Phanerogams: Definition, Characteristics & Importance | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Phanerogams, the Pinnacle of Plant Life
In 1883, the renowned German botanist A.W. Eichler made a groundbreaking classification of the plant kingdom, dividing it into two distinct categories: Phanerogams and Cryptogams. Phanerogams, often referred to as seed-producing plants, represent the zenith of plant evolution, boasting well-defined structures such as roots, stems, and leaves. They possess distinct reproductive organs responsible for the production of seeds, thus earning them their scientific moniker. These remarkable plants include familiar examples like pine trees, grasses, crops, flowers, and bamboo. This article delves into the essential facets of Phanerogams, from their definition to their classification, characteristics, examples, and overall importance.
Phanerogams Definition
Phanerogams, or Spermatophytes, are plants distinguished by their well-differentiated reproductive parts, ultimately leading to seed production. The term "Phanerogam" derives from the Greek words "Phaneros," meaning visible, and "Gamos," meaning marriage. This nomenclature underscores their characteristic trait of producing conspicuous seeds.
Characteristics of Phanerogams
Phanerogams exhibit several defining characteristics:
- Multicellular and Eukaryotic: These plants are always multicellular and possess eukaryotic cells.
- Distinct Plant Body: The plant body of Phanerogams is divided into discernible roots, shoots, and leaves.
- Diploid and Sporophytic Phase: The major phase in their life cycle is represented by diploid and sporophytic forms.
- Flowering Plants: Phanerogams are commonly known as flowering plants, as they produce specialized reproductive structures that give rise to seeds, encapsulating the potential for future generations.
- Chlorophyllous and Autotrophic: The majority of Phanerogams are chlorophyllous and autotrophic, capable of producing their own food through photosynthesis. However, some members exhibit parasitic or achlorophyllous tendencies.
- Conducting Elements: They contain conducting elements such as xylem and phloem, with variations in vessel presence.
- Wide Distribution: Phanerogams occupy diverse habitats across the globe, from terrestrial to aquatic environments, and adapt to various climatic conditions.
- Sexual and Vegetative Reproduction: These plants primarily reproduce through sexual reproduction, with the absence of asexual spores. Reproductive structures include flowers (or cones or strobili), and they exhibit alternation of generation, comprising sporophytic and gametophytic phases.
- Oogamous Reproduction: Sexual reproduction in Phanerogams follows an oogamous pattern, characterized by the union of gametes through siphonogamy.
Classification
Phanerogams are classified into two main categories:
- Gymnosperms (Naked Seed Plants): Gymnosperms, often referred to as primitive seed plants, exhibit the following features:
- They are predominantly found in colder regions of the world.
- Gymnosperms are primarily tall, woody, perennial trees, with some forms displaying a climbing habit.
- Many of them have adaptations for arid conditions (xerophytic).
- Xylem in gymnosperms typically lacks vessels, and they are heterosporous, producing both microspores (male) and megaspores (female).
- Instead of showy flowers, gymnosperms form cones (strobili), and their ovules are naked, lacking ovaries.
- Angiosperms (Covered Seed Plants): Angiosperms, commonly known as flowering plants, are characterized by the following traits:
- They thrive in diverse habitats, adapting to environmental conditions ranging from high mountains to deserts.
- Angiosperms come in various forms, including herbs, shrubs, trees, climbers, and more.
- Flowers, the hallmark of angiosperms, serve as specialized reproductive organs, attracting pollinators and facilitating sexual reproduction.
- They possess vessels in their xylem and companion cells in their phloem, with some exceptions.
- Angiosperms produce fruits, enclosing their seeds within protective structures.
Phanerogams Examples
Examples of Phanerogams include:
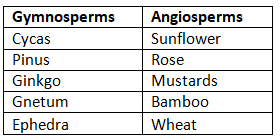
Importance of Phanerogams
Phanerogams play a pivotal role in the ecosystem due to their multifaceted importance:
- Food Source: Many angiosperms, such as rice and wheat, serve as crucial food sources for humans and various organisms. Some gymnosperms, like the seeds of Cycas, also contribute to human nutrition.
- Medicinal Value: Several angiosperms, including Belladonna and Rauwolfia, are used in traditional medicine. Gymnosperms like Taxus and Ephedra also yield valuable medicinal compounds.
- Habitat and Soil Conservation: Phanerogams provide habitat and sustenance to numerous animals and help prevent soil erosion, stabilizing terrestrial ecosystems.
- Oxygen Production: These plants are primary oxygen producers, vital for maintaining the balance of our ecosystem.
- Resource Material: Phanerogams serve as the primary sources of materials such as paper pulp, lumber, turpentine, resins, cotton, and rubber. They are also used as a fuel source.
- Ornamental and Decorative Use: Many Phanerogams, especially angiosperms, are cultivated for their ornamental value, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of gardens and landscapes.
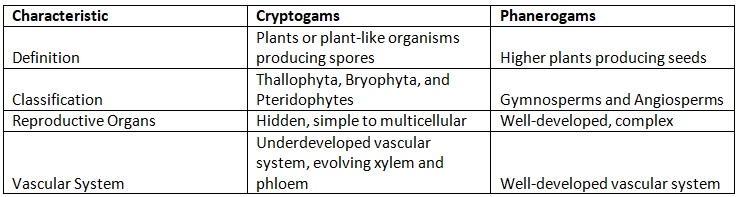
Difference between Cryptogams and Phanerogams
Conclusion
Phanerogams, a prominent subkingdom within the plant kingdom, encompass Gymnosperms and Angiosperms, representing the pinnacle of plant evolution. These seed-producing plants exhibit well-defined structures, a diverse range of habitats, and essential roles in sustaining life on Earth. Phanerogams offer valuable resources, contribute to human nutrition, and are pivotal in maintaining ecological balance. Understanding their characteristics and significance provides profound insights into the remarkable world of Phanerogams.
|
179 videos|143 docs
|
















