UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 3rd October 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Sanwariya Seth Temple
Subject: History

Why in News?
The Prime Minister recently offered prayers at the Sanwariya Seth Temple in Chittorgarh, Rajasthan.
About Sanwariya Seth Temple:
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Krishna, specifically to his beloved child form known as “Sanwariya Seth” or “Shyam Seth.
- Location: It is located in the village of Mandaphia in the Chittorgarh district of Rajasthan.
- It was built in 1840 A.D.
- Architecture:
- The temple follows the traditional architecture of Rajasthan, known for its intricate carvings, domes, and vibrant colors.
- The main structure of the temple is built using white marble.
- The temple is adorned with intricate carvings on the walls, pillars, and ceilings. These carvings depict scenes from Hindu mythology and various motifs.
- The temple features multiple domes that are adorned with decorative elements.
- The temple has a prominent spire, or shikhar, which is a tall, tapering structure that rises above the main sanctum.
- In the sanctum sanctorum of the temple, a black stone idol of Lord Krishna is installed.
- The temple has spacious pillared halls that provide a gathering space for devotees and visitors.
Source: PIB
Lesser known facts about Lal Bahadur Shastri
Subject: Modern History

Why in News?
October 2 is a day of double celebration as India remembers the birth anniversaries of two iconic leaders: Mahatma Gandhi, the ‘Father of the Nation,’ and Lal Bahadur Shastri, former Prime Minister.
- Both leaders made significant contributions to India’s freedom struggle and early years of nation-building.
Lal Bahadur Shastri: A Man of Humble Origins
[A] Rising from Modest Beginnings
- Early Struggles: Born in 1904 in Mughalsarai, Uttar Pradesh, Shastri faced adversity early in life, with his father passing away shortly after his birth.
- Simplicity: Raised in a lower-middle-class environment, he possessed only two kurtas and dhotis, symbolizing his humble beginnings.
- A Change of Name: In a demonstration of his early social consciousness, Shastri dropped his birthname “Varma.” In 1925, he acquired the title of ‘Shastri’ (one who knows the Shastras) from the Kashi Vidyapeeth in Benaras, adding it to his name.
[B] Resignation and Accountability
- A Serious Accident: While serving as the Union Minister for Railways and Transport in 1956, a tragic railway accident in Telangana resulted in the loss of 112 lives.
- Owning Responsibility: Deeply affected by the tragedy, Shastri took moral responsibility and tendered his resignation to Prime Minister Nehru. Although Nehru initially did not accept it, Shastri resigned again after another railway accident in Tamil Nadu in November 1956, further solidifying his moral stature.
[C] Championing the Slogan ‘Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan’
- A Return to Cabinet: Shastri made a comeback to the Union Cabinet, serving in roles such as Home Minister and Commerce and Industry Minister.
- Language Assurance: In response to concerns about Hindi domination, he assured the continued use of English as an official language alongside Hindi.
- Economic Challenges: In 1965, faced with economic stagnation and growing food demand, Shastri called upon farmers to increase production, traders to maintain fair prices, and consumers to exercise restraint. He coined the famous slogan, ‘Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan (Hail the soldier, hail the farmer!).’
[D] Leadership during the 1965 India-Pakistan War and Tashkent Agreement
- Unforeseen Conflict: The 1965 war with Pakistan erupted as Pakistan launched attacks in Jammu and Kashmir, believing India to be vulnerable after the 1962 war with China.
- Firm Response: Shastri approved an Indian counterattack, leading to hostilities on both sides.
- Tashkent Declaration: Soviet Premier Aleksey Kosygin invited Shastri and Pakistan President General Ayub Khan to Tashkent, Uzbekistan, where they signed the Tashkent Declaration on January 10, 1966, committing to long-term peace.
- Sudden Passing: Tragically, Shastri passed away due to a heart attack the following day in Tashkent, leaving behind speculation about the circumstances. However, available evidence suggests it was a natural death, dispelling doubts of external factors.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
According to the Review of Maritime Transport 2023 by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, in 2023, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from international shipping were 20 percent higher than in the last 10 years.
Key highlights of the review:
- Overall, the shipping industry contributes to over 80 percent of the world’s trade volume and nearly three percent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerised trade, which had declined by 3.7 per cent in 2022, is expected to grow by 1.2 per cent in 2023 and grow further by three per cent between 2024-2028.
- Oil and gas trade volumes showed robust growth in 2022, while tanker freight rates saw a strong revival driven by geopolitical events.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- It is the UN’s leading institution dealing with trade and development.
- It is a permanent intergovernmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1964.
- It supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalised economy more fairly and effectively.
