UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > Virus and Bacteria
Virus and Bacteria | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Viruses |

|
| Bacteria |

|
| Difference between Virus and Bacteria |

|
| Viroids |

|
| Difference Between DNA & RNA Viruses |

|
Introduction
Bacteria
- Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms.
- They exhibit a wide variety of shapes and structural features.
- Bacteria can thrive in diverse environments, including the human body.
- While many bacteria are harmless or even beneficial, some can cause infections in humans and are known as pathogenic bacteria.
- Bacterial infections can lead to various diseases, and antibiotics are often used to treat bacterial infections.
Viruses
- Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and are considered microscopic infectious agents.
- They come in diverse shapes and sizes and can infect a wide range of organisms, including humans.
- Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites, meaning they require a living host cell to replicate and reproduce.
- Once inside a host cell, viruses hijack the cellular machinery to replicate and produce more virus particles.
- Some viruses can damage or destroy host cells during the replication process, which can lead to diseases.
- Vaccines and antiviral medications are used to prevent and treat viral infections.
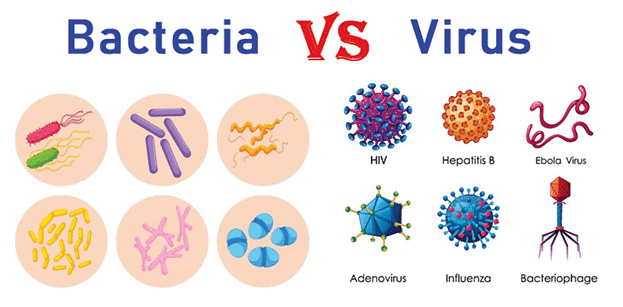
Viruses
- Viruses are not classified as true living organisms because they lack cellular structures.
- They are characterized by an inert crystalline structure outside a living cell.
- Viruses are obligate parasites, meaning they depend on a host cell to replicate and reproduce, often causing harm or cell death.
- The term "virus" was coined by Louis Pasteur and means "venom" or "poisonous fluid."
