Road.
- Coinage: Various dynasties issued their own coinage, reflecting their cultural influence.
V. Cultural Contributions
The Delhi Sultanate made noteworthy contributions to Indian culture:
- Literature and Languages: Persian became the court language, and many historical and literary works were translated or composed during this period.
- Music: The sultanate fostered the growth of Indian classical music, influencing subsequent developments.
- Architecture: The era is renowned for its architectural achievements, exemplified by structures like the Qutub Minar and the Alai Darwaza.
In conclusion, the Delhi Sultanate, with its diverse dynasties and rich cultural tapestry, left an indelible mark on Indian history. It was a period of dynamic political changes, economic prosperity, and cultural growth, making it a pivotal chapter in India's historical narrative.













