Science and Technology: August 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Akira Ransomware
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian government's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) issued a warning about the Akira ransomware, which has emerged as a significant cybersecurity threat, targeting both Windows and Linux devices.
- Ransomware is a type of malware that hijacks computer data and then demands payment (usually in bitcoins) in order to restore it.
What is Akira Ransomware?
- About:
- It is malicious software that poses a significant threat to data security.
- It targets both Windows and Linux devices, encrypting data and demanding a ransom for decryption.
- Key Characteristics of Akira Ransomware:
- Designed to encrypt data and create a ransomware note with a unique ".akira" extension appended to encrypted filenames.
- Capable of deleting Windows Shadow Volume copies and shutting down Windows services to prevent interference during encryption.
- Exploits VPN services and malicious files to infect devices, making it challenging to detect and prevent.
- Mode of Operation:
- Akira ransomware spreads through various methods, including spear phishing emails with malicious attachments, drive-by downloads, and specially crafted web links in emails.
- Insecure Remote Desktop connections are another avenue for ransomware transmission.
- Implications of an Akira Attack:
- Once infected, Akira ransomware steals sensitive data and encrypts it, rendering it inaccessible to the victim.
- Attackers then demand a ransom for decryption and threaten to leak the stolen data on the dark web if their demands are not met.
- Protection Measures Against Akira Ransomware:
- Regularly maintain up-to-date offline backups to prevent data loss in case of an attack.
- Keep operating systems and networks updated, including virtual patching for legacy systems, to address potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement security protocols such as Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Sender Policy for email validation.
- Enforce strong password policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance user authentication.
- Establish a strict policy for external device usage and ensure data-at-rest and data-in-transit encryption.
- Block attachment file types with suspicious extensions like .exe, .pif, and .url to avoid downloading malicious code.
- Educate users to be cautious about clicking on suspicious links to prevent malware downloads.
- Conduct regular security audits, especially for critical systems like database servers, to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Nuclear Rocket for Space Travel
Central Idea
- NASA, in collaboration with DARPA, has selected Lockheed Martin to design and build a nuclear-powered propulsion system for DRACO program.
- It is a breakthrough technology that could propel astronauts on a faster journey to Mars.
What is DRACO Program?
- DRACO stands for Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations.
- It aims to leverage nuclear reactions to significantly reduce travel time, making interplanetary missions more efficient and safer.
- The spacecraft will orbit at an altitude of approximately 700 to 1,994 kilometers, staying in orbit for over 300 years to ensure safe decay of radioactive elements.
How it is different from conventional spacecraft?
- DRACO, a nuclear thermal rocket (NTR) utilizes a nuclear reactor to heat propellant to extreme temperatures before exhausting the hot propellant through a nozzle to produce thrust.
- Compared to conventional space propulsion technologies, NTRs offer a high thrust-to-weight ratio.
- This thrust is around 10,000 times greater than electric propulsion, and a specific impulse (i.e., propellant efficiency) two-to-five times greater than in-space chemical propulsion.
Benefits of DRACO
- Shorter Journey to Mars: With nuclear-powered propulsion, astronauts could reach Mars in just three to four months, cutting the current travel time in half. The spacecraft could continue accelerating through the first half of the journey and then start slowing down again, reducing the need for extensive propellant storage.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: Nuclear reactions, using the splitting of uranium atoms, are far more efficient than conventional rocket engines that rely on fuel combustion. The DRACO engine features a nuclear reactor that heats hydrogen gas to generate thrust, offering greater fuel efficiency for interplanetary travel.
- Reduced Exposure to Deep Space: Faster journeys to Mars would minimize astronauts’ exposure to the harsh environment of deep space, reducing potential risks and health hazards.
Nuclear Propulsion: Historical Context
- Legacy: The concept of nuclear propulsion for space is not new. In the 1950s and 1960s, Project Orion explored using atomic bomb explosions to accelerate spacecraft. NASA’s Project Rover and Project NERVA in the same era aimed to develop nuclear-thermal engines for space missions.
- Advancements in Safety Protocols: Unlike earlier nuclear propulsion projects, DRACO uses a less-enriched form of uranium and incorporates advanced safety protocols. The reactor will only be activated in space to minimize the risk of a radioactive accident on Earth.