- Viruses contain genetic material, which can be either RNA or DNA, but not both simultaneously.
- Viruses that infect plants typically have single-stranded RNA, while those infecting animals may have single or double-stranded RNA or double-stranded DNA.
- Bacteriophages, which infect bacteria, are typically double-stranded DNA viruses.
- Viruses have a protective protein coat called a capsid, composed of smaller subunits known as capsomeres.
- Capsomeres can be arranged in helical or polyhedral geometric forms depending on the virus.
Some examples of viral infections include
- influenza
- common cold
- viral gastroenteritis
- chickenpox
- measles
- viral meningitis
- warts
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- viral hepatitis
- Zika virus
- West Nile virus
- COVID-19 is another illness caused by a virus. This virus commonly causes:
- shortness of breath
- fever
- dry cough
Bacteria
- Bacteria are single-cell, living organisms capable of independent survival without a host.
- They can thrive in various environments, including surfaces, soil, water, and air.
- Antibiotics are effective in treating bacterial infections by targeting and killing bacteria. However, antibiotics do not work against viruses.
- Some antiviral drugs can help prevent or manage viral infections by interfering with the virus's ability to enter host cells or reproduce.
- Bacteria typically reproduce through a simple process of cell division, where one cell splits into two.
- Bacterial infections can lead to various diseases, such as pneumonia and food poisoning.
- It's essential to note that not all bacteria are harmful; some beneficial bacteria play crucial roles in protecting human health and aiding in various bodily functions.
Some examples of bacterial infections include
