Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Important Question Answers - Introduction to Trigonometry
Short Answer Type Questions- I
Q1: In ΔABC , Right Angled at B, AB = 24cm, BC = 7cm.
Determine the Following Equations:
(i) sinA, cosA
Ans: Let us draw a right-angled triangle ABC, right angled at B.
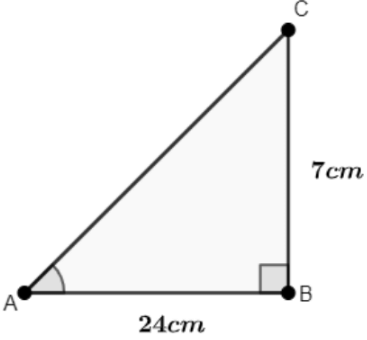
Using Pythagoras theorem, find AC.
AC2 = AB2+BC2
= (24)2+(7)2
= 576+49
= 625
∴ AC = 25cm
Then,
sin A = BCAC = 725
∴ sin A = 725
cos A = ABAC = 2425
∴ cos A = 2425
(ii) sinC, cosC
Ans: Let us draw a right-angled triangle ABC, right angled at B.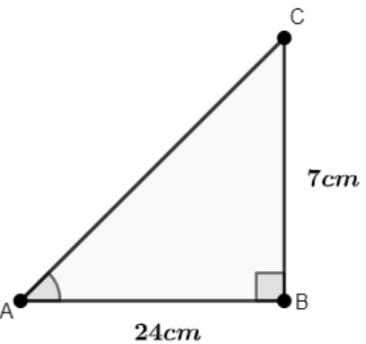
Using Pythagoras theorem, find AC.
AC2 = AB2+BC2
= (24)2+(7)2
= 576+49
= 625
∴ AC = 25cm
Then,
sin C = ABAC = 2425
∴ sin C = 2425
cos C = BCAC = 725
∴ cos C = 725
Q2: In Adjoining Figure, Find the Value of tanP − cotR.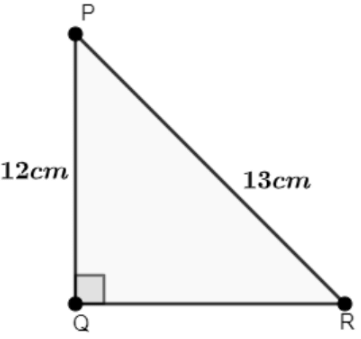
Ans: Using Pythagoras theorem,
PR2 = PQ2+QR2
(13)2 = (12)2+QR2
QR2 = 169−144⇒25
∴ QR = 5cm
Then find tanP − cotR,
First find the value of tanP.
tan P = side opp. to ∠Pside adj. to ∠P = QRPQ = 512
∴ tan P = 512
Now find the value of cot R:
We know that tan R = 1 / cot R
For that, we need to first find the value of tan R:
tan R = side opp. to ∠Rside adj. to ∠R = PQQR = 125
∴ cot R = 512
Then:
tan P − cot R = QRPQ − QRPQ
⇒ 512 − 512 ⇒ 0
∴ tan P − cot R = 0
Q3: If sinA = 3/4, Calculate the Value of cosA and tanA. 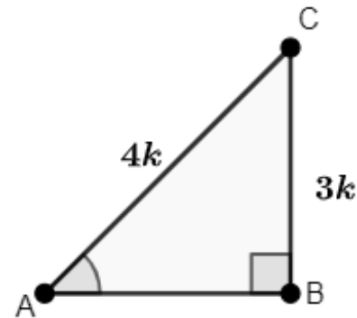
Ans: Given that the triangle ABC in which ∠B = 90º
Let us take BC = 3k and AC = 4k
Then using Pythagoras theorem,
AB = √((AC)² − (BC)²)
⇒ √((4k)² − (3k)²)
⇒ √(16k² − 9k²)
⇒ k√7
∴ AB = k√7
Calculate the value of cos A:
cos A = ABAC = k√74k = √74
∴ cos A = √7 / 4
Calculate the value of tan A:
tan A = BCAB = 3kk√7 = 3√7
∴ tan A = 3 / √7
Q4: Given 15cotA = 8, Find the Values of sinA and secA.
Ans: Given: 15cotA = 8
Let us assume a triangle ABC in which ∠B = 90º.
