Prion and Prion Hypothesis | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
 Fibril Model
Fibril Model
What are prions?
- Definition: Prions are unconventional infectious particles composed of protein that trigger a group of universally fatal neurodegenerative diseases known as spongiform encephalopathies through a highly distinctive mechanism.
- Coined Term: The term "prion" was introduced by Stanley B. Prusiner in 1982, formed by combining "protein" and "infection."
- Inactive Nature: Prions, similar to viruses, are not active entities themselves, although they can replicate by taking over the functions of living cells.
- Composition: Prions are minute infectious particles containing protein but lacking any detectable nucleic acids.
- Abnormal Structure: These proteins are abnormal due to their atypical folding structure characterized by β‐pleated sheets, whereas their normal counterparts within the host fold normally with 2 α‐helices.
- Unknown Function: The specific function of this protein, found on chromosome 20, is not yet understood.
- Aggregates Formation: Misfolded prion proteins aggregate, forming "amyloid" structures, which disrupt the normal functioning of cells.
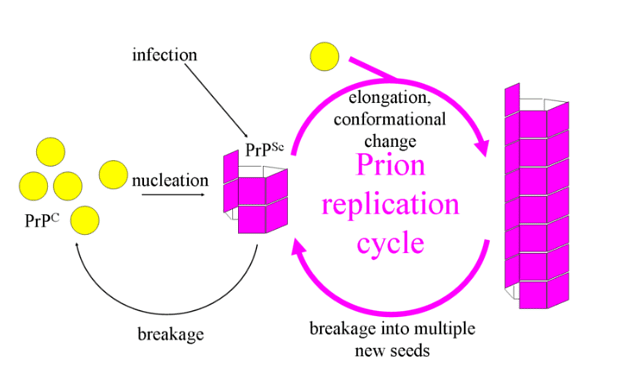
- Normal vs. Abnormal: The standard form of this protein is referred to as PrPc (prion protein cellular), whereas the abnormal variant is known as PrPsc (linked to scrapie, a transmissible infectious spongiform encephalopathy found in sheep and goats).
- Abnormal Information Transfer: Abnormal PrPsc proteins transmit their misfolded information to normal PrPc proteins, causing them to fold incorrectly.
- Tissue Damage: These abnormal protein aggregates lead to tissue damage, primarily impacting the brain, resulting in a slowly progressive encephalopathy that ultimately leads to death.
Structural Features of Infectious Prions
- Hypotheses on Protein Makeup: Several theories have been proposed regarding the composition of prions. However, the widely accepted hypothesis is the 'protein-only hypothesis,' initially suggested by Griffith in 1965 and subsequently reaffirmed by Prusiner.
- Key Prion Features:
- Absence of Nucleic Acids: Prions do not contain any nucleic acids, which distinguishes them from typical infectious agents like viruses.
- Aggregated Hydrophobic Glycoprotein: Prions consist of aggregated hydrophobic glycoproteins that are resistant to protease enzymes, which normally break down proteins.
- Cellular Prion Protein: In humans and other animals, the protein involved is called the cellular prion protein. It shares some similarities with the glycoprotein found in scrapie, also known as scrapie prion protein. This glycoprotein has a molecular weight ranging from 27,000 to 30,000 Da (Daltons). However, it differs from scrapie prion protein in its sensitivity to protease and its presence in the plasma membrane.
These features collectively characterize infectious prions and contribute to their unique nature in causing neurodegenerative diseases.
Mode of transmission of Prion Disease
- Oral Transmission: Prion diseases can be transmitted when an individual consumes contaminated tissue or products from infected animals. This can include consuming contaminated meat or other food products.
- Transcutaneous Transmission: Direct contact with infected tissues or body fluids, such as through cuts or abrasions on the skin, can also lead to the transmission of prion diseases.
- Bloodborne Transmission: Prions can potentially spread through the bloodstream, allowing the disease to be transmitted via blood transfusions or the use of contaminated medical instruments.
These modes of transmission highlight the potential for prion diseases to spread within and between species, making them a significant concern for both animal and human health.
Pathogenesis of Prion Disease
- Source of PrPsc: PrPsc, the abnormal scrapie protein responsible for prion diseases, can either be generated within the body (endogenously) or enter the body from external sources, such as infected animals or humans. How prions initially reach the central nervous system (CNS) remains unknown.
- Potential CNS Entry Routes: It is believed that prions may access the CNS via splanchnic nerves located at the level of the thoracic spinal cord and through parasympathetic fibers connecting to the brain. These routes provide a possible means for prions to reach the CNS.
- Binding to Cellular Prion Protein (PrPc): PrPsc binds to the normal cellular prion protein (PrPc) found in most tissues, with a higher concentration in the CNS, particularly in neurons.
- Ingestion by Neurons and Phagocytic Cells: PrPsc is taken up by neurons and phagocytic cells (cells that engulf foreign substances), but it does not undergo degradation as typical proteins do.