- strep throat
- urinary tract infection (UTI)
- bacterial food poisoning
- gonorrhea
- tuberculosis
- bacterial meningitis
- cellulitis
- Lyme disease
- tetanus
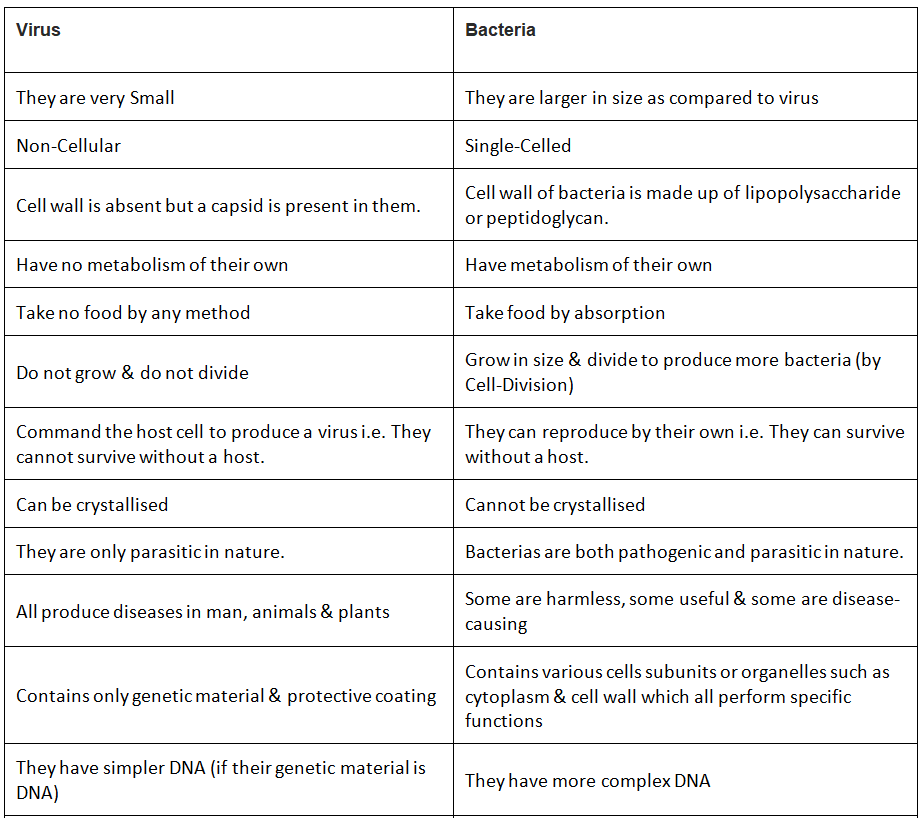
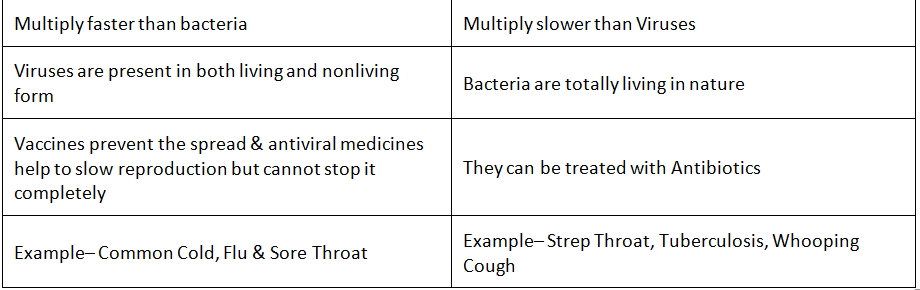
Difference between Virus and Bacteria
Viroids
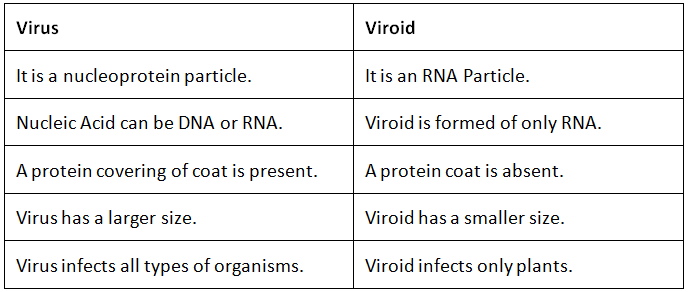
- Viroids are infectious agents that are smaller than viruses, making them one of the simplest known pathogens.
- Unlike viruses, viroids consist solely of a single, free RNA molecule and do not have a protective protein coat.
- The term "viroid" is derived from the combination of "virus" and "RNA" due to their nature as small, infectious RNA molecules.
- Viroids have a low molecular weight, as they are composed solely of RNA.
- Viroids are known to cause diseases in various plants. One notable example is the "potato spindle tuber disease," which is caused by a viroid.
Difference Between DNA & RNA Viruses
- DNA Viruses:
- Contain DNA as their genetic material.
- Typically double-stranded.
- Replicate in the nucleus of host cells.
- Generally stable.
- RNA Viruses:
- Contain RNA as their genetic material.
- Typically single-stranded.
- Replicate in the cytoplasm of host cells.
- Generally less stable and have a higher mutation rate than DNA viruses.
- Antigens:
- Substances recognized by the body as foreign, triggering an immune response.
- Antibodies:
- Blood proteins produced by the body in response to antigens, aiming to neutralize or eliminate them.
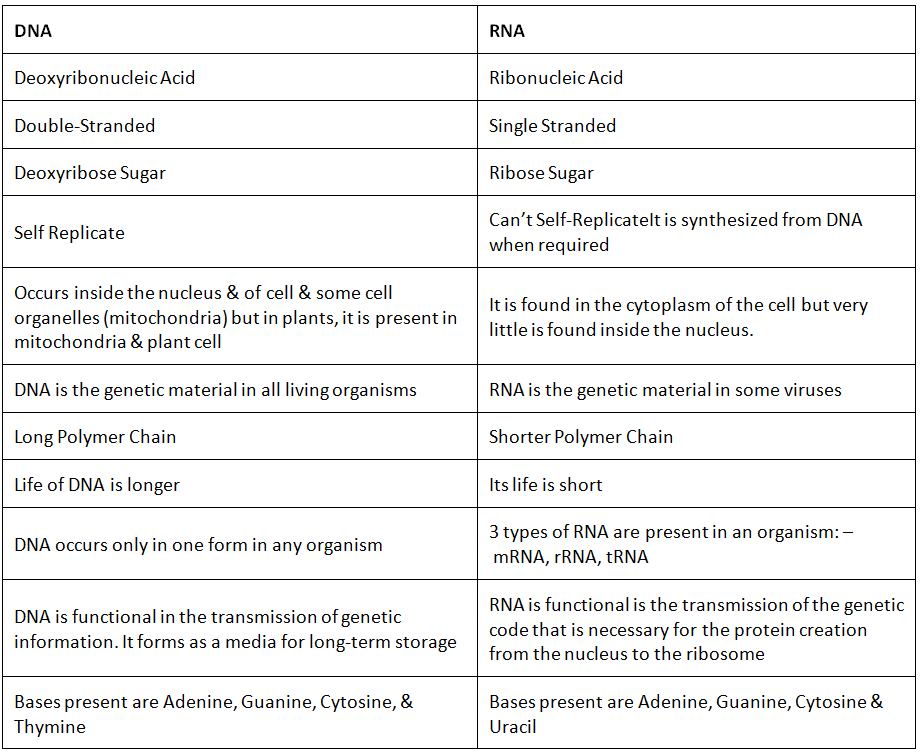
Difference between DNA vs RNA
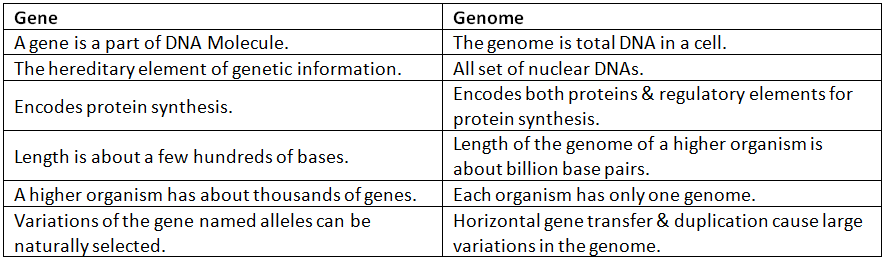
Difference between Gene & Genome
The document Virus and Bacteria | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
91 videos|517 docs|212 tests
|
Related Searches