- It provides economic and trade analysis, facilitates consensus-building and offers technical assistance to help developing countries use trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquarter: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Reports published by the UNCTAD
- Trade and Development Report
- World Investment Report
- The Least Developed Countries Report
Source: DTE
Controller General of Accounts (CGA)
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Central Government’s fiscal deficit in the first five months of 2023-24 touched 36 percent of the full-year target, according to the data released by the Controller General of Accounts (CGA).
About the Controller General of Accounts (CGA):
- CGA, in the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance, is the Principal Accounting Adviser to the Government of India.
- It was established in October 1975 to administer matters pertaining to the departmentalisation of the accounts of the Union.
- Functions:
- CAG is responsible for establishing and managing a technically sound management accounting system.
- The Office of CGA prepares monthly and annual analysis of expenditure, revenues, borrowings, and various fiscal indicators for the Union Government.
- It further formulates policies relating to general principles, forms, and procedures of accounting for the Central and State Governments.
- It administers the process of payments, receipts, and accounting in the Central Civil Ministries/ Departments.
- Through its Internal Audit Units in the respective Ministries/Departments, it is responsible for maintaining the requisite technical standards of accounting in the departmentalized accounting offices and for monitoring the financial performance and effectiveness of various programs, schemes, and activities of the civil ministries.
- It also administers banking arrangements for the disbursements of Government expenditures and the collection of government receipts and interacts with the Central Bank for the reconciliation of cash balances of the Union Government.
- CGA is also responsible for coordination and monitoring the progress of the submission of corrective/remedial action taken notes (ATNs) on the recommendations contained in Public Accounts Committee’s (PAC) reports as well as the Comptroller & Auditor General (CAG) reports through its web based Audit Para Monitoring System (APMS).
- It also looks after the pensions of the Central government employees.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
India’s rise is the big story. So where’s the FDI?
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
The Indian economy grew at 7.8 percent in the first quarter of the ongoing financial year. There is a decline in FDI.
Central idea
- Projections by experts, including the RBI and the IMF, indicate a prospective annual growth rate of 6–6.5 percent, reaffirming India’s status as a global growth powerhouse. However, beneath this optimistic narrative lies a concerning trend: foreign direct investment (FDI) in India has been steadily declining.
India’s growth prospects
- India is likely to grow at around 6–6.5 percent over the full year.
- Medium-term assessments, such as those by the IMF, peg growth at roughly 6 percent between 2023 and 2028.
- This momentum positions India as a formidable player in global growth, potentially rivaling China.
- Multinationals are increasingly eyeing India as an alternative investment destination, capitalizing on shifting geopolitical dynamics.
Declining trend in FDI in India
- FDI Decline: FDI inflows into India have been declining. In the fiscal year 2022–23, FDI stood at $71.3 billion, which marked a 16 percent decrease compared to the previous fiscal year (2021–22). This trend of decline continued in the first four months of the current fiscal year, with a 26 percent drop in FDI inflows compared to the same period the previous year.
- Equity Flows: A substantial portion of the decline has been in fresh equity flows. Equity flows decreased from approximately $59.6 billion in 2021–22 to around $47.6 billion in 2022–23. In the first four months of the current year, equity flows further plummeted to $13.9 billion, down from $22 billion the previous year.
- Policy Uncertainty: One possible explanation for the decline in FDI is the presence of policy uncertainty in India. An uncertain business environment, an uneven playing field, and the fear of arbitrary changes to rules and regulations may be acting as deterrents to foreign investors.
- Trade Agreements: India’s absence from major trading blocks, such as the RCEP agreement, and the lack of trade agreements with entities like the European Union can disadvantage India in the global manufacturing ecosystem. Comprehensive trade agreements with lower tariffs and other benefits can incentivize foreign investment.
- Comparative Analysis: Despite rising interest rates in developed economies, countries like Vietnam and Indonesia have managed to maintain or increase their FDI inflows.
Key sectors affected by the decline in FDI
- Automobile Industry: The decline in FDI has had an impact on the automobile industry in India. This sector plays a crucial role in the country’s manufacturing landscape and contributes significantly to both economic growth and employment.
- Construction (Infrastructure Activities): Infrastructure development is essential for India’s economic growth. The decline in FDI may slow down construction and infrastructure activities, potentially affecting the country’s development.
- Metallurgical Industries: Metallurgical industries, which include sectors like steel production, are also mentioned in the article as being affected by the decline in FDI. These industries are vital for various manufacturing processes and contribute to both domestic consumption and exports.
Areas that India might need to address to reverse this trend
- FDI Decline in Multiple Sectors: The decline in FDI is not limited to a specific sector but has affected various industries, including technology, the automobile industry, construction, and metallurgical industries. This broad-based decline underscores the need for comprehensive solutions.
