Aristotle’s Philosophy of Form and Matter | Philosophy Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Aristotle's Biography
Aristotle's Life and Background
- Aristotle, born in 384 BCE in Stagira, northern Greece, is a renowned ancient Greek philosopher and scientist.
- He hails from a family with a medical background, which likely influenced his interest in natural sciences.
Early Education and Teaching at Plato's Academy
- At 17, Aristotle moved to Athens to study at Plato's Academy, where he remained for two decades.
- After Plato's death, he ventured into travels and studies across different places, including Lesbos and Assos.
Tutoring Alexander the Great and Founding the Lyceum
- In 338 BCE, Aristotle became the tutor of Alexander the Great, the famous military leader.
- In 335 BCE, he returned to Athens and founded his own school, the Lyceum, where he dedicated his life to teaching, writing, and studying.
A Broad Intellectual Legacy
- Aristotle's extensive works span numerous fields, including logic, metaphysics, ethics, politics, and biology.
- His philosophy has had a profound and enduring impact on Western thought.
Influence of Plato on Aristotle
Aristotle's Development Beyond Plato
- Aristotle was initially influenced by Plato during his time at the Academy.
- However, his philosophical approach gradually diverged from Plato's.
Practical and Empirical Philosophy
- Aristotle's philosophy became more practical, empirical, and grounded in observation compared to Plato's abstract and idealized concepts.
Retaining Plato's Influence
- Despite differences, Plato's influence on Aristotle remained significant, especially in ethics, political philosophy, and logic.
Hylomorphism and Physical Entities
Defining Hylomorphism
- Hylomorphism, an ancient Greek philosophical doctrine developed by Aristotle, posits that physical entities comprise matter and immaterial form.
Form and Matter in Aristotle's Philosophy
Understanding Matter and Form
- Matter represents the substance of an object, while form signifies its specific configuration.
- Matter is the foundation of change, while form imparts actuality to matter.
Inseparable Relationship
- According to Aristotle, form and matter are inseparable and together constitute an object's substance.
- Hylomorphism explains how things come into existence without arising from nothing.
Aristotle's Rejection of Plato's Theory of Forms
Comparing Plato and Aristotle
- Aristotle, Plato's student, disagreed with Plato's idealistic Theory of Forms.
- Aristotle retained the concept of form but grounded it in the material world, emphasizing observation and experience.
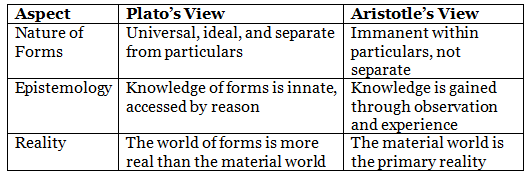
Aristotle's Critique of Plato's Forms
Comparing Plato and Aristotle
Plato's Ideal Forms vs. Aristotle's Practical Forms
- Plato believed in universal, ideal forms separate from particulars, while Aristotle saw forms as immanent within objects.
- Plato relied on innate knowledge, while Aristotle emphasized knowledge gained through experience.
Aristotle's Concept of Form
Retaining the Concept of Form
- Aristotle rejected Plato's Theory of Forms but kept the notion of form.
- Unlike Plato, Aristotle's forms are practical and connected to the material world.
Form as Essential Determination
Determining the Essence
- Form in Aristotle's view defines the essential characteristics and identity of an object.
- It is linked to the organic structure or essential determination of a thing.
Form in Aristotle's Philosophy
Defining Form
- Form in Aristotle's philosophy refers to an object's specific arrangement of matter that imparts identity and unity.
Form and Matter Together
Complementary Principles
- Form and matter are inseparable and jointly constitute an object's substance.
- Matter provides potential for change, while form gives identity and unity.
Form as Determining Principle
Defining Nature and Purpose
- Form determines an object's specific nature and purpose.
- It distinguishes one object from another based on its structure and function.
Unity of Form and Matter
Interdependent Principles
- Aristotle emphasizes the unity and interdependence of form and matter.
- This unity is central to understanding change and development in the natural world.
Aristotle's Four Causes
Overview of Aristotle's Four Causes
- Aristotle's Four Causes provide a framework for understanding change and the existence of things in the natural world.
Roles of Form and Matter
Form and Matter within the Four Causes
- Material Cause: Represents the physical substance.
- Formal Cause: Encompasses the form or pattern.
- Efficient Cause: Pertains to the agent or force causing change.
- Final Cause: Concerns the purpose or goal of a thing.
Example: Wooden Chair
- Material Cause: The wood used for construction.
- Formal Cause: The design or blueprint of the chair.
- Efficient Cause: The carpenter shaping the wood.
- Final Cause: The purpose of providing seating.
Applications of Hylomorphism in Scholastic Philosophy
Influence of Hylomorphism on Medieval Philosophy
- Hylomorphism greatly impacted medieval philosophy, especially scholasticism.
- Scholastic thinkers used hylomorphism to explain substance composition, the soul, ethics, and natural philosophy.
Applications in Scholastic Philosophy
Metaphysics: Hylomorphism clarified substance composition and relationships between universals and particulars.
Theology: Applied to the human soul, reconciling Aristotle with Christian beliefs.
Ethics: Used to explain virtues and vices shaping the soul's form.
Natural Philosophy: Employed for understanding substance generation, living organisms, and natural phenomena.
Hylomorphism in Contemporary Philosophy
Modern Revival of Hylomorphism
- Contemporary philosophy witnesses a resurgence of hylomorphic theories.
- Philosophers like Kit Fine, E.J. Lowe, and David Oderberg adapt and develop hylomorphism to address metaphysical, mind, and science-related questions.
Critiques and Challenges
Challenges to Contemporary Hylomorphism
- Some consider hylomorphism outdated and incompatible with modern science.
- Challenges exist in precisely explaining the relationship between form and matter.
Relevance in Modern Science
Applicability in Modern Science
- Hylomorphism remains relevant in understanding complex systems and emergent properties.
- It offers insights into aspects that elude reductionist approaches.
Conclusion
Aristotle's Enduring Impact
- Aristotle's hylomorphic philosophy, encompassing form and matter, profoundly shaped Western thought.
- Its relevance spans ethics, theology, metaphysics, and natural philosophy.
Contemporary Resurgence
- Hylomorphism experiences a modern revival, with philosophers adapting it to address current questions.
- It offers a comprehensive framework accommodating material and formal dimensions of reality.
Continued Enrichment
- Hylomorphism, despite its ancient origins, enriches contemporary discussions and our understanding of the world.
|
60 videos|168 docs
|
















