Sex Linkage | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Sex Linkage
Genetics, the study of heredity and the variation of traits, has revealed intricate mechanisms governing the transmission of genes from one generation to the next. Within the realm of genetics, one aspect that stands out is the concept of sex linkage, a phenomenon deeply intertwined with the nature of our chromosomes and their influence on the inheritance of specific traits. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of sex-linked genes, exploring their significance and the profound implications they have on various species, including humans.
Sex Chromosomes
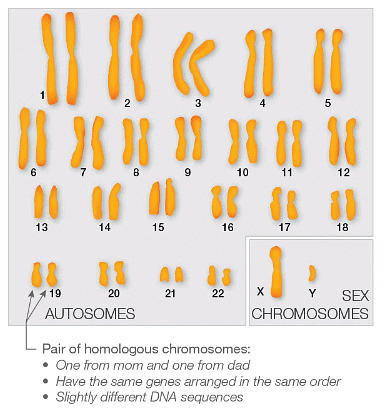
- Sex chromosomes are responsible for determining an individual's sex, with X and Y being the sex chromosomes in humans and other mammals. Females possess two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome.
- In contrast, autosomes, also known as non-sex chromosomes, come in pairs called homologous chromosomes, with both members of a pair containing the same genes arranged in the same order. Consequently, both males and females have two copies of genes located on autosomes.
- In the case of females, their two X chromosomes also contain identical genes arranged in the same order, resulting in two copies of every gene, including those on the sex chromosomes.
- However, the X and Y chromosomes have different sets of genes. Consequently, males possess only one copy of genes located on the sex chromosomes. While the Y chromosome carries relatively few genes, the X chromosome contains more than 1,000 genes, including well-known examples responsible for traits such as color blindness and male pattern baldness. These traits are referred to as sex-linked traits.
Inheritence of Sex Chromosomes in Mammals
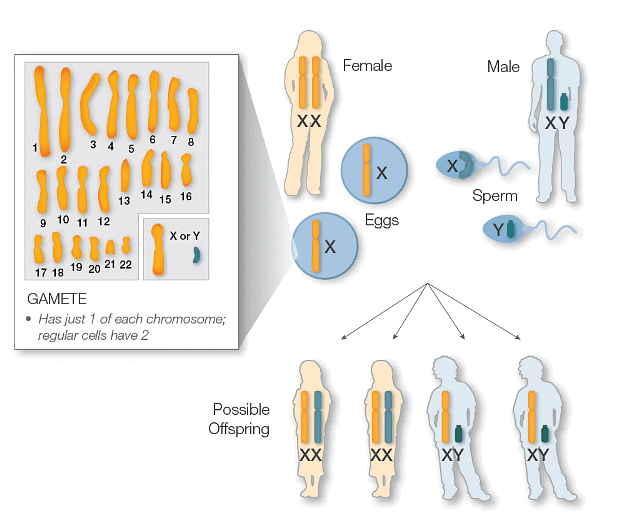
- In mammals, the inheritance of sex chromosomes occurs through the process of meiosis, which produces gametes (eggs and sperm) in most animals. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes is halved, ensuring that each gamete receives one set of autosomes and one sex chromosome.
- Female mammals produce eggs, which invariably carry an X chromosome, while males produce sperm that can carry either an X or a Y chromosome.
- When an egg and sperm unite, they form a zygote, which then develops into a new offspring. If an egg combines with an X-carrying sperm, it results in the birth of a female offspring. Conversely, if an egg combines with a Y-carrying sperm, a male offspring is produced.
- In the case of female offspring, they inherit one X chromosome from each of their parents. In contrast, male offspring inherit an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father.
- It's important to note that X chromosomes do not pass from fathers to sons, whereas Y chromosomes are consistently passed from fathers to their male offspring.
Sex Chromosomes in Pigeons
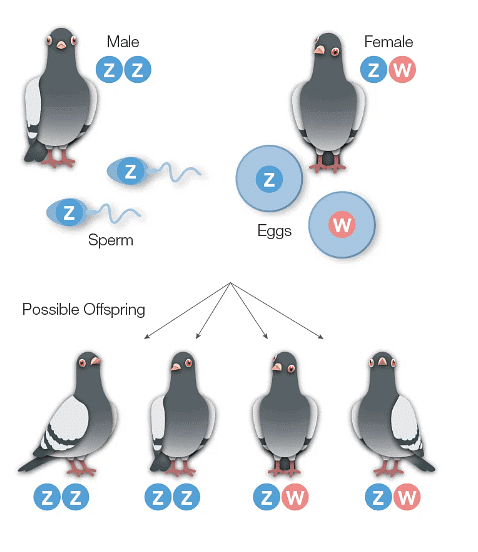
- The mechanism of sex determination in birds is essentially the opposite of how it operates in mammals. If you're familiar with the game Pigeonetics, you may already know that birds have sex chromosomes referred to as Z and W. In male birds, there are two Z chromosomes, while females possess one Z and one W chromosome. Male birds produce sperm containing a Z chromosome exclusively, while female gametes (eggs) can carry either a Z or a W chromosome.