- Navigating Policy Uncertainty: To attract foreign investors, India needs to provide a stable and predictable business environment, reduce regulatory uncertainty, and ensure a level playing field.
- Global Investment Landscape: India’s FDI decline is notable when compared to countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, which have managed to maintain stable FDI inflows. This highlights the need for India to remain competitive in the global investment landscape.
- The Trade Agreement Imperative: The absence of India from major trading blocks, such as the RCEP agreement, could be a factor contributing to the FDI decline. India may benefit from pursuing trade agreements that lower trade barriers and enhance market access.
Conclusion
- The decline in FDI flows to India raises pertinent questions about the country’s attractiveness as an investment destination. While India’s growth story appears promising, investors seek stability, policy clarity, and access to global trade networks. Addressing these concerns and leveraging India’s potential as a China plus one option requires a comprehensive strategy to reinvigorate FDI inflows and capitalize on its growth prospects.
Source: Indian Express
R21/Matrix-M vaccine
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
The R21 vaccine is the second malaria vaccine recommended by the WHO, following the RTS,S/AS01 vaccine, which received a WHO recommendation in 2021.
- WHO is now reviewing the vaccine for prequalification, which is the WHO stamp of approval, and will enable GAVI (a global vaccine alliance) and UNICEF to buy the vaccine from manufacturers.
About the R21/Matrix-M Vaccine:
- It is a new vaccine approved for the prevention of malaria in children.
- It was developed by the University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India with support from the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership ('EDCTP'), the Wellcome Trust, and the European Investment Bank ('EIB').
- It is the first malaria vaccine to reach the WHO’s target of 75% efficacy.
- It has already been approved for use in Burkina Faso, Ghana, and Nigeria.
- The vaccine will be rolled out in those African countries in early 2024 and will be available in mid-2024 in other countries.
What is malaria?
- It is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- There are 5 parasite species that cause malaria in humans, and 2 of these species, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, pose the greatest threat.
- Malaria is common in tropical areas where it’s hot and humid.
- Children under 5 years of age are the most vulnerable group affected by malaria.
- Symptoms:
- The signs and symptoms of malaria are similar to flu symptoms. They include:
- Fever and sweating.
- Chills that shake your whole body
- Headache and muscle aches.
- Fatigue.
- Chest pain, breathing problems, and cough.
- Diarrhoea,nausea and vomiting.
- As malaria gets worse, it can cause anemia and jaundice.
- The most severe form of malaria, which may progress to a coma, is known as cerebral malaria. This type represents about 15% of deaths in children and nearly 20% of adult deaths.
- The signs and symptoms of malaria are similar to flu symptoms. They include:
- Treatment:
- It is preventable and curable. With early treatment, most people with malaria will make a full recovery.
- Some drugs are given in combination with other drugs. The type of parasite will determine the type of medication.
- The main antimalarial drugs are:
- chloroquine
- hydroxychloroquine
- primaquine
- artemisinin-based therapy
- atovaquone-proguanil
Source: Indian Express
Green Ammonia
Subject: Environment and Ecology
Why in News?
Recently, V.O. Chidambaranar Port Authority, Tamil Nadu, successfully received and handled Green Ammonia Containers from Damietta Port, Egypt.
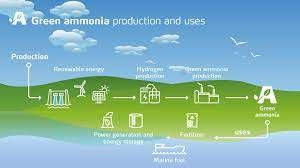
About Green Ammonia:
- It is produced by using hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air.
- These are then fed into the Haber process (also known as Haber-Bosch) which is powered by sustainable electricity.
- In the Haber process, hydrogen and nitrogen are reacted together at high temperatures and pressures to produce ammonia, NH3.
- Green ammonia production is where the process of making ammonia is 100% renewable and carbon-free.
- It can be used in
- Fuel for engines such as locomotives and shipping, replacing diesel and marine fuel oil
- Fuel source for electricity and power generation
- Building block to make fertilisers for use in agriculture;
- Feedstock for industrial and manufacturing applications ranging from water purification through to pharmaceuticals
Key facts about Ammonia
- It is a colourless, highly irritating gas with a sharp suffocating odor.
- It dissolves easily in water to form ammonium hydroxide solution which can cause irritation and burns.
- Ammonia gas is easily compressed and forms a clear, colorless liquid under pressure.
- It is usually shipped as a compressed liquid in steel cylinders.
- Ammonia is not highly flammable, but containers of ammonia may explode when exposed to high heat.
Source: PIB
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
















