UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 4th October 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Bihar Caste Survey
Subject: Geography
Why in News?
The Bihar government has released the results of its survey of castes in the state.
Findings
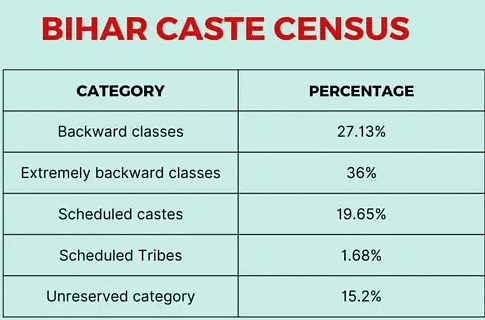
- Total Population: Bihar’s population, according to the survey, is 13,07,25,310, compared to the 10.41 crore recorded in the 2011 census.
- Hindus comprise 81.99% of the population, and Muslims 17.72%.
- The populations of Buddhists, Christians, Sikhs, Jains, and other religious denominations are minuscule.
- Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and Extremely Backward Classes (EBCs) constitute more than 63% of the population of Bihar.
- The EBCs are the biggest social group comprising 36.01% of the state’s population.
- The OBCs are 27.12%, and the Scheduled Castes (SCs) are 19.65%.
- Scheduled Tribes are 1.68%, the bulk of the tribal population having become part of Jharkhand after the bifurcation of the state in 2000.
- The “unreserved” category comprises 15.52% of the total population.
Source: Indian Express
Basohli Pashmina
Subject: History

Why in News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a more than 100-year-old traditional craft from Jammu and Kashmir's Kathua district, has got the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- It is a hand-spun product known for extreme softness, fineness and light-weight, has insulating properties and extended life.
- Pashmina products include shawls for both men and women, mufflers, blankets and basket.
- Pashmina refers to a fine variant of spun cashmere (the animal-hair fibre), that is derived from the downy undercoat of the Changthangi.
- It is obtained from a breed of mountain goats (Capra hircus) found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- A traditional producer of pashmina wool in the Ladakh region are a people known as the Changpa (nomadic people inhabit the Changthang plateau of Tibet).
Key facts about Geographical Indication Tag
- It is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical originand possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- This is typically used for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts and industrial products.
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999seeks to provide for the registration and better protection of geographical indications relating to goods in India.
- This GI tag is valid for 10 years following which it can be renewed.
Source: Hindustan Times
GS-II
Andhra Pradesh’s Guaranteed Pension System
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
Andhra Pradesh’s Guaranteed Pension System (GPS) blends elements from both old and new pension schemes, offering the advantages of a guaranteed pension while not overly straining the state’s finances.
- This innovative system holds the potential to preserve India’s hard-won pension reforms.
What is the Andhra Pension System?
- A Hybrid Approach: The Andhra Pradesh Guaranteed Pension System Bill, 2023, recently approved by the state assembly, introduces a unique blend of the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) and the New Pension Scheme (NPS) implemented in 2004.
- Contributory Guarantee: This system ensures government employees a monthly pension equivalent to 50% of their last-drawn salary, including dearness allowance relief.
- Reason for Introduction: Andhra Pradesh introduced GPS as a response to resistance against NPS, which was viewed by many as inferior to the earlier scheme. The return to OPS was considered fiscally unsustainable, with the potential to drive the state’s fiscal deficit to 8% by 2050.
Breakthrough created
- Long-standing Pension Reforms: India struggled for over a decade to implement pension reforms that led to the introduction of NPS in 2004.
- Growing Discontent: Over time, public sentiment favored those receiving pensions under the old scheme, leading to discontent.
- Political Promises: Political parties capitalized on this discontent, pledging to return to the old scheme if elected.
- Andhra’s Middle Path: Andhra Pradesh’s GPS offers a middle ground, preventing a regressive return to the old scheme while addressing concerns about NPS.
How does the Andhra System work?
- Enhancing Attractiveness: The contributory system guarantees a pension equivalent to 50% of the last drawn salary.
- Balancing Financial Burden: Any shortfall in NPS returns is covered by the government.
- Current NPS Pensions: Presently, NPS pensions amount to around 40% of an employee’s last drawn salary. Therefore, the government only has to fund the remaining balance.
Alternative to NPS
- Contributory Nature: NPS is a contributory scheme, with both employees and employers contributing to a corpus invested for returns.
- Uncertainty: In NPS, the pension amount is not guaranteed, as it depends on corpus returns influenced by market conditions.
- Ignoring Inflation: NPS does not consider inflation or pay commission recommendations.
- Market Dependency: Opposition to NPS is fueled by fears of further reductions in pension due to adverse market conditions.
Why not revert to the Old Pension Scheme?
