UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 6th October 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Sammakka-Sarakka University: A Tribute to Tribal Legends
Subject: History

Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the proposal to set up a central Sammakka-Sarakka Tribal University in Telangana.
- The establishment of this University was a commitment made by the Central government under the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014.
- Both Andhra Pradesh and Telangana were promised support to establish a tribal university each.
Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka
- Sammakka-Sarakka: The university is named after Sammakka-Sarakka, a revered mother-daughter duo among the local tribal community.
- Historical Significance: Sammakka was married to Pagididda Raju, a feudal chief of the Kakatiyas dynasty, and had two daughters, Sarakka and Nagulamma, along with a son named Jampanna. The legend revolves around their battle against local rulers in protest against taxing the Koya people.
- Sammakka Saralamma Jatara: This biennial festival, held in Mulugu, commemorates the 13th-century battle of the mother-daughter duo. It is considered one of the world’s largest tribal gatherings.
- Evolution of the Festival: Initially, only around 2,000 people, primarily from the Koya tribe, attended the festival. However, over time, it transformed into a large Hindu religious event, with millions of devotees attending.
- Political and Social Impact: The festival gained immense political and social significance, leading to its declaration as a state festival in 1996. Infrastructure development, including a motorable road, further boosted its popularity.
Significance of Sammakka and Sarakka
- Massive Footfall: The festival attracts around 1.5 crore devotees from various tribal and non-tribal communities, including those from multiple states such as Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Jharkhand.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs Participation: The Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government actively participate in the festival, with significant financial support.
- Infrastructure Development: Funds have been allocated for community shelters and infrastructure in and around Medaram, the festival’s location.
- Tribal Circuit Development: The Ministry of Tourism sanctioned funds for the integrated development of the tribal circuit, including the temple of Sammakka-Sarakka.
Significance of Mulugu
- Population and Demographics: Mulugu, a reserved Scheduled Tribes (ST) assembly seat, has a population of approximately 2.6 lakhs, with a 75% ST population as per the 2011 Census.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Ramappa Temple, located about 15 km from Mulugu, adds to the area’s cultural richness.
Source : Indian Express
Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Flash floods occurred in north Sikkim after the South Lhonak Lake burst due to incessant rains.
- For years, numerous studies highlighted the lake’s rapidly growing size and marked it as susceptible to glacial lake outburst flood.
About Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF):
- A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is a type of catastrophic flood that occurs when the dam containing a glacial lake fails, releasing a large volume of water.
- This type of flood is typically caused by rapid melting of glaciers or the buildup of water in the lake due to heavy precipitation or the inflow of meltwater.
- In February 2021, Chamoli district in Uttarakhand witnessed flash floods which are suspected to have been caused by GLOFs.
Source: Hindustan Times
GS-II
ED arrests AAP leader in Delhi excise policy case
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) has arrested senior Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) leader and member of Parliament (MP) in the Rajya Sabha, Sanjay Singh.
- Earlier, in February 2023, the then Deputy CM of Delhi Manish Sisodia was arrested in the same case.
- He was arrested in connection with its money laundering probe into irregularities in Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22.
Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22
- Also known as the new liquor policy, the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22 was implemented on November 17, 2021.
- It changed how liquor was sold in the city — with the government withdrawing from the business and allowing only private operators to run liquor shops.
- The main aim was to improve customer experience and stop black marketing.
- However, after the whole controversy around the new excise policy, Delhi reverted to the old excise regime.
Key features of the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22
- Under the new liquor policy, the city was divided into 32 zones inviting firms to bid on the zones.
- Instead of individual licences, bidding was done zone-by-zone.
- Also, licenses for 849 retail vends were issued through open bidding by the Excise department in 2021.
- Under the old liquor policy, Delhi had 864 liquor shops, including 475 run by the four government agencies, and 389 were private.
- For the first time, shops were allowed to offer discounts to retail customers and reduced the number of dry days to three from 21.
- The new policy also had a provision for home delivery of liquor. It even proposed lowering the drinking age from 25 to 21.
- It also suggested the opening of shops till 3 am. However, these were not implemented.
The controversy surrounding Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22
- Before the implementation, the policy had first to be examined by the Chief Secretary (CS) of Delhi Naresh Kumar.
- The CS allegedly found procedural lapses and irregularities in the new policy.
- In the report, Delhi Deputy CM Sisodia, who heads the excise department, was accused of making changes to the excise policy without the approval of the L-G.