- In the case of male offspring among birds, they inherit one Z chromosome from each of their parents. Conversely, female birds receive a Z chromosome from their father and a W chromosome from their mother.
- It's worth noting that Z chromosomes do not pass from mothers to their daughters, whereas W chromosomes are consistently passed from mothers to their female offspring.
- In birds, males possess two copies of every gene, while females have just one copy of the genes located on the sex chromosomes. The W chromosome is relatively small and contains few genes, while the Z chromosome contains numerous sex-linked genes, including those responsible for controlling feather color and color intensity.
- The X & Y system in mammals and the Z & W system in birds are just two examples of how sex determination occurs in the animal kingdom. Some animals even have the capacity to change from one sex to another.
Inheritance of Sex-Linked Genes
- When it comes to genes located on autosomes (non-sex chromosomes), everyone possesses two copies of each gene, with one inherited from each parent. These two copies can either be identical or different, and different versions of the same gene are known as "alleles." Genes provide instructions for making proteins, and it's the combined action of these two alleles that determines what we physically observe, also known as our "phenotype."
- Variations in genes play a significant role in shaping our inherited characteristics, accounting for the differences seen among individuals. For specific examples, you can refer to Observable Human Characteristics and The Outcome of Mutation.
- In female pigeons with ZW sex chromosomes, they have just one Z chromosome, and consequently, they possess only one allele for each gene located on it. For instance, a gene on the Z chromosome influences feather color, with three different alleles responsible for blue, ash-red, or brown feathers. In female birds (ZW), their single allele dictates their feather color. However, in males (ZZ), two alleles interact to determine feather color based on their dominance. Essentially, the dominant allele (e.g., 'ash-red') takes precedence over the others.
- Having two copies of a gene becomes crucial when one copy is defective or "broken." In such cases, a functional second copy can often compensate and prevent issues, serving as a backup. However, with sex-linked genes, male mammals (and female birds) lack this backup copy. In humans, several genetic disorders are sex-linked, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy and hemophilia, and they are more commonly observed in boys than in girls.
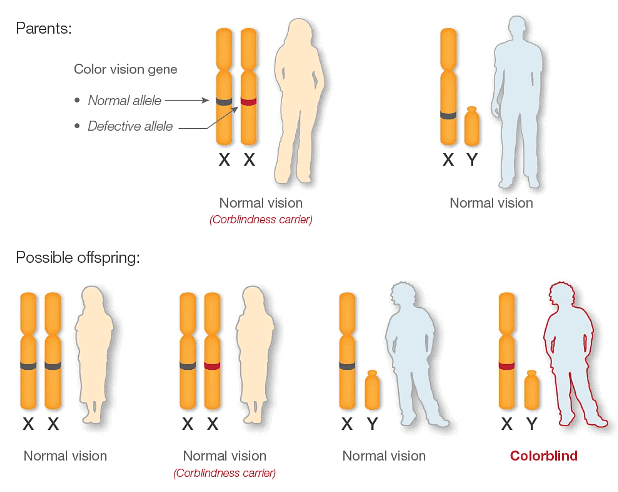
- For instance, red-green colorblindness is caused by a faulty gene located on the X-chromosome. To perceive red and green colors, at least one functional copy of this gene is necessary. Since boys have only one X-chromosome, which they inherit from their mother, inheriting one defective copy of the gene results in colorblindness. In contrast, girls possess two X-chromosomes, so to be colorblind, they must inherit two faulty copies, one from each parent. Consequently, red-green colorblindness is much more prevalent in boys (1 in 12) than in girls (1 in 250).
- It's worth noting that some genes code for functional RNAs, which also play a role in influencing our traits.
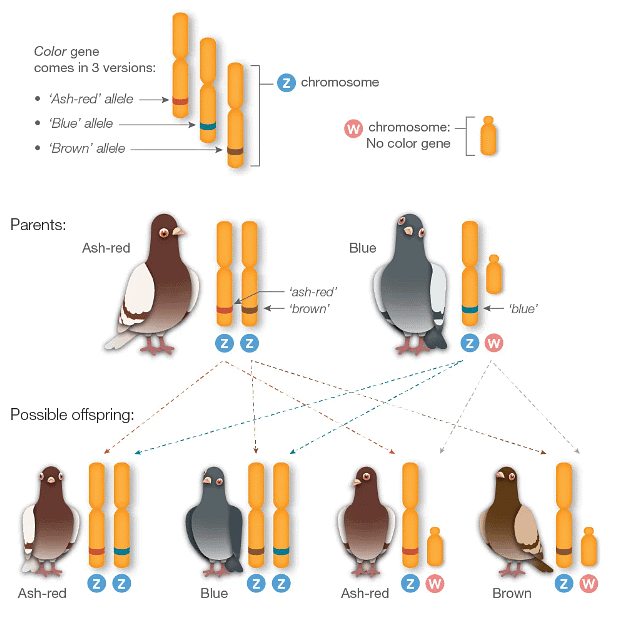
Note: The differences in sex chromosomes between males and females leads to specific inheritance patterns for sex-linked genes. (Above) Female pigeons inherit their color allele from their father. Males inherit one allele from each parent. In humans (below), the pattern is reversed.