Then, 15cotA = 8
⇒ cotA = 8/15
Since cotA = adjhyp = ABBC
Let us draw the triangle.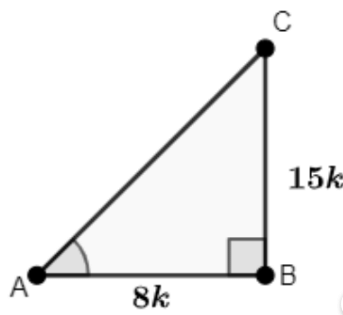
Given: AB = 8k, BC = 15k
Find the value of AC using the Pythagoras theorem:
AC = √((AB)² + (BC)²)
⇒ √((8k)² + (15k)²)
⇒ √(64k² + 225k²)
⇒ √(289k²)
⇒ 17k
∴ AC = 17k
Find the values of sin A and sec A:
sin A = BCAC = 15k17k = 1517
∴ sin A = 15 / 17
sec A = ACAB = 17k8k = 178
∴ sec A = 17 / 8
Q5: If ∠A and ∠B are Acute Angles Such That cosA = cosB, then show that ∠A = ∠B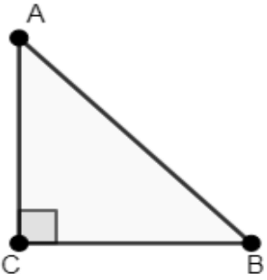
Ans: Given: cosA = cosB
In right triangle ABC,
cos A = side adj. to ∠Ahyp. = ACAB ...(1)
And, cos B = side adj. to ∠Bhyp. = BCAB ...(2)
Then, cos A = cos B:
Now, equate equations (1) and (2):
ACAB = BCAB
⇒ AC = BC
⇒ ∠A = ∠B
Therefore, Angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
Hence proved.
Q6: State Whether the Following are True or False. Justify Your Answer.
(i) The Value of tanA is Always Less than 1.
Ans: False because sides of a right triangle may have any length, so tanA may have any value. For example,
tan A = BCAB = 1510 = 32 = 1.5
(ii) secA= 12/5 for Some Value of Angle A.
Ans: True as secA is always greater than 1. For example,  As hypotenuse will be the largest side. So, it is true.
As hypotenuse will be the largest side. So, it is true.
(iii) cosA is the Abbreviation Used for the Cosecant of Angle A.
Ans: False as cosA is the abbreviation of cosineA. Because cosA means cosine of angle A and cosecA means cosecant of angle A.
(iv) cotA is the Product of cotand A.
Ans: False as cotA is not the product of cot and A. cot without A doesn’t have meaning.
(v) sinθ = 4/3 for Some Angle θ.
Ans: False as sinθ cannot be greater than 1. For example, sinθ = Since the hypotenuse is the largest side. So, sinθ will be less than 1.
Since the hypotenuse is the largest side. So, sinθ will be less than 1.
Q7: Express the Trigonometric Ratios sinA, secA and tanA in Terms of cotA.
Ans: Find the value of sinA in terms of cotA.
By using identity cosec2A−cot2A = 1.
Then, use cosecA= 1/sinA.
⇒ cosec² A = 1 + cot² A
⇒ 1sin² A = 1 + cot² A
⇒ sin² A = 11 + cot² A
⇒ sin A = 1√(1 + cot² A)
∴ sin A = 1√(1 + cot² A)
Now find the value for sec A in terms of cot A:
Using the identity sec² A − tan² A = 1:
⇒ sec² A = 1 + tan² A
⇒ sec² A = 1 + 1cot² A
⇒ sec² A = cot² A + 1cot² A
⇒ sec A = √(1 + cot² A)cot A
∴ sec A = √(1 + cot² A)cot A
And find the value for tanA in terms of cot A
By trigonometric ratio property, tanA= 1/cot A
Hence, tanA = 1/cot A
Therefore, sinA, secA and tanA are founded in terms of cotA.
Q8: Write the Other Trigonometric Ratios of A in Terms of secA.