- Neuronal Vacuolation: The presence of PrPsc within neurons may contribute to the development of vacuoles within these cells. Vacuolation is a key pathological alteration observed in prion-related encephalitis.
- Accumulation and Brain Damage: The accumulation of prions, especially at high concentrations, leads to damage in brain tissue. This damage includes the formation of amyloid-containing plaques and fibrils, as well as the proliferation and hypertrophy (enlargement) of astrocytes (a type of glial cell). Additionally, prion-related damage can result in the fusion of neurons with adjacent glial cells.
These pathological changes collectively contribute to the progressive neurodegeneration observed in prion diseases. While the exact mechanisms of prion propagation and their pathogenic effects are still areas of active research, these processes highlight the devastating impact of prion diseases on the central nervous system.
Clinical Symptoms Caused by Prion
Prion diseases are associated with a range of clinical symptoms, and they share several common characteristics across species:
- Amyloid Aggregation: Prions aggregate extracellularly within the central nervous system (CNS), forming plaques or amyloid structures that disrupt the normal tissue structure.
- Neurodegenerative Symptoms: These diseases often lead to neurodegenerative symptoms, which can include compulsive behaviors, dementia (progressive cognitive decline), ataxia (loss of coordination), and behavioral or personality changes.
- Characteristic Features: Prion diseases typically exhibit characteristic features, including a spongy appearance of the cerebral gray matter, an exceptionally long incubation period (time from infection to symptom onset), a slow and progressive course, a fatal outcome, a preference for affecting the CNS, a lack of an immune response, and a genetic predisposition in some cases.
Prion diseases can cause several specific conditions in humans, including:
- Kuru: A rare disease once found in Papua New Guinea, transmitted through cannibalism.
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD): A classic prion disease with various forms, including sporadic, inherited, and acquired.
- Variant CJD: Linked to the consumption of contaminated cattle products and often referred to as "mad cow disease."
- Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker (GSS) Syndrome: An inherited prion disease characterized by a range of neurological symptoms.
- Fatal Familial Insomnia: A rare inherited prion disease that primarily affects sleep and leads to severe neurological problems.
- Sporadic Fatal Insomnia: Another rare prion disease that primarily affects sleep patterns and neurological function.
In animals, prion diseases can cause conditions such as:
- Scrapie: A prion disease in sheep and goats.
- Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE): Also known as "mad cow disease," this affects cattle and can have implications for human health if contaminated meat products are consumed.
- Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy: Affects mink and other animals.
- Chronic Wasting Disease: Found in deer, mule deer, and elk, this disease poses ecological and wildlife management challenges.
These prion diseases collectively demonstrate the severe and often fatal consequences of abnormal protein aggregation within the CNS, leading to a range of neurological symptoms and tissue damage.
Laboratory Diagnosis of Prion Disease
Diagnosing prion diseases is indeed a challenging process, and various laboratory methods are employed for confirmation.
Here's an overview of the laboratory diagnosis of prion diseases:
- Histopathology of Brain Tissue: The most critical diagnostic method involves examining brain tissue through histopathology. This process allows pathologists to identify characteristic biological changes in the brain tissue, such as spongiform (sponge-like) changes, neuronal loss, and the presence of abnormal prion protein aggregates. The pattern of these changes helps in confirming the presence of prion disease.
- Absence of Serological Tests: Unlike many other infectious diseases, prion diseases do not have specific serological tests (tests that detect antibodies in the blood) that can reliably confirm the disease.
- Detection of Protein 14-3-3 in CSF: In some cases, particularly for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (sCJD) and related forms, the presence of the protein 14-3-3 in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can be detected using Western blot analysis. The presence of this protein is considered a biomarker for prion diseases and can help support the diagnosis.
- Uric Acid Level in CSF: Differential diagnosis between variant CJD (vCJD) and other forms of prion diseases can be challenging. Some studies have suggested that specific reductions in uric acid levels in the CSF may be observed in vCJD but not in sporadic CJD. This difference can assist in distinguishing between these forms of the disease.
It's important to note that the diagnosis of prion diseases is often complex, and a combination of clinical, pathological, and laboratory criteria is used to establish a definitive diagnosis. Due to the rarity and complexity of these diseases, diagnosis should be conducted by experienced medical professionals and specialists in prion diseases.
Treatment of Prion Disease
- No specific treatment is available.
- All known prion diseases are untreatable and fatal.
Prevention and control of Prion Disease
- Special care while handling materials from patients with CJD or VCJD.
- Special disinfection protocols have been developed by WHO for prevention of these diseases.
- Autoclaving at 15lbs for 1hr before handling infectious products
- Treatment with 0.1M NaOH and 5% hypochlorite solution before handling infectious products.
|
179 videos|143 docs
|





















