UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Botany Optional for UPSC > Chemiosmotic theory and ATP synthesis
Chemiosmotic theory and ATP synthesis | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
The Chemiosmotic Theory
- The chemi-osmotic theory, formulated by Peter Mitchell in 1961, established an electrochemical connection between respiration and phosphorylation and earned him the Nobel Prize in 1978.
- Chemi-osmosis involves the movement of chemical ions across a semi-permeable membrane, following their electrochemical gradient, akin to the movement of water through osmosis. One illustrative example is the production of ATP during cellular respiration or photosynthesis through the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane.
- This theory focuses on ATP generation by ATP synthase. It encompasses the pumping of protons (H+) through specialized channels in mitochondrial membranes, from the inner compartment to the outer compartment. Protons originating from the electron transport chain are transported across the membrane by the respiratory chain, moving from the M-side to the C-side of the mitochondrial inner membrane. This translocation leads to changes in pH and membrane potential.
- Since the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to protons, these ions can only pass through the Proton channel of the ATPase to reach the M-side. When H+ moves from the C-side to the M-side, the F1- ATPase, operating in reverse, facilitates ATP synthesis. Conversely, when F1-ATPase hydrolyzes ATP, it acts as a "proton pump," expelling H+ from the M-side to the C-side. For each oxidation of NADH, six protons are transported through the inner membrane. These six H+ ions, upon returning to the M-side through the F1-ATPase, yield three ATP molecules.
- According to this theory, the inner mitochondrial membrane serves as a transducer, converting energy from the electrochemical gradient into the chemical energy of ATP. This membrane is impermeable to both H+ and OH-, so differences in pH across the membrane create energy-rich gradients.
- When protons (H+) are expelled toward the cytoplasmic side (C-side) and OH- remains on the matrix side, a pH difference is established (lower pH on the C-side and higher pH on the M-side), resulting in an electrical potential. Under the influence of the protein motive force generated by the electron transfer through the respiratory chain and the release of protons on the C-side, the enzyme ATPase synthesizes ATP.
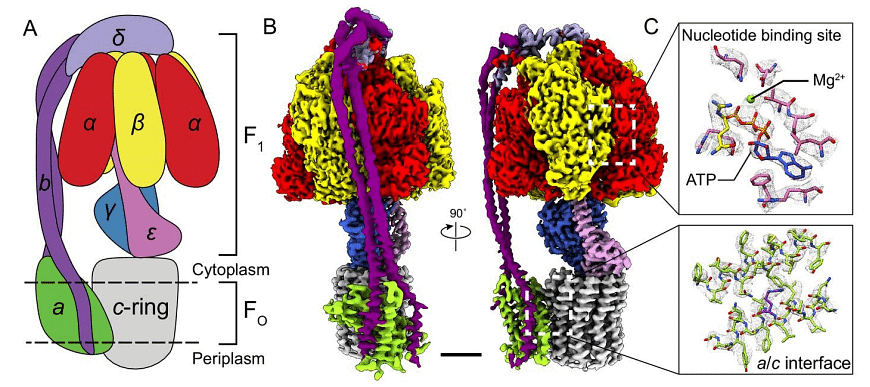
ATP synthase Structure
- ATP synthesis involves the conversion of its precursor, ADP, by the enzyme ATP synthase, also known as complex V, which is located in the cristae and inner mitochondrial membrane.
- ATP synthase comprises two parts: F0 and F1. The F0 portion, embedded within the mitochondrial membrane, consists of a c-ring and subunits a, as well as two b subunits. This component functions as a motor powered by the movement of H+ ions across the membrane.
- The F1 portion, located within the mitochondria, is composed of subunits alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. F1 possesses a water-soluble segment capable of hydrolyzing ATP. This part acts as another motor employed in ATP generation.
- The F0 region shares similarities with DNA helicase, an enzyme responsible for unzipping DNA strands during replication, while the F1-ATPase region is akin to H+ motors that enable its movement.
The document Chemiosmotic theory and ATP synthesis | Botany Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Botany Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
179 videos|143 docs
|
FAQs on Chemiosmotic theory and ATP synthesis - Botany Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the chemiosmotic theory? |  |
Ans. The chemiosmotic theory is a scientific concept that explains how ATP synthesis occurs in living organisms. It proposes that ATP is synthesized through the movement of protons across a membrane, coupled with the production of a proton gradient and the action of ATP synthase.
| 2. What is the structure of ATP synthase? |  |
Ans. ATP synthase is a complex enzyme found in the inner mitochondrial membrane and thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts. It is composed of two main components: a membrane-bound Fo portion and a soluble F1 portion. The Fo portion consists of a proton channel, while the F1 portion contains the catalytic sites responsible for ATP synthesis.
| 3. How does the chemiosmotic theory explain ATP synthesis? |  |
Ans. According to the chemiosmotic theory, ATP synthesis occurs as a result of the movement of protons across a membrane. During cellular respiration or photosynthesis, protons are pumped from the matrix or stroma side to the intermembrane or thylakoid lumen side, creating a proton gradient. This gradient provides the energy needed for the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase.
| 4. What role does the proton gradient play in ATP synthesis? |  |
Ans. The proton gradient serves as the driving force for ATP synthesis. As protons flow back through the Fo portion of ATP synthase, they cause conformational changes in the F1 portion, allowing it to catalyze the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. The energy released from the movement of protons is harnessed to drive this reaction.
| 5. How is the chemiosmotic theory relevant to UPSC exams? |  |
Ans. Understanding the chemiosmotic theory is important for UPSC exams as it forms the basis of ATP synthesis, a fundamental process in cellular metabolism. Questions related to the chemiosmotic theory may be asked in topics such as bioenergetics, cell biology, or molecular biology, making it essential for aspirants to have a clear understanding of this concept.
Related Searches





