Potential Applications and Future Testing
- Military Satellite Maneuvers: DARPA’s investment in the DRACO program indicates potential military applications, such as enabling rapid maneuvers of military satellites in Earth’s orbit.
- Nuclear-Thermal Engine Test: Lockheed Martin plans to launch the demonstration spacecraft in late 2025 or early 2026.
Same-Sex Behavior in Rhesus Macaques
Why in News?
- A recent study conducted by researchers from Imperial College London, titled "Genetics, Social Environment and Evolution of Male Same-Sex Behavior in Rhesus Macaques," has challenged conventional beliefs about same-sex behaviour (SSB) in animals.
- The engagement of animals in SSB has been considered a ‘Darwinian paradox’: if reproduction is critical to evolution, then SSB – which is non-reproductive – should have ceased to exist.
- This recent study found that male SSB in rhesus macaques is very common and doesn't harm evolution.
What are the Key Findings from the Study?
- Male Same-Sex Behavior (SSB) in Monkeys:
- The study focuses on male same-sex mounting behaviour observed in rhesus macaques, a common monkey model, in Cayo Santiago, an island east of Puerto Rico.
- 72% of observed male rhesus macaques engaged in same-sex mounting.
- Only 46% participated in different-sex mounting.
- It challenges the notion that SSB contradicts principles of evolution due to its non-reproductive nature.
- Role of Non-Genetic Factors:
- The study considers external factors like social interactions and the environment.
- These non-genetic elements contribute to the expression of SSB behaviour in male rhesus macaques.
- SSB-engaging monkeys form coalitions against common enemies.
- Male SSB could serve as a form of emotional communication and regulation.
- No Trade-off with Reproductive Fitness:
- The study disputes the assumption that SSB reduces reproductive opportunities, as sexually active males engage in both SSB and different-sex sexual behaviour (DSB).
- There is no direct correlation between SSB engagement and reduced offspring count in the macaque population.
- Future Research:
- Female SSB and other monkey species require further investigation to broaden understanding.
- The findings cannot be directly extrapolated to humans due to cultural and social influences.
LK-99: The Quest for a Room-Temperature Superconductor.
Context
Korean researchers claim to have developed a superconductor named LK-99 that operates at room temperature and ambient pressure, a significant breakthrough in the field of physics.
- Superconductors are materials that transmit electricity with nearly 100% efficiency and have various practical applications, such as in MRI machines and magnetic levitation trains.
- Room-temperature superconductors would have numerous benefits, including reducing the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, maglev train magnets, energy storage devices, and fusion reactors by saving on coolant expenses.
Significance
If validated, this discovery could revolutionize various industries, including computing.
Superconductors are essential for quantum computing, where quantum bits (qubits) process information simultaneously, providing immense computational power. Currently, physical qubits require super-cooling to avoid errors, but room-temperature superconductors could eliminate the need for elaborate cooling systems, making quantum computing more practical and accessible.
Chandrayaan-3 Successfully Lands on Moon’s South Pole
Why in News?
Chandrayaan-3 has made history by becoming the first mission to soft-land on the lunar south pole, a region that has never been explored before. The mission aimed to demonstrate safe and soft lunar landing, rover mobility, and in-situ scientific experiments.
- India now joins the United States, Russia, and China as one of the few countries to successfully land on the Moon.
How did Chandrayaan-3 Prevail Over Obstacles Encountered in the Previous Mission?
- Chandrayaan-3's successful landing came after the setback of the Chandrayaan-2 mission's landing failure in 2019.
- The Vikram lander of Chandrayaan-2 had lost control and communication during descent, leading to a crash on the lunar surface.
- Lessons from the Chandrayaan-2 mission were applied to Chandrayaan-3, focusing on a "failure-based" design approach to anticipate and mitigate potential issues.
- Critical changes included strengthening the lander's legs, increasing fuel reserves, and enhancing landing site flexibility.
Why did Chandrayaan-3 Choose Moon's Near Side for Landing?
- Chandrayaan-3 aimed to investigate "permanently shadowed regions" near the South Pole for potential water-ice and resources.
- The Vikram lander's controlled descent achieved one of the closest approaches to the Moon's South Pole.
- While a notable achievement, Vikram's landing occurred on the Moon's near side, unlike China's Chang'e 4 on the far side.
