Covid Tests: Different Types of Coronavirus Testing | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Covid-19 Virus: Structure |

|
| Types of Viral Tests for Covid-19 |

|
| Antibody Tests for Covid-19 (Serological Tests) |

|
| Things to know about Coronaviruses |

|
Introduction
COVID-19 has necessitated various types of tests to diagnose and confirm infections. Two primary categories of tests are viral tests and antibody tests. This article explores the different types of COVID-19 tests available.
Covid Testing: What are the different types of Tests?
There are two kinds of tests available for COVID-19: antigen tests and antibody tests.
- Viral Test: A viral test tells if the patient has a current infection.
- Antibody Test: An antibody test may tell if the patient had a past infection.
Covid-19 Virus: Structure
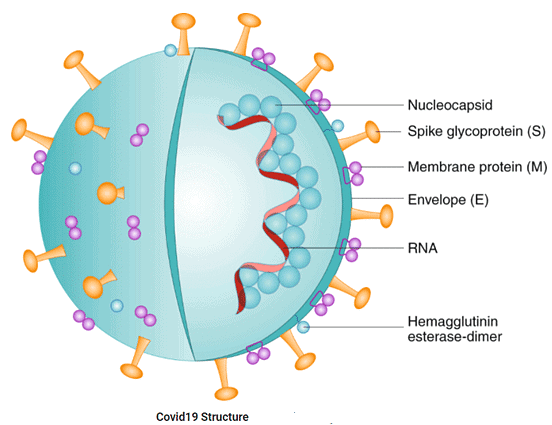
- The COVID-19 virus, also known as SARS-CoV-2, is composed of proteins and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid).
- Viral tests are designed to identify viral components present in an infected patient, which can include either viral proteins or RNA.
- Antibody tests, on the other hand, do not search for viral components directly. Instead, they detect antibodies that are produced by the infected patient's body in response to the virus.
Types of Viral Tests for Covid-19
Viral tests for COVID-19 can be categorized based on what the test specifically detects, either viral proteins or nucleic acids (RNA). Two popular types of viral tests are the Rapid Antigen Test and the RT-PCR Test, and there is also mention of the TruNAT test:
1. Rapid Antigen Test
- Specimen: Nasopharyngeal swab
- What the test detects: Antigens (Proteins) of the COVID-19 Virus
- Process: Nasal samples are collected and tested for specific antigens found in the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This test can be conducted outside a traditional laboratory setting and provides quick diagnostic results.
- Interpretation: A positive result is generally confirmatory, but negative results in symptomatic individuals require further confirmation with an RT-PCR test. The concentration of the antigen cannot be quantified by this test.
2. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR)
- Specimen: Nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal swab
- What the test detects: Nucleic acids (RNA) of the COVID-19 Virus
- Process: A sample is collected from deep within the nose and throat, and the RNA is isolated by removing proteins and fats. The RNA is then analyzed using an RT-PCR machine in a laboratory to detect the virus's genetic material.
- Interpretation: RT-PCR is a molecular test that looks for the genetic material of the virus. Positive results indicate the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Negative results do not necessarily rule out infection and should be considered alongside clinical and epidemiological information.
3. TruNAT
- Specimen: Nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal swab
- What the test detects: RdRp enzyme found in the RNA of the COVID-19 Virus
- Process: The TruNAT machine identifies the RdRp enzyme present in the virus's RNA in nasal or oral swabs.
- Information: TruNAT is similar to RT-PCR but offers faster results and uses a smaller kit. It is also used for detecting tuberculosis and HIV in addition to COVID-19.
These tests serve different purposes and have varying sensitivities and specificities. It's important to interpret their results in the context of clinical information and follow-up testing when necessary.
Antibody Tests for Covid-19 (Serological Tests)
Here's a concise summary of the key points regarding antibody tests for COVID-19:
- Antibody tests identify antibodies produced by the body's immune system in response to SARS-CoV-2.
- These tests can indicate whether an individual has had a previous COVID-19 infection but are not suitable for diagnosing current infections.
- Antibodies typically appear in the blood about 1 to 2 weeks after the onset of symptoms, potentially missing early infections.
- Antibodies are also referred to as immunoglobulins (Ig).
- The commonly tested antibodies are Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and Immunoglobulin M (IgM).
- Rapid antibody tests involve collecting a blood sample from the finger and examining it for IgM antibodies (early infection) and IgG antibodies (later infection).
- Antibodies can take varying amounts of time to develop after exposure to SARS-CoV-2, and their persistence in the blood is uncertain.
- Antibody tests do not directly detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus for diagnosing COVID-19.
- These tests can yield negative results, particularly in early infections when antibodies have not yet formed, or false-positive results if antibodies to other coronaviruses are present.
- A positive antibody test does not guarantee immunity from future SARS-CoV-2 infections, nor does it indicate whether an individual can transmit the virus to others.
In summary, antibody tests serve as a tool to assess past exposure to the virus but should not be relied upon for diagnosing current infections or determining immunity definitively. Public health measures should continue to be followed regardless of antibody test results to mitigate the spread of COVID-19.
Things to know about Coronaviruses
- Coronaviruses are a group of viruses characterized by non-segmented, positive-stranded RNA genomes that are approximately 30 kilobases (kb) in size and enclosed by a protein envelope. They typically have an envelope with a diameter ranging from 80 to 120 nanometers, making them relatively large among RNA viruses. In fact, their genetic material is the largest among all RNA viruses.
- Most coronaviruses are known to cause diseases in specific host species, and those that have the ability to jump between species, including humans, pose a significant threat to public health. One such species is the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV), which can infect humans, bats, and certain other mammals. It falls under the genus Betacoronavirus and the subgenus sarbecoronavirus.
- There are two notable strains of this virus:
- SARS-CoV: This strain caused the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak between 2002 and 2004.
- SARS-CoV-2: This strain is responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, which began in December 2019 in Wuhan, Hubei province, China. COVID-19 is the official name given to this disease by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Common signs of a person infected with a coronavirus include respiratory symptoms, fever, cough, shortness of breath, acute respiratory syndrome, and dyspnea (difficulty breathing). It's essential to monitor and address these symptoms, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, as early detection and appropriate measures can help reduce the spread of the virus.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of COVID-19 tests, including viral tests and antibody tests, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management of the disease. Additionally, comprehending the characteristics of coronaviruses helps in assessing the threat they pose to public health.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|















