Time, Speed and Distance: Shortcuts & Tricks | Quantitative Techniques for CLAT PDF Download
Speed: The distance covered per unit time is called speed. Speed is directly proportional to distance and inversely to time
- Speed = Distance/Time;
- Time = Distance/Speed
- Distance = Speed × time
Units
- Time : Seconds, minutes, hours
- Distance : meter, kilometer
- Speed : km/ hr, m /sec
Conversion of Units:
- 1 km/hr = 5/18 metre/second
- 1 metre/second = 18/5 km/hr
- 1 Km/hr = 5/8 mile/hr
- 1 mile/hr = 22/15 foot/second
Example 1: A scooter travels at the speed of 45 kmph. What is the distance covered by the scooter in 4 minutes?
Sol: Speed of scooter = 45 km/hr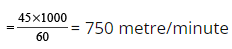
∴ Distance covered in 4 minutes = 4 × 750 = 3000 metre
Average Speed
The average speed is given by total distance divided by total time taken; this is the formula to be remembered all the time.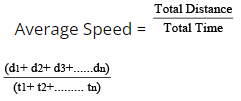
The average speed in case of a journey from X to Y at speed of A m/sec and returning back to X at a speed of B m/sec, is
Example 2: Sunil travels from Delhi to Patna at the speed of 40 km/hr and returns at the speed of 50 km/hr, what is the average speed of the journey?
Sol: Using the formula,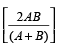
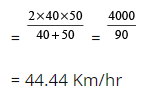
While travelling a certain distance d, if a man changes his speed in the ratio m:n, then the ratio of time taken becomes n:m.
If a body travels a distance ‘d’ from A to B with speed ‘a’ in time t₁ and travels back from B to A i.e., the same distance with m/n of the usual speed ‘a’, then the change in time taken to cover the same distance is given by:
Change in time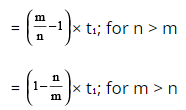
If first part of the distance is covered at the rate of v₁ in time t₁ and the second part of the distance is covered at the rate of v₂ in time t₂, then the average speed is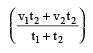
Relative Speed
As the name suggests, the concept is regarding the relative speed between two or more objects. The basic concept in relative speed is that speeds get added in case objects are moving from opposite direction, and get subtracted in case objects are moving in the same direction. For example, if two trains are moving in opposite direction with a speed of X km/hr and Y km/hr respectively, then (X + Y) is their relative speed. In the other case if two trains are moving in the same direction with a speed of X km/hr and Y km/hr respectively, then (X – Y) is their relative speed.
For the first case the time taken by the trains in passing each other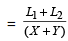 hours, where L₁ and L₂ are length of trains.
hours, where L₁ and L₂ are length of trains.
For the second case the time taken by the trains in passing each other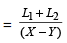 hours, where L₁ and L₂ are length of trains.
hours, where L₁ and L₂ are length of trains.
Example: Two trains, 100 m and 80 m in length are running in the same direction. The first runs at the rate of 51 m/s and the second at the rate of 42 m/s. How long will they take to cross each other?
Sol: Here Length of first train = 100m,
Length of second train = 80m
And Speed of first train = 51 m/s
Speed of second train = 42 m/s
Relative speed = 51 – 42 = 9 m/s
(since trains are running in the same direction)
As per the formula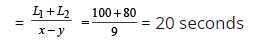
Example: The driver of a maruti car driving at the speed of 68 km/h locates a bus 40 metres ahead of him. After 10 seconds, the bus is 60 metres behind. The speed of the bus is
(a) 30 km/h
(b) 32 km/h
(c) 25 km/h
(d) 38 km/h
Ans: b
Sol: Let speed of Bus = SB km/h.
Now, in 10 sec., car covers the relative distance = (60 + 40) m = 100 m
∴ Relative speed of car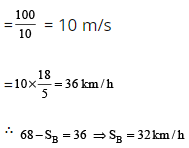
|
51 videos|172 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Time, Speed and Distance: Shortcuts & Tricks - Quantitative Techniques for CLAT
| 1. What is average speed? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate average speed? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between time, speed, and distance? |  |
| 4. How can I find the distance traveled if the speed and time are known? |  |
| 5. Can average speed be greater than the maximum speed? |  |





















