UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 7th September 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Classical dances of Kerala
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
Various classical dances of Kerala were performed during Onam celebrations held recently.
Background:-
- This year, Onam festivities began on 20th August 2023 and Thiruvonam fell on August 31 as the 10-day harvest festival was observed across the South Indian state of Kerala.
- It marks the beginning of the Malayalam year, called Kolla Varsham, and commemorates the return of the mythical King Mahabali with great enthusiasm and cultural fervor.
About Classical dances of Kerala:-
- Kerala is known for its rich cultural heritage.
- It includes various classical dance forms, some of these performed during Onam 2023 celebrations include:-
Kathakali:-
- It originated in Kerala over 300 years ago.
- It is one of the most famous classical dance forms of the state.
- It is One of the eight classical dances of India.
- It is a highly stylized and dramatic art form combining the elements of dance, music, acting, devotion, drama, costumes, and make-up.
- Kathakali performances retell the great stories of the past, mostly from Indian epics, or depict episodes from the Mahabali legend or other mythological stories associated with the festival, using hand and facial gestures and expressions.
Mohiniyattam:–
- It is a graceful and lyrical dance form.
- It is performed in honor of the Hindu god Vishnu in his incarnation as the enchantress Mohini.
- It is One of the eight classical dances of India.
- It is performed exclusively by women.
- It is characterized by gentle, flowing movements and expressive storytelling, narrating the stories related to King Mahabali during the Onam festival.
Koodiyattam:-
- It is recognized as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
- It is one of the oldest classical theater forms in the world.
- It involves elaborate and ritualistic performances with traditional costumes and makeup.
- It depicts stories from Hindu epics and Puranas that are sometimes staged during Onam.
Thiruvathirakali:-
- It is a traditional group dance.
- It involves graceful circular movements by the women and clapping of their hands to the rhythm of the music.
- This group dance is often performed by women.
- It is considered a celebration of womanhood.
- It is mostly performed in the evening under the moonlight.
Chakyar Koothu:-
- It is a traditional solo performance.
- It has the artist narrating episodes from epics like the Ramayana and the Mahabharata in a humorous and dramatic manner on Onam.
- It is not a dance form per se.
It is an integral part of Kerala’s performing arts tradition.
Ottamthullal:-
- The dance form was created by the renowned Malayalam poet Kunchan Nambiar.
- It involves a single performer narrating stories with dance and song in a satirical and humorous style.
- The performance is accompanied by a mridangam (barrel-shaped drum).
Source: Hindustan Times
GS-II
India’s ASEAN Engagement and Upcoming Summits
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Prime Minister departed for Indonesia to participate in the 20th ASEAN-India summit and the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Jakarta.
- During the visit, he will meet with leaders from the ten ASEAN countries and attend the EAS, including leaders from ASEAN nations, Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, Russia, and the U.S.
Why discuss this?
- India-ASEAN relations have evolved significantly over the years, moving from a distant past to a robust partnership.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) | |
| Established | August 8, 1967 |
| Member Countries | Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam |
| Objective | To promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among member countries. |
| Key Areas of Cooperation | – Economic Integration – Political and Security Cooperation – Social and Cultural Cooperation |
| Significance | Promotes economic growth, stability, and peace in the Southeast Asian region. It is also a forum for diplomatic dialogue and conflict resolution. |
| ASEAN Secretariat | Jakarta, Indonesia (The ASEAN Secretariat is the organization responsible for coordinating ASEAN activities.) |
Evolution of India-ASEAN Relations
- 1950s and Early 1960s: During this period, India played a significant role in supporting the decolonization efforts of Southeast Asian countries.
- 1960s to 1980s: India maintained some distance from the region due to internal issues and viewed ASEAN as a product of the Cold War.
- 1990s to 2010s: India adopted the ‘Look East Policy,’ leading to a full dialogue partnership with ASEAN in 1995 and becoming a full member of the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) in 1996.
- 2010s to Present: India-ASEAN cooperation intensified with the ‘Act East Policy,’ resulting in the elevation to a Strategic Partnership in 2012 and a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2022.
Key Areas of Cooperation
- Trade Relations: The India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA) and substantial trade volumes have strengthened economic ties, with commodity trade reaching $98.39 billion in the period April 2021-February 2022.
- Business & Investment: ASEAN is a major source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) for India, with cumulative FDIs from ASEAN to India totaling $117.88 billion between 2000-2021. The ASEAN India-Business Council (AIBC) promotes collaboration between private sector players from India and ASEAN.