- The near side, visible from Earth due to synchronous rotation, covers 60% of the Moon.
- The far side, though not always in darkness, remained hidden until the Soviet spacecraft Luna 3 captured images in 1959.
- Astronauts aboard the Apollo 8 mission in 1968 became the first humans to observe the far side directly.
- The near side boasts smoother surfaces and numerous 'maria' (large volcanic plains), while the far side features massive craters from asteroid impacts.
- The lunar crust on the near side is thinner, causing volcanic lava to flow and fill craters over time, creating flat terrains.
- The decision to land on the near side was driven by the mission's primary goal of a controlled soft landing.
- Landing on the far side would require a relay for communication due to the lack of direct line-of-sight with Earth.
What are the Intended Actions for Chandrayaan-3 after its Landing?
- Chandrayaan-3 is expected to operate for at least one lunar day (14 Earth days) on the lunar surface.
- The Pragyan rover will move around the landing site within a radius of 500 meters, conducting experiments and sending data and images to the lander.
- The Vikram lander will relay the data and images to the orbiter, which will then transmit them to Earth.
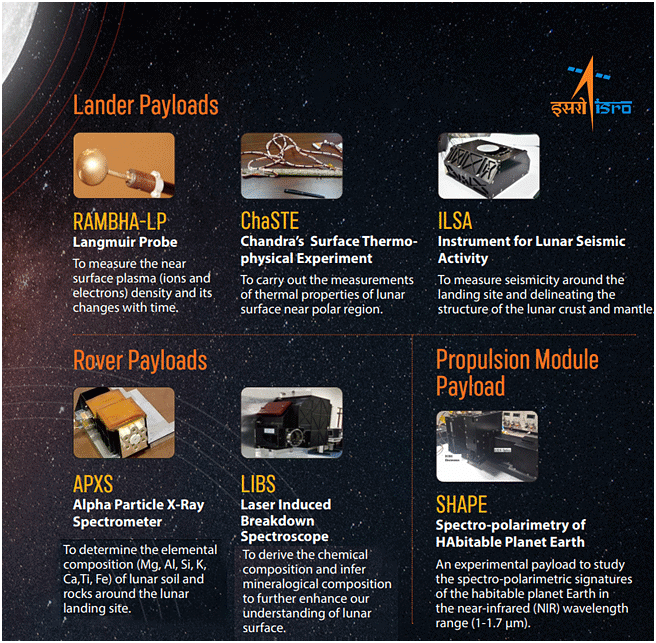
- Lander and Rover modules are collectively equipped with advanced scientific payloads.
- These instruments are designed to conduct comprehensive investigations into diverse facets of lunar characteristics, encompassing terrain analysis, mineralogical composition, surface chemistry, atmospheric attributes, and crucially, the exploration for water and potential resource reservoirs.
- The propulsion module that carried the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit also has a Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.
What are ISRO's Future Expeditions?
- Chandrayaan-4: Navigating the Path of Lunar Evolution
- Building upon past missions, Chandrayaan-4 emerges as a potential candidate for a sample return mission.
- If successful, it could mark the next logical step after Chandrayaan-2 and 3, offering the capability to retrieve lunar surface samples.
- The mission holds promise for advancing our understanding of the Moon's composition and history.
- Building upon past missions, Chandrayaan-4 emerges as a potential candidate for a sample return mission.
- LUPEX: Lunar Polar Exploration (LUPEX) mission, a collaborative effort between ISRO and JAXA(Japan), is poised to explore the Moon's polar regions.
- It will be specifically designed to venture into permanently shaded areas.
- Investigating the presence of water and assessing the potential for a sustainable long-term station are among LUPEX's objectives.
- Aditya-L1: Aditya L1 will be the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun.
- The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth.
- Observing the sun's corona, emissions, solar winds, flares, and coronal mass ejections are the primary focus areas of Aditya-L1.
- XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite): It is India’s first dedicated polarimetry mission to study various dynamics of bright astronomical X-ray sources in extreme conditions.
- The spacecraft will carry two scientific payloads in a low earth orbit.
- NISAR: NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) is a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory being jointly developed by NASA and ISRO.
- NISAR will map the entire globe in 12 days and provide spatially and temporally consistent data for understanding changes in Earth’s ecosystems, ice mass, vegetation biomass, sea level rise, ground water and natural hazards including earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes and landslides.
