Defence Research and Development Organisation | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Genesis & Growth |

|
| Mission |

|
| Defence Space Research Agency |

|
| Defense Acquisition Organization (DAO) |

|
| Nuclear Command Authority |

|
Introduction
- The Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) operates under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India. Its primary mission is to establish a world-class science and technology base in India. DRDO aims to provide India's defense services with cutting-edge systems and solutions, giving them a decisive edge in terms of technological capabilities.
- In pursuit of this mission, DRDO conducts research and development across various domains, including aerospace, missile systems, electronics, naval systems, combat vehicles, and more. The organization is responsible for developing and delivering advanced technologies and equipment to strengthen India's defense capabilities and ensure national security.
- DRDO's work is integral to India's defense strategy, as it enables the country to develop and maintain state-of-the-art defense systems, thereby enhancing its preparedness and effectiveness in safeguarding its borders and national interests.
Genesis & Growth
The Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has a rich history and has grown significantly since its establishment:
- Genesis: DRDO was founded in 1958 through the merger of several defense-related entities, including the Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army, the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP), and the Defence Science Organisation (DSO). This consolidation aimed to streamline and enhance India's defense research and development efforts.
- Growth: DRDO began its journey with 10 laboratories, and since then, it has expanded into a vast network comprising 52 laboratories. These laboratories are actively involved in the development of defense technologies across a wide range of disciplines, including aeronautics, armaments, electronics, combat vehicles, engineering systems, instrumentation, missiles, advanced computing and simulation, special materials, naval systems, life sciences, training, information systems, and agriculture.
- Human Resources: DRDO's workforce has also grown substantially. It is currently supported by over 5,000 scientists and approximately 25,000 other scientific, technical, and supporting personnel. This dedicated team plays a crucial role in advancing defense research and technology for the nation.
- Projects and Achievements: DRDO is engaged in several major projects focused on the development of missiles, armaments, light combat aircraft, radars, electronic warfare systems, and more. The organization has achieved significant milestones in these technologies, contributing to India's defense capabilities and national security.
DRDO's continuous growth and achievements underscore its commitment to advancing defense technology and providing the Indian armed forces with cutting-edge systems and solutions to meet evolving security challenges.
Mission
DRDO's mission is multifaceted and geared towards strengthening India's defense capabilities:
- Technology Development: Design, develop, and oversee the production of advanced sensors, weapon systems, platforms, and related equipment for the Indian Defence Services. This involves creating cutting-edge technology to enhance the country's defense capabilities.
- Optimizing Combat Effectiveness: Provide technological solutions to the armed forces with the aim of optimizing their combat effectiveness. DRDO works to equip the military with state-of-the-art tools and systems to ensure they are well-prepared to address security challenges.
- Troop Well-being: Promote the well-being of the troops by developing technologies and solutions that enhance the safety, health, and overall quality of life for military personnel. This includes innovations that improve living conditions and healthcare for soldiers.
- Infrastructure Development: Establish and enhance infrastructure to support defense research and development activities. This includes the creation of state-of-the-art facilities and laboratories.
- Quality Manpower: Develop a pool of highly skilled and committed personnel capable of driving technological advancements in defense. DRDO places a strong emphasis on building a talented and dedicated workforce.
- Indigenous Technology: Build a robust indigenous technology base, reducing reliance on foreign sources for critical defense technologies. This ensures self-reliance and security in the defense sector.
Defence Space Research Agency
The Defense Space Research Agency (DSRO) is a newly established agency with the mandate to develop space warfare weapon systems and related technologies for India's defense.
Here are some key points about DSRO and its role:
- Establishment: DSRO was approved by the Cabinet Committee on Security, chaired by the Prime Minister, as a specialized agency dedicated to space warfare research and development.
- Scientific Team: DSRO will be staffed with a team of scientists who will work closely with integrated defense staff officers from the three armed services.
- Support to Defence Space Agency (DSA): One of DSRO's primary functions is to provide research and development support to the Defence Space Agency (DSA). DSA is responsible for enhancing India's capabilities in space warfare and securing its interests in space.
- Warfighting in Space: DSA has been established to prepare and equip India to engage in conflicts that may occur in space, such as defending against potential threats to its space assets.