- Socio-Cultural Cooperation: Cultural affinities between ASEAN and India foster people-to-people interactions through initiatives like student exchange programs.
- ASEAN-India Projects: Collaboration in agriculture, science & technology, environment, renewable energy, and defense promotes mutual growth. The ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund (AISTDF) contributes $1 million to support joint collaborative R&D research projects.
- Strategic Cooperation: Platforms like the ASEAN Post Ministerial Conference (ASEAN PMC) and ADMM-Plus facilitate dialogue on security issues.
- Defense Cooperation: India is enhancing arms sales and defense ties with ASEAN countries to promote regional security, such as the recent approval by the Philippines for a USD 374 million purchase of the BrahMos shore-based anti-ship missile system in January 2022.
- Technological Cooperation: ISRO’s collaboration supports ASEAN countries in space science and technology.
- Connectivity: Projects like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and Kaladan Multimodal Project enhance regional connectivity.
Why India Needs ASEAN?
- Significant Trade & Commercial Relations: ASEAN is a major destination for India’s service sectors and a vital source of foreign investments.
- Development of North East India: ASEAN provides an alternate route for India’s access to North Eastern India, facilitating development and strategic interests.
- Countering Chinese Expansion: Strengthening ties with ASEAN countries helps India counter Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Maritime Freedom: Collaboration with ASEAN ensures a free and peaceful Indo-Pacific region based on a rules-based order.
- Facing Politico-security Challenges: Cooperation in addressing security threats like climate change, terrorism, and refugee crises benefits both sides.
- Support for Indian Initiatives: ASEAN’s support is crucial for India’s success in regional policies and initiatives.
- Emerging Market: India benefits from ASEAN’s agricultural and industrial products, while ASEAN relies on India’s demographic dividend.
- Global Reforms: ASEAN’s global influence aligns with India’s vision for reforms in international forums.
- Diaspora: Southeast Asia’s significant Indian diaspora fosters cultural ties and people-to-people relations.
- Elevating India’s Global Status: Partnership with ASEAN enhances India’s geopolitical standing.
Challenges to Stronger Cooperation
- Large Trade Deficit: Trade imbalance and issues with the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) have impacted India’s economic relations with ASEAN, with the trade deficit rising from around $5 billion in FY11 to USD 21.8 billion in FY19.
- Balancing China: ASEAN countries’ engagement with China and concerns over military capabilities impact the depth of cooperation with India.
- Delays in Connectivity Projects: Long gestation periods for connectivity projects hinder progress.
- Issues within ASEAN: Different political systems and human rights issues pose challenges to stronger cooperation.
Way Forward
- Enhance Trade Relations: Focus on the blue economy and sustainable development to boost economic ties.
- Accelerate Connectivity Projects: Expedite the completion of infrastructure projects and build new trade and transport linkages.
- Strengthen Regional Role: India must play a more prominent role in the region to address geopolitical challenges.
- Establish Dedicated Departments: Dedicated departments under central ministries can facilitate better cooperation with ASEAN.
Conclusion
- India’s commitment to ASEAN signifies its strategic engagement with the Indo-Pacific region.
- Despite challenges, enhancing cooperation in trade, connectivity, defence, and socio-cultural aspects can pave the way for mutual growth and regional peace.
Source: The Hindu
Africa Climate Summit 2023
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Recently, Africa Climate Summit 2023 was inaugurated.
Background:-
- Despite having a small carbon footprint, Africa disproportionately bears the human toll of climate change.
- Thus, highlighting the urgent need for regional and global action, President William Ruto reminded us while inaugurating the Africa Climate Summit, 2023 (ACW23) on September 4, 2023, in Nairobi, Kenya.
About Africa Climate Summit 2023:-
- Date: 4th to 6th September 2023.
- Venue: Nairobi, Kenya. (Africa)
- The summit aims to address the increasing exposure to climate change and its associated costs, both globally and particularly in Africa.
- At the Africa Climate Summit, leaders will be called upon to make ambitious pledges and commitments.
- A comprehensive “Pledging and Commitment Framework” will be developed to guide these actions.
- The outcomes of the summit are critical for the African continent to arrive at a consensus and mobilize action in the lead-up to the upcoming 28th Conference of Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to be hosted in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
Theme & Focus Areas:-
- Climate Action Financing.
- Green Growth Agenda for Africa.
- Climate Action and Economic Development.
- Global Capital optimization.