- Gaganyaan: Gaganyaan mission aims to send humans to space and return them safely to Earth. The mission will consist of two unmanned flights and one manned flight, using the GSLV Mk III launch vehicle and a human-rated orbital module.
- The manned flight will carry three astronauts, including a woman, for up to seven days in low Earth orbit.
- Shukrayaan 1: It is a planned mission to send an orbiter to Venus, the second planet from the Sun. It is expected to study Venus’s geological and volcanic activity, emissions on the ground, wind speed, cloud cover, and other planetary characteristics.
NASA’s STEREO-’s Earth Flyby
Context
- In a significant development, NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO-A) spacecraft underwent its first Earth flyby, nearly 17 years after its initial launch.
- This event presents a unique opportunity for collaboration with other missions in Earth's vicinity, promising fresh insights into the behavior of our Sun.
Details
- Mission Background
- Launched from Cape Canaveral on October 25, 2006, the STEREO mission consists of twin spacecraft: STEREO-A and STEREO-B.
- The primary objective of the mission was to provide a stereoscopic view of the Sun, enabling a multi-perspective understanding of solar phenomena.
- Milestone Achieved
- On February 6, 2011, a significant milestone was accomplished as the two spacecraft achieved a 180-degree separation in their orbits.
- This configuration allowed humanity to witness the Sun as a complete sphere for the first time.
- Stereoscopic Vision and Earth Flyby
- The upcoming Earth flyby will enable STEREO-A to once again employ stereoscopic vision, a technique that extracts 3D information from two-dimensional images. This approach mimics the human depth perception created by our two eyes.
- STEREO-A will combine its views with data from other missions, including NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), operated by both NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA).
- As STEREO-A's distance from Earth changes during the flyby, it will adjust its stereo vision to observe solar features of varying sizes, akin to focusing a vast telescope spanning millions of miles.
- This optimized perspective will enable scientists to study active regions beneath sunspots and uncover 3D structural information. Additionally, a new theory suggesting that coronal loops might be optical illusions will be tested.
- Understanding Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
- One of the key objectives of the flyby is to study the evolution of the magnetic field within coronal mass ejections (CMEs) as they journey towards Earth.
- CMEs, which are plumes of solar material, can disrupt satellite communications, radio signals, and power grids. By obtaining multipoint measurements from within a CME, scientists aim to enhance their computational models of these solar eruptions.
- Changing Solar Activity
- The timing of this Earth flyby marks a notable contrast to STEREO-A's early days in 2006 when the Sun was relatively tranquil due to the solar minimum. Presently, as the Sun approaches the solar maximum predicted for 2025, it exhibits heightened activity.
- This shift in solar behavior offers STEREO-A a fresh perspective, granting researchers access to a range of solar phenomena that were less prevalent during its earlier observations.
- Mission Objectives
- Observing Solar Phenomena: STEREO aims to provide 3D images of the Sun, allowing scientists to observe and understand solar phenomena such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), solar flares, and other dynamic processes.
- Space Weather Prediction: By tracking solar activities, STEREO helps in improving space weather predictions, which are crucial for protecting satellites, astronauts, and technological infrastructure from the harmful effects of solar radiation and energetic particles.
- Studying Solar Wind: The mission aims to study the solar wind's behavior as it travels through space, interacting with Earth's magnetosphere and shaping the space environment around our planet.
- Spacecraft Design
- Twin Spacecraft: STEREO consists of two nearly identical spacecraft: STEREO-A (Ahead) and STEREO-B (Behind). They were launched together and followed separate trajectories to achieve their respective positions around the Sun.
- Orbit: STEREO-A moves ahead of Earth, gradually moving ahead of our planet's orbit, while STEREO-B trails behind, gradually falling behind Earth's orbit. This positioning enables the stereoscopic observation of solar events.
- Instruments: Each spacecraft is equipped with instruments such as the In-situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients (IMPACT) suite, which includes various sensors to measure solar wind characteristics, magnetic fields, and particle energies.
- Scientific Discoveries
- CME Evolution: STEREO data revealed the evolution of CMEs as they travel through space, helping scientists model their trajectories and potential impacts on Earth.
- Solar Wind Properties: The mission's measurements of solar wind properties, including speed, density, and magnetic field strength, have deepened our knowledge of the solar wind's behavior.