Ans: Find the value of sinA in terms of secA
By using identity, sin2A+cos2A = 1
sin² A = 1 − cos² A
⇒ sin² A = 1sec² A
⇒ sin² A = sec² A − 1sec² A
⇒ sin A = √(sec² A − 1)sec A
∴ sin A = √(sec² A − 1)sec A
Find the value for cos A in terms of sec A:
By trigonometric property:
cos A = 1sec A
Find the value for tan A in terms of sec A:
Using the identity sec² A − tan² A = 1:
⇒ tan² A = sec² A − 1
⇒ tan A = √(sec² A − 1)
∴ tan A = √(sec² A − 1)
Find the value for cosec A in terms of sec A:
By trigonometric property:
cosec A = 1sin A
Substitute the value of sin A:
cosec A = 1√(sec² A − 1)sec A
⇒ cosec A = sec A√(sec² A − 1)
∴ cosec A = sec A√(sec² A − 1)
Find the value for cot A in terms of sec A:
By trigonometric property:
cot A = 1tan A
Substitute the value of tan A:
cot A = 1√(sec² A − 1)
∴ cot A = 1√(sec² A − 1)
Q9: Show that Any Positive Odd Integer Is of the Form 6q + 1, or 6q + 3, or 6q + 5, where q is some integer.
Ans: Let a be any positive integer and b= 6.
Then, by Euclid’s algorithm, a=6q+r for some integer q ≥ 0, and r = 0,1,2,3,4,5 because 0 ≤ r < 6.
Therefore, a = 6q or 6q+ 1 or 6q+ 2or 6q +3or 6q+ 4or 6q+ 5
Also, 6q+1 = 2×3q+1 = 2k1+1, where k1 is a positive integer 6q+3 = (6q+2)+1 = 2(3q+1)+1 = 2k2+ 1,
Where k2 is an integer 6q+5 = (6q+4)+1 = 2(3q+2)+1 = 2k3+1, where k3 is an integer
Clearly, 6q+1, 6q+3, 6q+5 are of the form 2k+ 1, where k an integer is.
Therefore, 6q + 1, 6q + 3, 6q + 5 are not exactly divisible by 2.
Hence, these expressions of numbers are odd numbers.
And therefore, any odd integer can be expressed in the form 6q+1, or 6q+3, or 6q+5.
Q10: An Army Contingent of 616 Members are to March Behind an Army Band of 32 Members in a Parade. The Two Groups Are to March in the Same Number of Columns. What Is the Maximum Number of Columns in Which They Can March?
Ans: We have to find the HCF(616, 32) to find the maximum number of columns in which they can march.
To find the HCF, we can use Euclid’s algorithm.
616 = 32×19+8
⇒ 32 = 8×4+0
Hence, HCF(616, 32) is 8.
Therefore, they can march in 8 columns each.
Short Answer Type Questions- II
Q11: Given secθ= 13/12, Calculate the Values for All Other Trigonometric Ratios.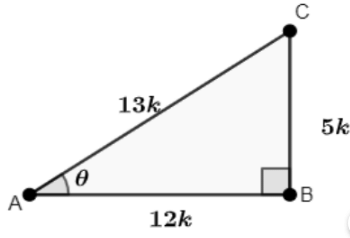
Ans: Given: secθ = 13/12
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which ∠A = θ and ∠B = 90º
Let AB = 12k and AC = 13k
Then, find the value of BC
BC = √((AC)² − (AB)²)
⇒ √((13k)² − (12k)²)
⇒ √(169k² − 144k²)
⇒ √(25k²)
⇒ 5k
∴ BC = 5k
Find the trigonometric ratios:
Since sec θ = 13/12,
sin θ = BCAC = 5k13k = 513
cos θ = ABAC = 12k13k = 1213
tan θ = BCAB = 5k12k = 512
cot θ = ABBC = 12k5k = 125
cosec θ = ACBC = 13k5k = 135
Q12: If cotθ= 7/8, then Evaluate the Followings Equations:
(i) (1 + sin θ)(1 − sin θ)(1 + cos θ)(1 − cos θ)
Sol:
Given: cot θ = 7/8
Let us consider a triangle ABC where ∠A = θ and ∠B = 90°.
Then, AB = 7k and BC = 8k
Using Pythagoras theorem, find AC:
AC = √((BC)² + (AB)²)
⇒ √((8k)² + (7k)²)
⇒ √(64k² + 49k²)
⇒ √(113k²)
⇒ √113k
∴ AC = √113k
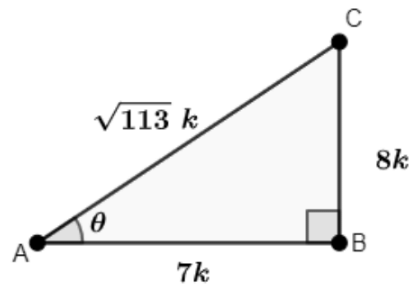
Now find the value of trigonometric ratios.
sin θ = BCAC = 8k√113k = 8√113 , and cos θ = ABAC = 7k√113k = 7√113
Then,
(1 + sin θ)(1 − sin θ)(1 + cos θ)(1 − cos θ)
We know that cos² θ + sin² θ = 1.