- Based on the Chief Secretary’s note, the LG asked for a detailed report by the Vigilance Department.
- After reviewing the report by the Vigilance Department, the L-G suggested a CBI probe into the matter.
Main allegations in the Vigilance Department’s report (on the basis of which the CBI has built its case)
- Delhi liquor policy: Discounts, ‘1+1’ schemes
- Hefty discounts being offered by liquor retailers were causing severe market distortions.
- Licensees were issuing advertisements and promoting liquor and their shops through various means in violation of Delhi Excise Rules 2010.
- The government failed to take penal action against licensees for this.
- Undue benefits were given to liquor licensees by revising the rates of foreign liquor and removing the import pass fee of Rs 50 per case of beer.
- This made foreign liquor and beer cheaper for retail, leading to a loss of revenue for the state exchequer.
- Number of dry days
- The new excise policy reduced the number of dry days from 21 in the 2021 calendar year to three in 2022.
- This was done without approval from the Council of Ministers, and without seeking the LG’s opinion.
- Extension of licences
- The licences issued to liquor retailers were extended from April 1, 2022 to May 31, 2022, and then from June 1, 2022 to July 31, 2022.
- Such extensions were allegedly given by Excise officials on their own, without any increase in the tendered licence fee.
- This contravened an earlier proposal approved by the Council of Ministers, which said that the licence fee may be increased at the end of 2021-22 after considering the real time-based actual sale data.
- No such exercise was undertaken by the officers of the department.
- The extension of the licence period without an increase in fee prima facie led to undue benefit to the licensees without any justification.
- Waivers, licence fees
- The report flagged the blanket relaxation given by the Excise Department in case of default in the payment of licence fees.
- It said licence fees worth Rs 144.36 crore were waived in January 2022 on pretext of COVID restrictions as relief to the Liquor Cartel.
- This was done despite the Accounts Branch of the Excise Department having specifically recommended that no compensation should be allowed to licensees.
Source: Indian Express
Seventh India-EU Cyber Dialogue
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
The Seventh India-EU Cyber Dialogue was held recently.
About Seventh India-EU Cyber Dialogue:-
- Date: 05 October 2023.
- Venue: Brussels, Belgium.
- In the context of the vibrant Strategic Partnership between India and the EU, the two sides expressed appreciation for the Cyber Dialogue mechanism.
- Objective: to provide a platform to discuss a wide range of issues related to cyberspace.
- Both sides exchanged views on cyber policies, strategies, and areas of mutual interest.
- They discussed cyber cooperation in multilateral fora, including at the United Nations, and in regional settings, including at OSCE, ARF, and G20.
- They also discussed cooperation in promoting capacity building in cyberspace and combating the criminal use of ICTs.
About India-EU Relations:-
- The EU is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe.
- The union and EU citizenship were established when the Maastricht Treaty came into force in 1993.
- India was one of the first countries to establish relations with the European Economic Community in the 1960s.
- The retreat of the U.S. from global leadership has provided opportunities for EU-India cooperation.
Political Cooperation:-
- 2000: The first India-EU Summit was held in 2000 which marked a watershed in the development of the relationship.
- 2004: The relationship was upgraded to a ‘Strategic Partnership’ during the 5th India-EU Summit held in 2004.
- 2018: the EU’s strategy on India entitled “A Partnership for Sustainable Modernization and Rules-based Global Order” was issued by the European Commission and the EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy.
Trade:-
- India is an important trade and investment partner for the EU.
- It is the second-largest destination for Indian exports after the United States.
- India’s bilateral trade with the EU amounted to USD 116.36 billion in 2021-22.
- Despite the global disruptions, bilateral trade achieved impressive annual growth of 43.5% in 2021-22.
- The trade agreement with the EU would help India further expand and diversify its exports of goods and services, including securing the value chains.
Defense & Security:-
- EU and India have instituted several mechanisms for greater cooperation on pressing security challenges like counterterrorism, maritime security, and nuclear non-proliferation.
- Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region in New Delhi (IFC-IOR) has recently been linked up with the Maritime Security Centre – Horn of Africa (MSC-HOA) established by the EU Naval Force (NAVFOR).
Climate Change:-
- EU and India also underline their highest political commitment to the effective implementation of the Paris Agreement and the UNFCCC.
- The India-EU Clean Energy and Climate Partnership was agreed at the 2016 Summit.