- Solar Flare Insights: STEREO has provided insights into the development of solar flares and their association with magnetic activity on the Sun's surface.
- Legacy and Impact
- Space Weather Research: STEREO's data continues to be valuable for space weather researchers, aiding in the development of predictive models and strategies to mitigate the impacts of space weather on technology and infrastructure.
- Solar Physics Advancements: The mission's observations have led to advancements in our understanding of solar physics, contributing to broader knowledge about the Sun's behavior and its effects on the solar system.
- Technological Innovation: STEREO's success in using twin spacecraft for stereoscopic imaging has influenced the design of future space missions that require multiple viewpoints for enhanced observations.
Conclusion
The STEREO spacecraft mission has significantly contributed to our understanding of the Sun's dynamics and its impact on space weather. Through its innovative twin spacecraft design and advanced instruments, STEREO has provided groundbreaking insights into solar phenomena, improving our ability to predict and manage space weather events for the benefit of Earth and its technological infrastructure.
Demon Particle
What is Demon Particle?
Scientists recently discovered a 'demon particle' that could lead to superconductors that conduct electricity at room temperature.
About Demon Particle
- The demon particle was first predicted by theoretical physicist David Pines in 1956.
- Pines theorised that electrons passing through a solid would exhibit unique behaviours and that these behaviours could lead to the formation of a new type of particle that he called a "demon particle."
- They are massless, chargeless, and transparent to light.
- They are also able to form plasmons, which are collective units of electrons that behave like waves.
- Plasmons are important in superconductivity, and the discovery of demon particles could lead to the development of new superconducting materials that operate at room temperature.
What is Superconductivity?
- It is a phenomenon whereby a charge moves through a material without resistance.
- In theory, this allows electrical energy to be transferred between two points with perfect efficiency, losing nothing to heat.
- It was first discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes when he observed the sudden drop in electrical resistance of mercury at extremely low temperatures.
- Superconductivity is generally observed at very low temperatures, often close to absolute zero (0 Kelvin or -273.15°C).
- Meissner-Ochsenfeld Effect:
- Superconductors expel magnetic fields from their interior when they enter the superconducting state.
- This effect, known as the Meissner-Ochsenfeld effect, causes the superconductor to repel magnetic fields, leading to the phenomenon of magnetic levitation.
- When a magnet is brought near a superconductor in its superconducting state, it will float above the superconductor due to this repulsion.
Project Worldcoin
Why in News?
- Recently, a project called Worldcoin has been launched by OpenAI, an Artificial intelligence company. The project claims to be building the world’s largest identity and financial public network.
What is Project Worldcoin?
- About:
- Worldcoin is an initiative to create a digital network in which everyone can claim some kind of stake, and join the digital economy.
- Worldcoin Working Process:
- The initiative uses a device called “Orb” to collect biometric (iris) data and help participants get a World ID through the World app.
- With the app, participants can collect a cryptocurrency called Worldcoin [WLD].
- Users need to be willing to scan irises and/or get their own irises scanned to make the Worldcoin network possible.
- Those who have their irises scanned and collect a World ID can use this to claim the WLD crypto, which they may use for transactions (if possible and legal) or hold on to the asset in the hope that its price might rise.
- Worldcoin claims that using biometric information to avoid duplication is a valid method for including everyone in its network.
- This process is called “proof of personhood” and makes sure that people do not sign themselves up multiple times in exchange for crypto.
- Worldcoin in India:
- The company claimed that India had “proven the effectiveness of biometrics” through its Aadhaar system.
- Worldcoin lists 18 locations in India — largely in Delhi, Noida, and Bangalore — where Orb operators are scanning people’s eyes.
- Criticism of Worldcoin:
- Worldcoin faced early criticisms, with concerns raised about privacy, data security, and the validity of biometric scans.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Science and Technology: August 2023 UPSC Current Affairs - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is Akira Ransomware? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of a room-temperature superconductor in LK-99: The Quest for a Room-Temperature Superconductor? |  |
| 3. How does same-sex behavior in Rhesus Macaques relate to human behavior? |  |
| 4. How does the successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 on the Moon's South Pole impact space exploration? |  |
| 5. What is the objective of NASA's STEREO's Earth Flyby mission? |  |
