Then,
1 − sin² θ1 − cos² θ ⇒ cos² θsin² θ
= 4911364113 = 4964
∴ (1 + sin θ)(1 − sin θ)(1 + cos θ)(1 − cos θ) = 4964
(ii) cot2θ
Ans: Given: cot2θ
We know that, cotθ= cosθ/sinθ
Then,
⇒ cos² θsin² θ = 4911364113 = 4964
∴ cot² θ = 4964
Hence, (1 + sin θ)(1 − sin θ)(1 + cos θ)(1 − cos θ) and cot² θ are the same.
Q13: If 3cot A = 4, then show that: 1 − tan²A1 + tan²A = cos²A − sin²A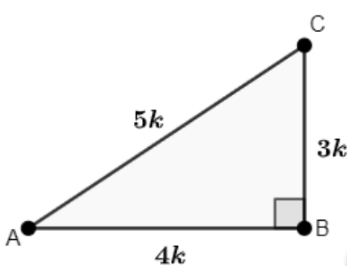
Ans: Given: 3cot A = 4
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which ∠B = 90°
Then, 3cot A = 4 ⇒ cot A = 4/3
Let AB = 4k and BC = 3k
Using Pythagoras theorem, find AC:
AC = √((BC)² + (AB)²)
⇒ √((3k)² + (4k)²)
⇒ √(9k² + 16k²)
⇒ √25k²
⇒ 5k
∴ AC = 5k
Find the values of trigonometric ratios:
sin A = BCAC = 3k5k = 35
cos A = ABAC = 4k5k = 45
tan A = BCAB = 3k4k = 34
To prove:
1 − tan²A1 + tan²A = cos²A − sin²A
Left-hand side:
L.H.S = 1 − tan²A1 + tan²A
Substitute the value of tan A:
= 1 − 9161 + 916
= 1616 − 9161616 + 916
= 725
Right-hand side:
R.H.S = cos²A − sin²A
= 1625 − 925
= 725
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S
Hence proved.
Q14: In ΔABC, right-angled at B, if A = 1√3, then find the value of the following equations:
- sin A cos C + cos A sin C
- cos A cos C − sin A sin C
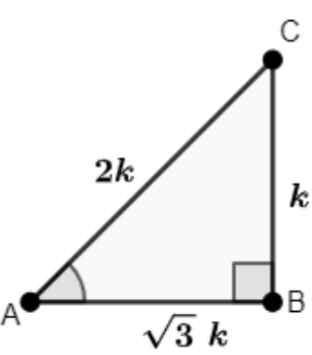
Ans: Let us consider a triangle ABCin which ∠B = 90°
Let BC = k and AB = 3 − √3k
Using Pythagoras theorem, find AC:
AC = √((BC)² + (AB)²)
⇒ √((k)² + (√3k)²)
⇒ √(k² + 3k²)
⇒ √(4k²)
⇒ 2k
∴ AC = 2k
Find the values of trigonometric ratios:
sin A = BCAC = k2k = 12
cos A = ABAC = √3k2k = √32
(i) sin A cos C + cos A sin C:
= 12 × 12 + √32 × √32
= 14 + 34 = 44 = 1
(ii) cos A cos C − sin A sin C:
= √32 × √32 − 12 × 12
= 34 − 14 = 24 = 0
Q15: In ΔPQR, right angled at Q, PR + QR = 25cm and PQ = 5cm. Determine the Values of sinP, cosP and tanP.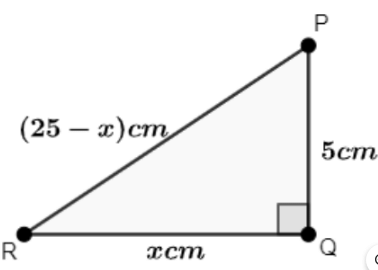
Ans: Given: In ΔPQR, right angled at Q
And PR+QR = 25cm, PQ = 5cm
Let us take QR = x cm and PR = (25−x)cm
By using Pythagoras theorem, find the value of x.