- EU and India also cooperate closely on the Clean Ganga initiative.
Research and Development:-
- The India-EU Science & Technology Steering Committee meets annually to review scientific cooperation.
- Both have official mechanisms in fields such as Digital Communications, 5G technology, Biotechnology, artificial intelligence, etc.
- ISRO has had a long-standing cooperation with the European Union, since the 1970s.
- It has contributed to the EU’s satellite navigation system Galileo.
Challenges:-
- Deadlock over BTIA: The negotiations for a Broad-based Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) were held between 2007 to 2013 but have remained dormant/suspended since then.
- EU primarily remains a trade bloc: This has resulted in a lack of substantive agreements on matters such as regional security and connectivity.
- China’s influence: The EU has a high dependence on the Chinese market.
- It is a major partner in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Ukrainian war: EU expects India to criticize Russia.
Source: AIR
Freedom House Report’s Findings
Subject: International Relations
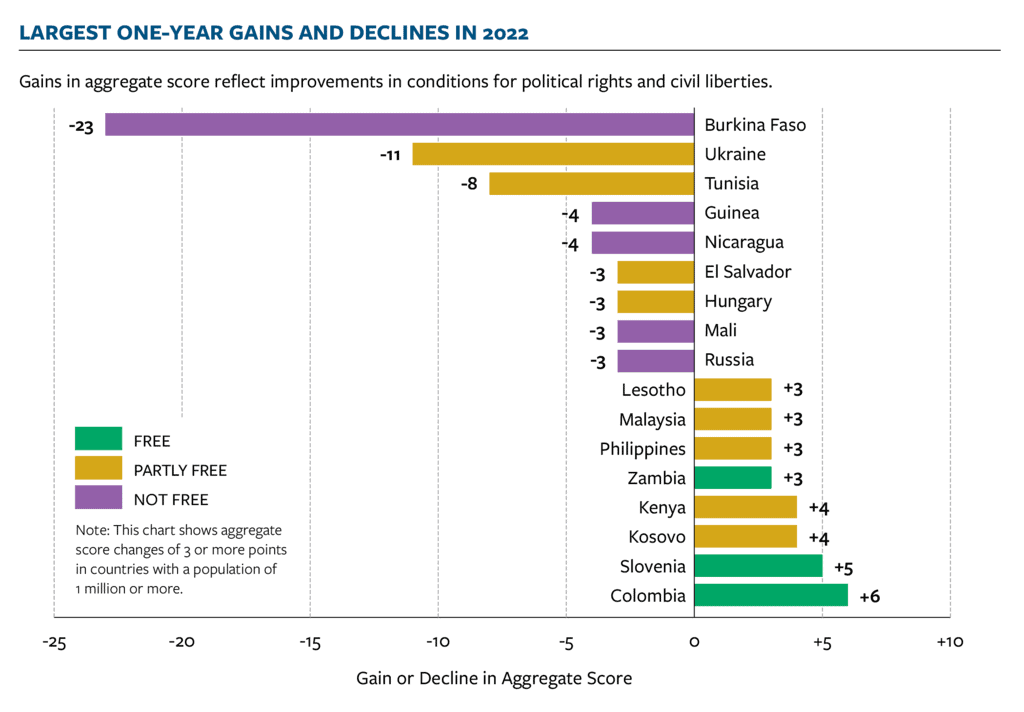
Why in News?
According to a new report by Freedom House, global Internet freedom has declined for the 13th consecutive year.
About the Report:
- Freedom House is a non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C. It was established in 1941.
- It is best known for political advocacy surrounding issues of democracy, political freedom, and human rights.
- Recently, the Freedom House published a report titled ‘Freedom on the Net 2023: The Repressive Power of Artificial Intelligence’.
- It is the 13th edition of an annual study of human rights online, covers developments between June 2022 and May 2023.
- It evaluates Internet freedom in 70 countries, accounting for 88% of the world’s Internet users.
- The report evaluates countries on five censorship methods:
- Internet connectivity restrictions,
- Blocks on social media platforms,
- Blocks on websites,
- Blocks on VPNs, and
- Forced removal of content
Major Findings of the Report:
- W.r.t. World:
- As per the report, the environment for human rights online has deteriorated in 29 countries, with only 20 countries registering net gains.