Source: DTE
National Commission for Schedule Tribes (NCST)
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
Kalahandi Gram Sabhas wrote to the National Commission for Schedule Tribes (NCST), invoking an atrocities act against the Jharkhand Divisional Forest Officer (DFO), recently.
Background of the issue:-
- DFO illegally seized a consignment of kendu leaves being transported from Odisha to West Bengal, a federation of Gram Sabhas alleges.
- The Kasturapadar and Khasiguda Gram Sabhas of the federation had issued transit permits to a company, Green India, for carrying kendu leaves (also known as tendu), which are used to roll beedi, from Kalahandi to Dhulian in West Bengal in May this year.
- On May 31, the company’s truck, along with 400 sacks of kendu, was seized during transit by the DFO of Simdega forest division in Jharkhand.
- The Mahasangh has alleged that the seizure is in violation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 (FRA) and the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989.
- Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989: It is an Act to prevent the commission of offenses of atrocities against the members of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes.
- It provides for Special Courts for the trial of such offenses for the relief and rehabilitation of the victims of such offenses and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The letter dated June 19, 2023, appealed NSCT to take legal action against the Simdega DFO for “illegal interference with the enjoyment of forest rights of Schedule Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers”.
About the National Commission for Schedule Tribes (NCST):-
- Establishment:
- Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It was established by amending Article 338 and inserting a new Article 338A.
- It was done through the Constitution through the Constitution (89th Amendment) Act, 2003.
- By this amendment, the erstwhile National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes was replaced by two separate Commissions namely:-
- National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC), and
- National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST)
- The commission submits its report to the President annually.
- It gives data on the working of safeguards and measures required for the effective implementation of Programmers/ Schemes relating to the welfare and socio-economic development of STs.
Structure:-
- Term of office of Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and each member: three years from the date of assumption of charge.
- Chairperson has been given the rank of Union Cabinet Minister.
- Vice-Chairperson that of a Minister of State
- Other Members have the ranks of a Secretary to the Government of India.
Powers:-
- NCST is empowered to investigate and monitor matters relating to safeguards provided for STs under the Constitution under other laws or under Govt. order.
- It is also authorized to inquire into specific complaints relating to the rights and safeguards of STs and to participate.
- It can advise in the Planning Process relating to the socio-economic development of STs and evaluate the progress of their development under the Union and States.
Source: DTE
GS-III
One-hour trade settlement
Subject: Indian Economy

Why in News?
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which had in July announced it was working to launch real-time settlement of trades, is now planning to implement one-hour settlement of trades first.
About one-hour trade settlement:
- In a one-hour settlement, if an investor sells a share, the money will be credited to their account in an hour, and the buyer will get the shares in their demat account within an hour.
What is trade settlement?
- Settlement is a two-way process which involves the transfer of funds and securities on the settlement date.
- A trade settlement is said to be complete once purchased securities of a listed company are delivered to the buyer and the seller gets the money.
- The current cycle of T+1 means trade-related settlements happen within a day, or 24 hours of the actual transactions.
- The migration to the T+1 cycle came into effect in January 2023.
- India became the second country in the world to start the T+1 settlement cycle in top-listed securities after China.
What is a Demat Account?
- A Demat Account or Dematerialised Account provides the facility of holding shares and securities in an electronic format.
- During online trading, shares are bought and held in a Demat Account, thus, facilitating easy trade for the users.
- It holds all the investments an individual makes in shares, government securities, exchange-traded funds, bonds and mutual funds in one place.
Source: The Hindu
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO)
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
A NASA moon probe has snapped an aerial photo of India's Chandrayaan-3 lander, the first craft ever to successfully touch down near the lunar south pole.
About Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO):
- It is a NASA spacecraft that was launched on June 18, 2009.
- Primary Objective: To make a 3D map of the Moon's surface from lunar polar orbit.
- It has also been used to study the Moon's geology, mineralogy, and environment.
- It orbits the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit.
- LRO is equipped with 7 science instruments, the most well-known of which is a 195-millimeter (7.7-inch) telescope and camera system that can see details up to 2.5 meters across.
- LRO is equipped with a laser altimeter that produces 3D maps by shooting lasers at the surface and measuring reflection times.
- The spacecraft also carries two instruments suited to peering into dark craters to search for signs of water ice, and a temperature instrument that led to the discovery of the coldest place in the solar system.
Source: The Hindu
Japan discovers Earth-like Planet in Kuiper Belt
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Two Japanese astronomers have uncovered potential evidence of an “Earth-like planet” within our solar system.