RP2 = RQ2+QP2
⇒ (25−x)2=(x)2+(5)2 ⇒ 625 − 50x + x2 = x2+25
⇒ −50x =−600 ⇒ x =12
Hence, RQ=12cmand RP=25−12=13cm
Now, find the values of sinP, cosP and tanP.
sin P = RQRP = 1213
cos P = PQRP = 513
tan P = RQPQ = 125
Q16: If tan(A+B) =√3 and tan(A−B) = 1√3; 0°<A + B ≤ 90° ; A>B. Find A and B.
Ans: Given: tan(A+B) =√3 and tan(A−B)= 1/√3.
We know that, tan60° =√3 and tan 30° = 1/√3.
Then,
tan(A+B) = tan60°
⇒ A+B = 60° …… (1)
tan(A−B) = tan30°
⇒ A−B = 30° …… (2)
Adding equation (1) and (2). We get,
A+B+A−B = 60°+30° ⇒ 2A=90° ⇒ A = 45°
∴A = 45°
Put A = 45° in equation (1).
A+B = 60°
⇒ 45°+B = 60° ⇒ B= 60°−45° ⇒ B=15°
∴ B = 15°
Hence, A = 45° and B = 15°.
Q17: If xcosθysinθ = a, xsinθ+ycosθ = b, Prove that x2+y2 = a2+b2.
Ans: Given:
xcosθysinθ = a …… (1)
xsinθ+ycosθ = b …… (2)
Squaring and adding the equation (1) and (2) on both sides.
x2cos2θ+y2sin2θ−2xycosθsinθ+x2sin2θ+y2cos2θ+2xycosθsinθ = a2+b2
⇒ x2(cos2θ+sin2θ)+y2(sin2θ+cos2θ) = a2+b2
⇒ x2+y2 = a2+b2
∴ x2+y2 = a2+b2
Hence proved.
Q18: Prove that sec2θ+cosec2θ Can Never Be Less Than 2.
Ans: Given: sec2θ+cosec2θ
We know that, sec2θ = 1+tan2θ and cosec2θ = 1+cot2θ.
⇒ sec2θ+cosec2θ = 1+tan2θ+1+cot2θ
⇒ sec2θ+cosec2θ = 2+tan2θ+cot2θ
Therefore, sec2θ+cosec2θ can never be less than 2.
Hence proved.
Q19: If sinφ= 1/2, show that 3cosφ−4cos3φ = 0
Ans: Given: sinφ = 1/2
We know that sin30° = 12.
While comparing the angles of sin, we get
⇒ φ = 30°
Substitute φ = 30° to get
3cosφ−4cos3φ = 3cos(30°)−4cos3(30°)
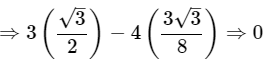
Therefore, 3cosφ−4cos3φ = 0.
Hence proved.
Q20: If 7sin2φ+3cos2φ = 4, then Show that tanφ = 1/√3.
Ans: Given: 7sin2φ+3cos2φ = 4
We know that, sin2φ+cos2φ = 1 and tanθ = 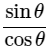
Then, 7sin2φ+3cos2φ = 4(sin2φ+cos2φ)
⇒ 7sin2φ−4sin2φ = 4cos2φ−3cos2φ
⇒ 3sin2φ = cos2φ
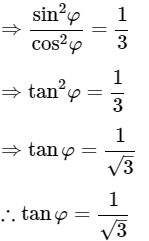
Hence proved.
Q21: If cosφ+sinφ = √2cosφ, Prove that cosφ−sinφ = √2sinφ.
Ans: Given: cosφ+sinφ = √2cosφ
Squaring on both sides, we get
⇒ (cosφ+sinφ)2 = 2cos2φ
⇒ cos2φ+sin2φ+2cosφsinφ = 2cos2φ
⇒ sin2φ = 2cos2φ−cos2φ−2cosφsinφ
⇒ sin2φ = cos2φ−2cosφsin
Add sin2φ on both sides
⇒ 2sin2φ = cos2φ−2cosφsinφ+sin2φ
⇒ 2sin2φ = (cosφ−sinφ)2
∴ cosφ−sinφ = √2 sinφ
Hence proved.
Q22: If tanA+sinA = m and tanA−sinA = n, then Show that m2−n2 = 4√mn.
Ans: Given:
tanA + sinA = m …… (1)
tanA − sinA = n …… (2)
Now to prove m2−n2= 4√mn.
