Area Related to Circles Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 11
| Table of contents |

|
| Important Formulas related to Circle |

|
| Minor Arc and Major Arc |

|
| Sector of a Circle and its Area |

|
| Segment of a Circle and its Area |

|
Important Formulas related to Circle
- Circumference of a circle = 2πr
- Area of a circle = πr2 …[where r is the radius of a circle]
- Area of a semi-circle =πr2/2
- Area of a circular path or ring:
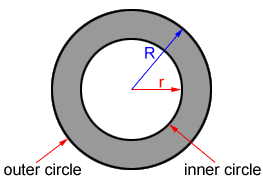 Let ‘R’ and ‘r’ he radii of two circles
Let ‘R’ and ‘r’ he radii of two circles
Then area of shaded part = πR2 – πr2 = π(R2 – r2) = π(R + r)(R – r)
Minor Arc and Major Arc
An arc length is called a major arc if the arc length enclosed by the two radii is greater than a semi-circle.
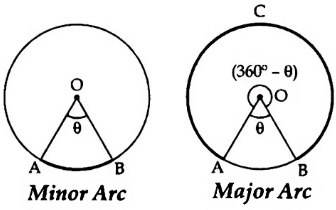
If the arc subtends angle ‘θ’ at the centre, then the
Length of minor arc = 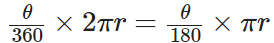
Length of major arc = 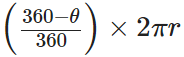
Sector of a Circle and its Area
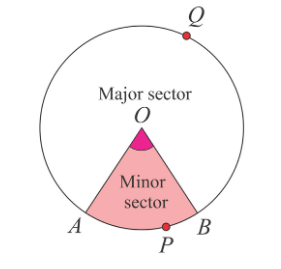
A region of a circle is enclosed by any two radii and the arc intercepted between two radii is called the sector of a circle.
Minor Sector
A sector is called a minor sector if the minor arc of the circle is part of its boundary.
OAPB is minor sector.
 Area of minor sector =
Area of minor sector = 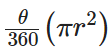
Perimeter of minor sector = 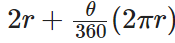
Major Sector
A sector is called a major sector if the major arc of the circle is part of its boundary.
OAQB is major sector
Area of major sector = 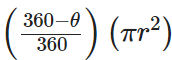
Perimeter of major sector = 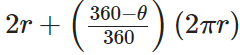
Segment of a Circle and its Area
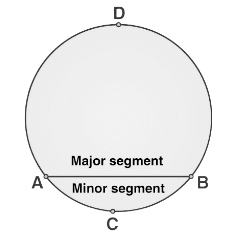
Minor Segment
The region enclosed by an arc and a chord is called a segment of the circle. The region enclosed by the chord AB & minor arc ACB is called the minor segment.
Area of Minor segment = Area of the corresponding sector – Area of the corresponding triangle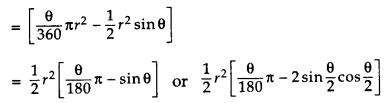
Major Segment
The region enclosed by the chord AB & major arc ADB is called the major segment. Area of major segment = Area of a circle – Area of the minor segment
Area of major sector + Area of triangle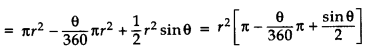
Example: A chord of a circle of radius 12 cm subtends an angle of 120° at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding segment of the circle. (Use π = 3.14 and √3 = 1.73).
Sol:
We use the concept of areas of sectors of circles to solve the question.
In a circle with radius r and the angle at the centre with degree measure θ:
(i) Area of the sector = θ/360 πr2
(ii) Area of the segment = Area of the sector - Area of the corresponding triangle
Let's draw a figure to visualize the given question.
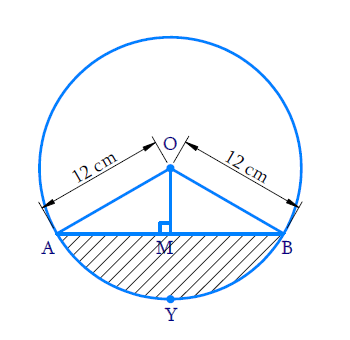
Here, radius, r = 12 cm, ∠AOB = θ = 120°
Visually it’s clear from the figure that AB is the chord that subtends 120° angle at the centre.
To find the area of the segment AYB, we have to find the area of the sector OAYB and the area of the ΔAOB
(i) Area of sector OAYB = θ/360° πr2
(ii) Area of ΔAOB = 1/2 × base × height
For finding the area of ΔAOB, draw OM ⊥ AB then find base AB and height OM using the figure as shown above.
Area of sector OAYB = 120°/360° × πr2
= 1/3 × 3.14 × (12 cm)2
= 150.72 cm2
Draw a perpendicular OM from O to chord AB
In ΔAOM and ΔBOM
AO = BO = r (radii of circle)
OM = OM (common side)
∠OMA = ∠OMB = 90° (perpendicular OM drawn)
∴ ΔAOM ≅ ΔBOM (By RHS Congruency)
⇒ ∠AOM = ∠BOM (By CPCT)
Therefore, ∠AOM = ∠BOM = 1/2 ∠AOB = 60°
In ΔAOM,
AM/OA = sin 60° and OM/OA = cos 60°
AM/12 cm = √3/2 and OM/12 cm = 1/2
AM = √3/2 × 12 cm and OM = 1/2 × 12 cm
AM = 6√3 cm and OM = 6 cm
⇒ AB = 2 AM
= 2 × 6√3 cm
= 12√3 cm
Area of ΔAOB = 1/2 × AB × OM
= 1/2 × 12√3 cm × 6 cm
= 36 × 1.73 cm2
= 62.28 cm2
Area of segment AYB = Area of sector OAYB - Area of ΔAOB
= 150.72 cm2 - 62.28 cm2
= 88.44 cm2

Table for Area and Perimeter of Circle
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Area Related to Circles Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 11
| 1. What are the formulas for calculating the circumference and area of a circle? |  |
| 2. How do you differentiate between a minor arc and a major arc in a circle? |  |
| 3. What is a sector of a circle and how can we calculate its area? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a segment of a circle and a sector? |  |
| 5. How do you find the area of a segment of a circle? |  |