Recombination and Sex-Linked Genes
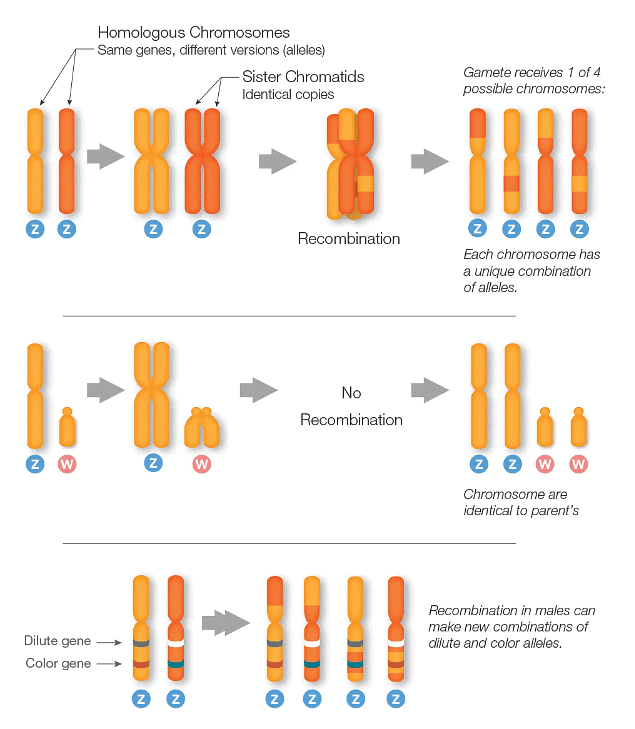
- During the formation of gametes (egg and sperm), chromosomes undergo a process known as recombination. This process involves the pairing up of homologous chromosomes and the exchange of DNA segments between them. Recombination results in the creation of new combinations of alleles, which can then be inherited by offspring.
- When sex chromosomes lack a homologous partner, such as in XY male mammals and ZW female birds, they do not undergo recombination. Instead, these sex chromosomes are passed down from parent to offspring without any changes. However, in cases where sex chromosomes have homologous counterparts, like in XX female mammals and ZZ male birds, recombination occurs, leading to the formation of new combinations of alleles.
- In pigeons, traits like color and color intensity are controlled by two genes located on the Z chromosome. In males, recombination between homologous Z chromosomes can generate novel combinations of alleles for color and color intensity (though some offspring may still inherit the same allele combination as their father). However, in females, where the Z chromosome does not undergo recombination, the two alleles are always inherited together by offspring.
- It's worth noting that there is a partial exception to the lack of recombination in sex chromosomes, as certain regions of the X and Y chromosomes, known as "pseudoautosomal regions," do pair up and undergo recombination. These regions contain the same genes and are not considered sex-linked, despite being located on the sex chromosomes.
Sex-Linked Genes Can Also Be Genetically Linked
- In pigeons, it's important to note that the color and dilute genes are not only sex-linked but also genetically linked.
- When genes are unlinked, whether they are on the same chromosome or different chromosomes, they are inherited independently approximately 50% of the time. In contrast, genetically linked genes are inherited together more frequently than 50% of the time. The likelihood of recombination events between linked genes decreases as the distance between them on the chromosome decreases.
- In the case of pigeons, the color and dilute genes are separated by recombination about 40% of the time, but this linkage primarily applies to males. In other words, in males, the color and dilute genes are not very closely positioned on the chromosome, as they can still undergo recombination. However, this genetic linkage means that these genes tend to be inherited together more often than if they were unlinked, especially in males.
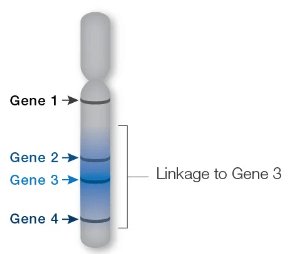
Note: Gene 3 is more closely linked to Gene 2 than to Gene 4. Gene 1 and Gene 3 are not linked, but by chance they will still stay together 50% of the time, the same as if they were on separate chromosomes.
|
179 videos|143 docs
|





