- Location: The Defense Space Agency is headquartered in Bengaluru and is led by an Air Vice Marshal-rank officer. It will gradually take over the space-related responsibilities and capabilities of the three armed services.
- Integration: Existing military space agencies, including the Defence Imagery Processing and Analysis Centre (located in New Delhi) and the Defence Satellite Control Centre (located in Bhopal), will be merged into DSA to streamline and coordinate space-related efforts.
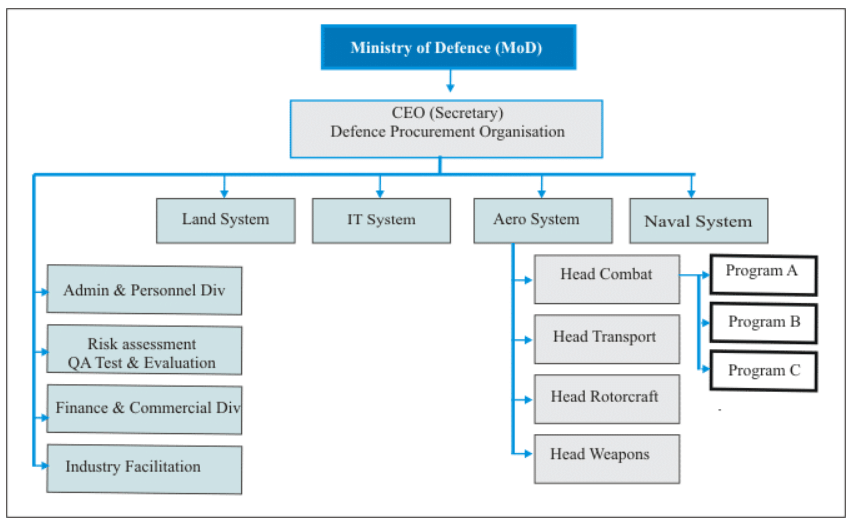
Defense Acquisition Organization (DAO)
The Defense Acquisition Organization (DAO) is a proposed autonomous body under the Ministry of Defence (MoD) in India. It is intended to streamline and improve the defense procurement process while enhancing accountability.
Here are some key points about DAO:
- Background: The concept of DAO was recommended by the Pritam Singh Committee as a response to the need for a more efficient and effective defense procurement system.
- Autonomous Organization: DAO is designed to be an autonomous entity operating within the Ministry of Defence. This autonomy is intended to allow it to function independently and expedite procurement processes.
- Responsibilities: DAO will have a range of responsibilities, including formulating policy, planning, and executing weapons and equipment purchases for the Indian Armed Forces.
- Funding: To maintain its autonomy, DAO will be funded with a certain percentage of the funds it utilizes each financial year. In the initial year, this funding is estimated to be around Rs 400 crore.
- Objective: The primary objective of establishing DAO is to create a procurement organization that can operate more efficiently and is not bound by the standard government rules and regulations. This is expected to contribute to the "Make in India" initiative by facilitating indigenous defense production.
Principles and Organizational Structure
Basic guiding principles suggested for its functioning to be an autonomous, decentralized decision-making defense procurement organization(DPO) with accountability and transparency with a managed delivery within the agreed PTCR (Performance, Cost, Time, and Risk) envelope as per the annual acquisition plans based on:
- Risk management rather than risk avoidance
- Individual rather than group accountability.
- A quarterly measure of performance with the internal customers (Army, Navy, Air Force)
- The process should be differentiated into three broad steps with autonomy and accountability.
- Technical requirements identification.
Nuclear Command Authority
- The Nuclear Command Authority (NCA) in India is responsible for overseeing command, control, and operational decisions related to India's nuclear weapons program. It was established on January 4, 2003, with the formation of the Political Council and the Executive Council within the NCA. These councils play essential roles in authorizing nuclear actions when necessary.
- Political Council: Chaired by the Prime Minister, the Political Council is responsible for authorizing nuclear attacks. It provides the final approval for any nuclear action.
- Executive Council: Headed by the National Security Advisor (NSA), the Executive Council offers its opinion to the Political Council. It plays a crucial role in ensuring civilian control over India's nuclear arsenal and maintaining a sophisticated command and control system to prevent accidental or unauthorized use of nuclear weapons.
- The Strategic Forces Command (SFC), also known as the Strategic Nuclear Command, is part of the NCA. The SFC is responsible for managing and administering India's tactical and strategic nuclear weapons stockpile.
- The directives of the NCA are executed by the Strategic Forces Command, led by a Commander-in-Chief of the rank of Air Marshal or its equivalent. This individual oversees the management and administration of India's tactical and strategic nuclear forces.
- Additionally, the Indian Ministry of Defence established the Defence Planning Committee (DPC) in April 2018. The DPC is chaired by the National Security Adviser (NSA) and includes members such as the Foreign Secretary, Defence Secretary, Chief of Defence Staff, service chiefs, and others. The DPC's main mandates include drafting a National Security Strategy, developing a capability development plan, addressing defense diplomacy matters, and enhancing India's defense manufacturing capabilities.
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) is the highest-ranking serving officer in the Indian Armed Forces and the chief executive of the Department of Military Affairs. The CDS serves as the main military adviser to the government of India and the Ministry of Defence. This role involves leading the Joint Commanders and Staff Committee and providing professional guidance to the armed forces.
- The CDS is supported by a deputy, the Vice Chief of Defence Staff, and the chiefs of staff of the army, navy, and air force, who lead their respective branches. General Bipin Rawat is the current Chief of Defence Staff, serving since January 1, 2020.
- The CDS is responsible for enhancing coordination, tri-service effectiveness, and the overall combat capabilities of the Indian armed forces. This position is crucial in modern warfare scenarios and helps streamline military advice to the government and Defence Minister. While the Defence Secretary remains the primary civilian defense adviser, the CDS serves as the key military adviser, filling a significant role in India's defense structure.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|




















