Important Equations and Definitions: Acids, Bases and Salts | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Acids
Acids are substances that can donate protons (H+) or accept electron pairs.- Acids have a sour taste and turn blue litmus paper red.
- Examples: Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3), Acetic acid (CH3COOH).
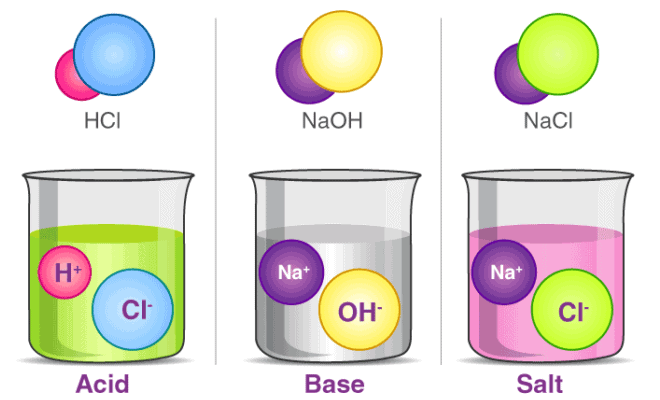
Bases
Bases are substances that can accept protons (H+) or donate electron pairs.- Bases have a bitter taste and turn red litmus paper blue.
- Examples: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2], Potassium hydroxide (KOH), and Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
Salt
A compound formed by the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base.- Hydrogen Ion (H+): Positively charged ion formed when an acid dissociates in water.
- Hydroxide Ion (OH-): A negatively charged ion formed when a base dissolves in water.
Neutralization Reaction
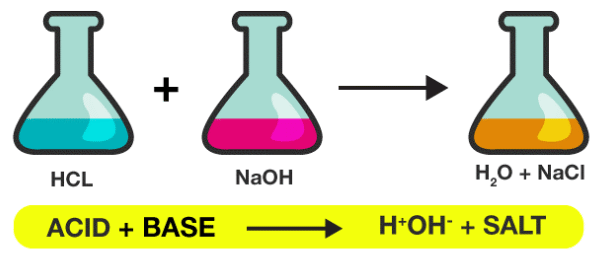
- A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water.
- General equation: Acid + Base → Salt + Water.
pH Scale
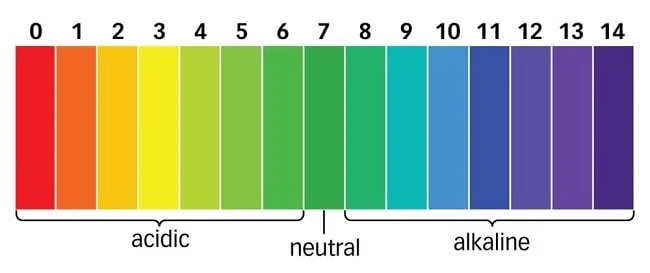
- The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution.
- pH values range from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating basicity.
Litmus Paper: Litmus paper is a natural indicator that turns red in the presence of acids and blue in the presence of bases.
Olfactory Indicators: Olfactory indicators are substances whose odor changes in acidic or basic media. Examples: Vanilla, Onion, Clove.
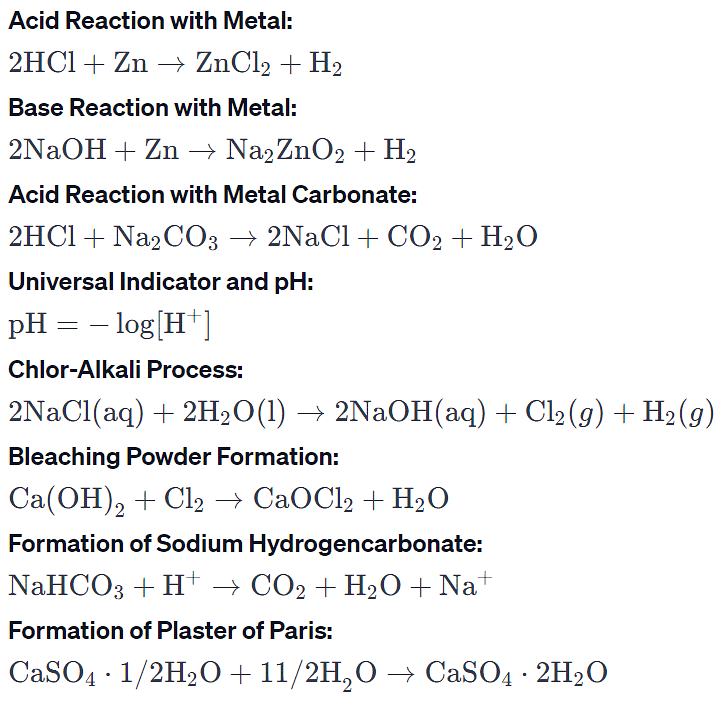
Reaction of acids and bases with metals
Acids, in general, react with metals to produce salt and hydrogen gas. Bases, in general, do not react with metals and do not produce hydrogen gas.
1. Acid + active metal → salt + hydrogen + heat
2HCl + Mg → MgCl2 + H2 (↑)
Hydrochloric acid + Magnesium → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
2. Base + metal → salt + hydrogen + heat
2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2 (↑)
Sodium hydroxide + Zinc → Sodium zincate + Hydrogen
A more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its base.
2Na + Mg (OH)2 → 2NaOH + Mg
Sodium + Magnesium hydroxide → Sodium hydroxide + Magnesium
Reaction of acids with metal carbonates and bicarbonates
Acid + metal carbonate or bicarbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide.
2HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
H2SO4 + Mg (HCO3)2 → MgSO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
Effervescence indicates the liberation of CO2 gas.
Reaction of Acid with Base
1. Reaction of metal oxides and hydroxides with acids
Metal oxides or metal hydroxides are basic in nature.
Acid + base → salt + water + heat
H2SO4 + MgO → MgSO4 + H2O
2HCl + Mg (OH)2 → MgCl2 + 2H2O
2. Reaction of non-metal oxides with bases
Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature
Base + Nonmetal oxide → salt + water + heat
2NaOH + CO2→ Na2CO3 + H2O
3. Reaction of acids and base
HCl (strong acid) + NaOH (strong base) → NaCl (salt) + H2O (water)
Water of Crystallisation
Fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt.
For Example: CuSO4.5H2O Hydrated Copper Sulphate
Preparation of Bleaching Powder
Preparation – Ca(OH)2(aq)+Cl2(g)→CaOCl2(aq)+H2O(l)
Preparation of Washing Soda (Sodium hydrogen carbonate)
a. Limestone is heated: CaCO3→CaO+CO2
b. CO2 is passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride and ammonia:
NaCl(aq)+NH3(g)+CO2(g)+H2O(l)→NaHCO3(aq)+NH4Cl(aq)
Equations:
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Equations and Definitions: Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Class 10
| 1. What are acids and how are they defined in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are bases and how do they differ from acids? |  |
| 3. What is the pH scale and what does it measure? |  |
| 4. How do acids and bases neutralize each other? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |






















