Somatic Hybrids and Cybrids | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is the Difference Between Cybrids and Hybrids |

|
| What are Cybrids? |

|
| What are Hybrids? |

|
| What are the Similarities Between Cybrids and Hybrids? |

|
What is the Difference Between Cybrids and Hybrids
The key distinction between cybrids and hybrids is the process of their generation:
- Cybrids: Cybrids are produced by fusing nucleated cells with cytoplasts. Cytoplasts are cells that lack a nucleus. In cybrid formation, a nucleated cell from one organism is fused with a cytoplast from another organism, resulting in a hybrid cell with genetic material from one nucleus and the cytoplasmic components from another.
- Hybrids: Hybrids, on the other hand, are generated by fusing two nucleated cells. In this case, two cells with nuclei from different organisms are fused together to create a hybrid cell with genetic material from both parent cells.
Both cybrids and hybrids find applications in various fields of biology, including disease studies, gene expression studies, population genetics, evolution, malignant transformation, viral replication, gene or chromosome mapping, and monoclonal antibody production through hybridoma technology.
What are Cybrids?
- Cybrids are generated by fusing nucleated cells with cytoplasts or enucleated cells. They are also known as cytoplasmic hybrids or heteroplasts. Cytoplasts, which are cells lacking a nucleus, can be referred to as enucleated cells. The process of enucleation involves subjecting the cell to centrifugal force and treatment with an agent that disrupts the cytoskeleton to remove the nucleus.
- Cybrids play a crucial role in mitochondrial research. They provide suggestive evidence of the involvement of mitochondria in various diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other medical conditions.
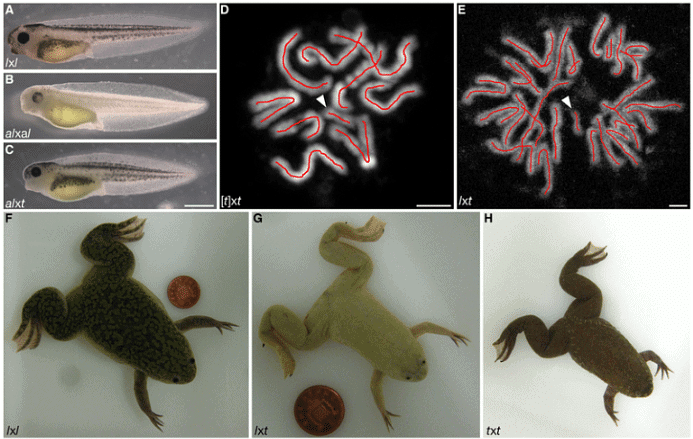
- In recent years, mixed human-animal cybrid embryos have been created for medical purposes. These cybrids are primarily human (99.9%) with a small animal component (0.1%). They can be maintained for a maximum of 14 days, up to the development of the brain and spinal cord. During this limited timeframe, stem cells can be harvested from the cybrids for medical research and therapeutic purposes. However, it is strictly prohibited to implant such cybrids into a human uterus due to ethical concerns.
- The research involving cybrid embryos has encountered legal issues and ethical dilemmas, which have raised significant challenges and controversies in the field of cybrid research.
What are Hybrids?
Hybrids are created by fusing two nucleated cells, a process known as somatic hybridization. This technology is widely utilized in both plant genetic studies and animal genetic studies.
In plants, somatic hybridization enables the production of a new hybrid plant by fusing cells from two distinct plant species. The resulting somatic hybrid plant inherits characteristics from both parent varieties. In animal cells, somatic hybridization involves the fusion of somatic cells from different species, such as human and mouse cells. This fusion can be achieved by merging human cells, such as fibrocytes or leukocytes, with continuous cell lines derived from mice.
In animal cells, somatic hybridization involves the fusion of somatic cells from different species, such as human and mouse cells. This fusion can be achieved by merging human cells, such as fibrocytes or leukocytes, with continuous cell lines derived from mice.
Applications of hybrids in research are extensive and can include:
- Control of Cell Division and Gene Expression: Hybrids are valuable for studying the regulation of cell division and gene expression, providing insights into cellular processes.
- Investigation of Malignant Transformation: Hybrids can be used to investigate the transformation of normal cells into malignant cells, contributing to cancer research.
- Viral Replication: They can be employed to study viral replication mechanisms, aiding in virology research.
- Gene or Chromosomal Expression: Hybrids are useful for examining gene or chromosomal expression patterns in mixed genetic backgrounds.
- Monoclonal Antibody Production: Hybridoma technology, which involves the fusion of antibody-producing cells with immortalized cells, allows for the production of monoclonal antibodies for various applications, including diagnostics and therapeutics.
Somatic hybridization provides a versatile tool for exploring genetics, cell biology, and various aspects of molecular biology in both plant and animal systems.
What are the Similarities Between Cybrids and Hybrids?
Cybrids and hybrids are indeed two types of eukaryotic cell lines created through fusion, and they share several common characteristics:
- Cytogenetics: Both cybrids and hybrids are widely utilized in cytogenetics, a branch of genetics that focuses on the study of chromosomes and their role in inheritance and cell function.
- Genetic Modifications: They are genetic modifications resulting from the fusion of cells from different sources, combining genetic material from two or more organisms.
- Versatility: Both cybrids and hybrids find applications in diverse fields, including disease studies, gene expression studies, evolutionary studies, and more.
However, there are also some distinctions:
- Cybrids vs. Hybrids: Cybrids involve the fusion of nucleated cells with cytoplasts or enucleated cells, while hybrids result from the fusion of two nucleated cells.
- Expense: The production of both cybrids and hybrids can be costly, but the expenses may vary depending on the specific techniques and resources involved.
- Legal and Ethical Issues: Both cybrids and hybrids have faced legal challenges and ethical concerns, particularly when human cells are involved, raising important ethical questions about their use in research and potential applications.
In summary, cybrids and hybrids are valuable tools in genetics and cell biology research, and while they share many similarities, they also have differences in their generation methods and applications. Their use is subject to ethical considerations and may involve legal complexities.
Summary – Cybrids vs Hybrids
Cybrids and hybrids are two eukaryotic cell lines that are made by fusion. They are genetic modifications that are very popular in cytogenetics. Cybrids are generated by fusing nucleated cells with cytoplasts, while hybrids are generated by fusing two nucleated cells. So, this is the key difference between cybrids and hybrids. However, both these face numerous legal issues in modern days due to their ethical implications.
|
179 videos|143 docs
|