- China, for the ninth straight year, ranked as the world’s worst environment for Internet freedom, with Myanmar the world’s second most repressive for online freedom.
- As per the report, the sharpest rise in digital repression was witnessed in Iran, where authorities shut down Internet service, blocked WhatsApp and Instagram, and increased surveillance in a bid to quell anti-government protests.
- Global Internet freedom declined for 13th consecutive year:
- Digital repression intensified in Iran, home to this year’s worst decline, as authorities shut down internet service, blocked WhatsApp and Instagram, and increased surveillance in a bid to quell anti-government protests.
- Attacks on free expression grew more common around the world:
- In a record 55 of the 70 countries, people faced legal repercussions for expressing themselves online, while people were physically assaulted or killed for their online commentary in 41 countries.
- The most egregious cases occurred in Myanmar and Iran, whose authoritarian regimes carried out death sentences against people convicted of online expression-related crimes.
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) threatens to supercharge online disinformation campaigns:
- At least 47 governments deployed commentators to manipulate online discussions in their favor during the coverage period, double the number from a decade ago.
- Meanwhile, AI-based tools that can generate text, audio, and imagery have quickly grown more sophisticated, accessible, and easy to use.
- Over the past year, the new technology was utilized in at least 16 countries to sow doubt, smear opponents, or influence public debate.
- W.r.t. India:
- As per the report, India engages in all of the above-mentioned censorship methods except one (VPN blocking).
- On a range of 1 to 100 where ‘100’ represented highest digital freedom and ‘1’ the worst repression, India scored 50.
- On the other hand, Iceland, with 94, emerged as the country with the best climate of Internet freedom.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
The banking sector is leading the journey towards an Atmanirbhar Bharat
Subject: Economy
Why in News?
Central ideaDespite facing numerous challenges in the past quarter-century, including economic crises, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions, India’s banking and financial sector has continued to evolve and adapt.
- India’s remarkable growth and stability over the past 25 years have placed the country at the forefront of global optimism. This shift is attributed to the nation’s governance structures and policy apparatus, which have fostered innovation and positioned India as a hub of novel public goods. Among the sectors driving this transformation, banking and finance stand out as key contributors.
- Maturation of Banking in India: Over a period of 75 years, India’s banking sector has matured and grown into a vibrant and robust industry.
- Reforms and Critical Enablers: The past 30 years have seen critical reforms that have played a pivotal role in enabling the growth and transformation of the banking sector.
- Diversity in Banking: India’s banking sector now boasts a diverse landscape that includes public sector banks, private banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and a burgeoning fintech ecosystem. This diversity has made the financial sector more inclusive and dynamic.
- Addressing Legacy Issues: Reforms and changes in the sector have addressed legacy issues such as non-performing assets (NPAs), making the banking system more resilient.
- Internal Accruals: The internal accruals have become a significant source of growth capital for banks, enhancing their financial stability.
- Technological Advancements: Banks in India have moved away from traditional, brick-and-mortar models to embrace advanced technology. Products such as mobile banking apps, UPI, Aadhaar e-KYC, and digital payment systems have transformed the banking landscape.
- Knowledge-Based Regime: India’s banking system is undergoing a transition toward a knowledge-based regime, primarily driven by AI and cognitive computing technologies. This shift represents a move away from traditional banking practices toward more data-driven and intelligent operations.
- Personalization of Customer Engagement: AI is enabling banks to personalize customer engagement. Through AI-powered capabilities, banks can gain a deeper understanding of individual customer preferences and needs. This personalization enhances the overall customer experience.
- Deeper Understanding of Customers: AI facilitates a more profound insight into customers’ behaviors and financial needs. By analyzing data and utilizing machine learning algorithms, banks can develop a comprehensive understanding of their customers, allowing for more targeted services.
- Adaptation to a Changing Business Environment: In a landscape characterized by constant change, AI serves as a valuable tool for ensuring banks remain agile and responsive to shifting demands.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While AI presents significant opportunities for banks, it also poses challenges. Banks must address issues related to data privacy, ethical considerations, and the potential biases inherent in AI algorithms.
- Key to Future Success: AI will be a pivotal factor in differentiating successful banks in the coming years. Banks that effectively harness AI technologies are likely to maintain their competitiveness and adapt to the changing demands of customers and the business landscape.
- Digitalization Challenges: The digitalization of banking services has introduced several challenges. These include the proliferation of unregulated digital lending apps, the emergence of cryptocurrencies, and the risk of cyberattacks.