- This mysterious planet is believed to have resided in the Kuiper Belt, a circumstellar disk beyond Neptune’s orbit that consists of outer solar system objects.
- The Kuiper Belt, like the planets, orbits the Sun.
What is the Kuiper Belt?
- The Kuiper Belt, also known as the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt, is a flat ring of small icy bodies orbiting the Sun beyond Neptune’s orbit.
- Gerard Kuiper, a Dutch-American astronomer, first hypothesized its existence in the 1950s.
- This belt contains millions of icy objects, collectively referred to as Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs) or trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).
- It is considered a remnant from the early history of our solar system.
- The Kuiper Belt is thought to be the source of many short-period comets that orbit the Sun in less than 20 years.
- It primarily consists of small icy bodies, including dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets.
- Pluto, once classified as the ninth planet, is one of the most well-known objects in the Kuiper Belt but was reclassified as a dwarf planet by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2006, partly due to its location within this belt.
The Astronomers’ Findings
- The Japanese researchers suggest that if this new planet exists, it would be 1.5 to 3 times the size of Earth.
- The discovery challenges previous theories of a distant “Planet Nine” and posits the possibility of a planet closer to us, within the Kuiper Belt.
- The astronomers predict the existence of an Earth-like planet and several trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) on unique orbits that could serve as observational signatures of this potential planet’s perturbations.
- They estimate that this planet could be situated between 200 and 500 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, tilted about 30 degrees. For reference, Pluto is 39 AU from Earth.
Source: Times of India
Unemployment: Measurement Challenges in Developing Economies
Subject: Indian Economy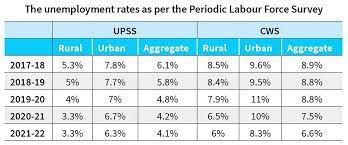
Why in News?
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) in 2017 revealed India’s highest-ever recorded unemployment rate at 6.1%.
- The 2021-22 PLFS indicated a reduction to 4.1%, still higher than some developed economies like the U.S., where unemployment rates varied from 3.5% to 3.7% between July 2022 and July 2023.
- Comparing India and the U.S. unemployment rates is complex due to their vastly different economies.
About Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)
| Established | 2017 (The PLFS was initiated in 2017 as part of the larger National Sample Survey (NSS) program) |
| Administered by | National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India |
| Objective | To collect data on labor force participation, employment, and unemployment in India. |
| Key Data Collected | – Workforce Participation – Employment Types and Sectors – Unemployment – Demographic and Socioeconomic Characteristics |
| Significance | Provides vital information for policymaking, research, and analysis related to the labor market in India. |
| Frequency | Periodic surveys conducted at regular intervals. |
Defining Unemployment
- Unemployment, as per the International Labour Organization (ILO), involves being jobless, available for work, and actively seeking employment.
- The unemployment rate is the ratio of the unemployed to the labor force, but it can decrease if the economy lacks job creation or people stop job hunting.
Measuring Unemployment in India
- In developing economies, like India, social norms can limit job search decisions.
- The 2009-10 National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) survey revealed that many women who engaged in domestic work would work if opportunities were available within their households but are not considered unemployed since they aren’t actively seeking jobs.
- Measuring unemployment in India is complicated due to the informal job market, where individuals hold various roles throughout the year.
Different Metrics for Classification
- The Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS) and the Current Weekly Status (CWS) are two major measures for classifying individuals in India.
- UPSS considers an individual employed even if they worked for more than 30 days in a subsidiary role.
- CWS counts an individual as employed if they worked at least one hour on one day within the past week.
- UPSS typically yields lower unemployment rates than CWS since finding work over a year is more likely than in a week.
Impact of Informal Economy
- The low bar for classifying individuals as employed means that unemployment rates are lower in rural areas than urban regions in agrarian economies.
- Definitions may ‘underestimate’ unemployment but are designed to capture the informal economy’s nuances.
The Lockdown Effect
- The lockdown in March 2020 disrupted the Indian economy, but PLFS unemployment rates did not reflect this immediately.
- UPSS status may still consider those who lost jobs during the lockdown as employed if they spent most of the previous year working.
- CWS criteria show higher unemployment rates due to shorter reference periods but may not fully capture the long-term impact of the lockdown when aggregated across different periods.
Conclusion
- Unemployment is becoming a significant factor in upcoming elections, making it crucial to understand its definition and measurement complexities in developing economies.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5283 docs|1116 tests
|
