- Budgetary Constraints: Under OPS, pensions were financed through the budget.
- Unsustainable Growth: Pension liabilities for all states saw a compound annual growth rate of 34% for a 12-year period ending in 2021-22.
- Budgetary Impact: In 2020-21, pension outgo accounted for 29.7% of states’ revenues.
- Development Challenges: A return to OPS would strain government funds, hindering development efforts and operational financing.
- Competitiveness Concerns: Such a shift could negatively impact India’s ease of doing business and overall competitiveness.
Source: Indian Express
Press Freedom and Free Speech in Southeast Asia
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
Southeast Asian nations consistently rank among the worst globally for press freedom and media rights.
- Autocratic governments in the region have increasingly resorted to closing independent newspapers and imprisoning activists who criticize the authorities.
Press Freedom Rankings
- Pew Research Findings: According to the Pew Research Center’s report on religion and politics in South and Southeast Asia, the embrace of free speech and democracy is not widespread in the region.
- Global Press Freedom Rankings: Organizations like “Reporters without Borders” annually rank nations in terms of press freedom. In the latest World Press Freedom Index, Vietnam and Myanmar were among the worst-ranked countries, with Malaysia being the exception.
- Deteriorating Standards: Declining press freedom worldwide is attributed to increasing aggressiveness by authorities, growing animosity towards journalists on social media, and the proliferation of fake content.
Freedom on the Net Rankings
- Online Free Speech Monitoring: Freedom House’s Freedom On The Net index evaluates online free-speech conditions. Myanmar, China, Vietnam, and Thailand ranked poorly, highlighting online restrictions and censorship.
Public Perspectives on Free Speech
- Notion of National Harmony: Governments in Southeast Asia, which encompass a diverse range of political systems, generally concur on the need to limit free speech to safeguard national “harmony.”
- Pew Research Focus: Unlike traditional press freedom rankings, the Pew study delves into the views of ordinary people on free speech issues.
- Key Findings: The report revealed that the majority of respondents in three out of four Southeast Asian states prioritize national “harmony” over free speech. However, a notable minority in Malaysia and Singapore held a contrasting view.
Various impacts on Free speech
- Age and Education Impact: Younger and more educated respondents were more likely to advocate for the right to criticize the government and prioritize free speech over social harmony.
- Religious Influence: The report also noted differences in attitudes based on religion. For instance, Thai Muslims were more inclined to prioritize social harmony over free speech compared to Thai Buddhists.
Government Justifications
- Lese-Majeste Laws: Thai authorities argue that strict lese-majeste laws are necessary to protect “Thainess” and the monarchy.
- Cambodian Government: Cambodia’s government defends stringent restrictions by portraying opposition politicians and independent media as threats to the nation’s hard-won peace.
- Communist Governments: Vietnam and Laos assert that collective interests take precedence over individual rights.
- Singapore’s Approach: Singapore, a multi-ethnic state, expanded “hate speech” laws, emphasizing the importance of not allowing any race or religion to be attacked or insulted.
Critique of Laws
- Effectiveness Questioned: Critics argue that harsh “hate speech” and other laws in the region may not genuinely preserve social harmony and can restrict freedoms.
- Asia Centre Report: A 2021 report from the Asia Centre contends that such laws reinforce the dominance of the ethno-religious majority, limit freedom of religion or belief, and muzzle grievances from minority communities.
- Political Exploitation: Ethno-religious dominant governments are accused of exploiting societal divisions for political gain.
Conclusion
- Balancing the preservation of national “harmony” with the protection of individual liberties remains a contentious issue.
- As younger, more educated individuals express stronger support for free speech, it suggests the potential for evolving perspectives in the future.
Source: Indian Express
Southeast Asia’s First High-Speed Railway
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Indonesian President Joko Widodo inaugurated Southeast Asia’s first high-speed railway.
About
- It is a key project under China’s Belt and Road infrastructure initiative.
- The railway connects Jakarta with Bandung, the heavily populated capital of West Java province, and will cut travel time from the current three hours to about 40 minutes.
- It has speeds of up to 350 kph and is named as “Whoosh,”which means “timesaving, optimal operation, reliable system” in Indonesian language.
- Its use of electrical energy is expected to reduce carbon emissions.
- It was financed with a loan from the China Development Bank for 75% of the cost. The remaining 25% came from the consortium’s own funds.
- The project is part of a planned 750-kilometer (466-mile) high-speed train line that would cut across four provinces on Indonesia’s main island of Java and end in the country’s second-largest city, Surabaya.
China’s Connectivity Projects in Southeast Asia
- China is one of the largest sources of foreign direct investment in Southeast Asia, a region home to more than 675 million people.
- Amid crackdowns by the United States and its allies, China is expanding trade with ASEAN countries and infrastructure projects are playing key roles.