- Cybersecurity Risks: There is a need to address cybersecurity risks. As digitalization advances, banks are increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks.
- Critical Support Infrastructure: With the increasing reliance on digital banking channels, ensuring the availability of critical support infrastructure becomes paramount. This encompasses maintaining secure payment settlement systems, safeguarding ATMs, and ensuring the continuity of internet and mobile banking services.
- Data Challenges: As banks increasingly rely on data for decision-making and personalization, addressing methodological and data challenges is essential. Ensuring data accuracy, security, and compliance with privacy regulations is a responsibility that banks must prioritize.
- Customer Grievances: The digital banking era comes with added responsibilities related to addressing customer grievances efficiently. Banks must establish mechanisms to handle and resolve customer complaints promptly to ensure the uninterrupted delivery of banking services.
- Regulator frameworks: These digitalization-related challenges require banks to adopt robust security measures and regulatory frameworks to protect both customers and the financial system.
- Climate Change Imperative: Initiatives for decarbonization present opportunities in renewables, green hydrogen, and green goods trade. Banks are expected to be major financiers in combating climate change, necessitating robust risk management practices.
- Investment in Human Resources: In an ever-changing environment, the quality of human resources becomes a critical differentiator. Banks and financial institutions must attract, train, and retain talent while fostering adaptability and upskilling.
- Innovation and Governance: Financial services must invest in research and embrace out-of-the-box ideas for seamless service delivery and product personalization. Governance remains the backbone of institutions and is crucial for financial stability.
- India’s banking sector has endured and evolved, emerging from a challenging decade more resilient and adaptable. With a focus on robust governance, innovation, and a growing domestic market, it is poised to play a crucial role in India’s journey towards an Atmanirbhar Bharat, promoting equitable and sustainable development.
Source: Indian Express
Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary
Subject: Environment

Why in News?
Recent studies show that Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary is losing its distinctive grasses & and hornbills to erratic weather.
Background:-
- Rising temperature, and changing rainfall patterns may have affected the growth of plants essential to the native ecosystem.
About Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary:-
- Location: Uttara Kannada District, Karnataka.
- Area: 16 square kilometers.
- The Dandeli sanctuary covers part of the rich forests of the Uttara Kannada District.
- It lies on the banks of the river Kali.
- The Kali River or Kaali Nadi is a river flowing through Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state in India.
- The river rises near Kushavali, a small village in Uttar Kannada district.
- Mouth: Arabian Sea.
- The Kali exits at Supa Dam near Kurandi then flows east towards Dandeli.
- In the jungles of Dandeli, one can spot several animals as well as birds including many endangered species.
- The government declared the Dandeli forest, a National Wildlife Sanctuary in 1956.
- This sanctuary is the second-largest wildlife sanctuary in Karnataka.
- Along with its adjoining Anshi National Park, Dandeli is an abode of 40 tigers.
- Cultural attractions: Kavala caves, Magod Falls, Molangi Falls, Syntheri Rock, Shivaji Fort.
- Flora: Eucalyptus, Tectona grandis, Grevillea robusta, T. bellerica, Adina cordifolia, Mitragyna parviflora, Acacia etc.
- Fauna: Malabar Giant Squirrel or Ratufa Indica, Barking Deer, Gaur, Indian Pangolin, tigers, flycatchers, woodpeckers, etc.
Source: DTE
SAMPRITI-XI
Subject: Defence

Why in News?
The 11th edition of the Exercise SAMPRITI, began recently.
About SAMPRITI-XI:-
- Date: October 3, 2023.
- Venue: Umroi, Meghalaya, India.
- SAMPRITI, was initiated in 2009.
- Objective: to boost interoperability, share tactical expertise, and promote best practices between the Indian and Bangladeshi armies.
- It is an annual joint military exercise, between India and Bangladesh.
- This exercise, alternates between the two nations.
- It highlights the strong bilateral defense cooperation between the two countries.
- SAMPRITI-XI is scheduled for a duration of 14 days.
- It will involve approximately 350 personnel from both India and Bangladesh.
- Focus: enhancing cooperation and interoperability while conducting Sub-Conventional Operations as per Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
- It consists of a Command Post Exercise (CPX), a Field Training Exercise (FTX), and a Validation Exercise.
Source: PIB
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