- A semi-high-speed railway linking China with Laos was inaugurated in December 2021. It runs through Laos’ mountain ranges to connect the southeastern Chinese city of Kunming with Vientiane, the capital of Laos.
- The $6 billion infrastructure was financed mostly by China under the Belt and Road policy.
- There are plans for a high-speed train down through Thailand and Malaysia to Singapore.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Exercise SAMPRITI
Subject: Defence

Why in News?
India and Bangladesh commenced the 11th edition of exercise SAMPRITI on 03rd October 2023 in Umroi, Meghalaya.
About Exercise SAMPRITI:
- It is an annual joint military exercise between India and Bangladesh.
- It was started in Jorhat, Assam in 2009, the exercise has witnessed ten successful editions till 2022.
- This exercise, alternatingly organised by both countries, signifies strong bilateral defence cooperation initiatives.
- SAMPRITI-XI, scheduled for 14 days, will engage approximately 350 personnel from both sides.
- The exercise underscores the importance of enhancing interoperability between the two armies, sharing tactical drills, and promoting best practices.
- The exercise will also witness participation by personnel from diverse units such as artillery, engineers and other supporting arms and services from both sides.
- Centered on the conduct of Sub-Conventional Operations as per Chapter VII of the UN mandate, SAMPRITI-XI will include a Command Post Exercise (CPX) and a Field Training Exercise (FTX), culminating in a Validation Exercise.
- This exercise promises to further enhance defence cooperation between India and Bangladesh, fostering deeper bilateral relations, cultural understanding, and mutual benefits from shared experiences in Sub Conventional Operations.
Source: PIB
New Development Projects in MP, Rajasthan and Telangana
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone of various projects in Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Telangana .
About the Projects
- In MP : various development projects worth around Rs 19,260 crores.
- The projects include the dedication of Delhi-Vadodara Expressway to boost connectivity across the country, Grih Pravesh of over 2.2 lakh houses built under under PMAY – Gramin and dedication of houses constructed under PMAY – Urban, laying the foundation stone for Jal Jeevan Mission projects, 9 health centers under Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission to boost the health infrastructure, dedication of academic building of IIT Indore and laying the foundation stone for hostel and other buildings on campus and a Multi-Modal Logistics Park in Indore.
- In Rajasthan: Various development projects worth about Rs 7,000 crore in Chittorgarh, Rajasthan.
- The projects include the Mehsana – Bhatinda – Gurdaspur Gas Pipeline, the LPG Plant of HPCL at Abu Road, additional storage at the Ajmer Bottling Plant, IOCL, and the permanent campus of Indian Institute of Information Technology, Kota.
- The Prime Minister dedicated a 4-lane road on NH-12 (New NH-52) on the Darah-Jhalawar-Teendhar section.
- The foundation stone for constructing and widening the Railway Over Bridge (ROB) from two-lane to four-lane in Sawai Madhopur will also be laid
- The railway projects dedicated to the nation by the Prime Minister include the projects involving the doubling of the Chittorgarh – Neemuch Railway line and Kota – Chittorgarh Electrified Railway line.
- The Prime Minister dedicated tourism facilities developed at Nathdwara under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme.
- Nathdwara is the major center of faith for millions of followers of the Pushtimarg propagated by Saint Vallabhacharya.
- Telangana: Multiple developmental projects worth more than Rs 13,500 crore in Mahbubnagar, Telangana.
- The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone of key road projects that are part of Nagpur – Vijayawada Economic Corridor.
- The projects include – 108 km long ‘four-lane access controlled Greenfield highway from Warangal to Khammam section of NH-163G’ and 90 km long ‘four-lane access controlled greenfield highway from Khammam to Vijayawada section of NH-163G.
- The Prime Minister dedicated to the nation a road project – ‘four laning of 59 km long Suryapet to Khammam section of NH-365BB’.
- The project is a part of Hyderabad – Visakhapatnam Corridor and is developed under Bharatmala Pariyojana.
- He dedicated ‘37 Kms of Jaklair – Krishna New Railway Line’
- He dedicated the nation to the ‘Hassan-Cherlapalli LPG Pipeline Project’.
- He also laid the foundation stone of the ‘Multiproduct Petroleum Pipeline of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd (BPCL) from Krishnapatnam to Hyderabad (Malkapur)’.
- He also inaugurated ‘five new buildings of University of Hyderabad’ i.e. School of Economics; School of Mathematics & Statistics; School of Management Studies; Lecture Hall Complex – III; and Sarojini Naidu School of Arts & Communication.
- The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone of key road projects that are part of Nagpur – Vijayawada Economic Corridor.
Source: Live Mint
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