Take left-hand side
Left-hand side:
m² − n² = (tan A + sin A)² − (tan A − sin A)²
⇒ tan²A + sin²A + 2tanA sinA − tan²A − sin²A − 2tanA sinA
⇒ 4tanA sinA
∴ m² − n² = 4tanA sinA .....(3)
Right-hand side:
4√(mn) = 4√((tan A + sin A)(tan A − sin A))
= 4√(tan²A − sin²A)
= 4√(sin²Acos²A − sin²A)
= 4√(sin²A(1cos²A − 1))
= 4sinA√(sec²A − 1)
= 4sinA tanA
Hence, 4√mn = 4tanAsinA
∴ m2−n2 = 4√mn
Hence proved.
Q23: If secA = x + (1/4x), then prove that secA+tanA = 2x or (1/2x).
Ans: Given: secA = x+ (1/4x)
Squaring on both sides.
⇒ sec²A = (x + 14x)²
We know that sec²A = 1 + tan²A
⇒ 1 + tan²A = (x + 14x)²
⇒ tan²A = (x + 14x)² − 1
⇒ tan²A = x² + 116x² + 12 − 1
⇒ tan²A = x² + 116x² − 12 ⇒ (x − 14x)²
Taking square root on both sides,
⇒ tan A = ±(x − 14x)
Now, find sec A + tan A:
If tan A = x − 14x, then
sec A + tan A = x + 14x + x − 14x = 2x
If tan A = −x + 14x, then
sec A + tan A = x + 14x − x + 14x = 12x
Conclusion:
∴ sec A + tan A = 2x or 12x
Hence proved.
Q24: If A, B are Acute Angles and sinA = cosB, then Find the Value of A+B.
Ans: Given: sinA = cosB
We know that sinA = cos(90°−A)
While comparing the values to get
cosB = cos(90°−A)
⇒ B = 90°−A ⇒ A+B = 90°
∴ A+B = 90°.
Q25: Evaluate the Following Questions:
(i) Solve for ϕ, if tan5ϕ = 1.
Ans: Given: tan5ϕ = 1
We know that, tan−1(1) = 45°
5ϕ = tan−1(1) ⇒ 45°
5ϕ = 45°
ϕ = 45°/5 ⇒ 9°
∵ϕ = 9°
(ii) Solve for φ, if sin φ1 + cos φ + 1 + cos φsin φ = 4
Ans:
Given:
sin φ1 + cos φ + 1 + cos φsin φ = 4
⇒ sin² φ + 1 + cos² φ + 2 cos φsin φ (1 + cos φ) = 4
⇒ sin² φ + (1 + cos φ)²sin φ (1 + cos φ) = 4
⇒ 2 + 2 cos φsin φ (1 + cos φ) = 4
⇒ 2(1 + cos φ)sin φ (1 + cos φ) = 4
⇒ 2sin φ = 4
⇒ sin φ = 12
We know that sin 30° = 12
sinφ = sin30° ⇒ φ = 30°
∴ φ = 30°.
Q26: If cos αcos β = m and cos αsin β = n show that (m2+n2)cos2β = n2.
Ans: Given:
cos αcos β = m ...(1) cos αsin β = n ...(2)
Squaring equations (1) and (2), we get:
m2 = cos2 αcos2 β, n2 = cos2 αsin2 β
To prove: (m2 + n2) cos2 β = n2
Take the left-hand side:
(m2 + n2) cos2 β = cos2 αcos2 β + cos2 αsin2 β cos2 β
= cos2 α sin2 β + cos2 α cos2 βcos2 β sin2 β cos2 β
= cos2 αcos2 β sin2 β cos2 β
= cos2 αsin2 β = n2
Conclusion:
∴ (m2 + n2) cos2 β = n2
Hence proved.
Q27: If 7cosecφ−3cotφ = 7, then prove that 7cotφ−3cosecφ = 3.
Ans: Given: 7cosecφ−3cotφ=7
Then prove that, 7cotφ−3cosecφ=3
7cosecφ−3cotφ=7
Squaring on both sides, we get
49cosec2φ+9cot2φ−42cosecφcotφ=49
We know that, cosec2φ=1+cot2φ and cot2φ=cosec2φ−1.
49(cot2φ+1)+9(cosec2φ−1)−42cosecφcotφ=49
49cot2φ+49+9cosec2φ−9−2(3cosecφ⋅7cotφ)=49
(7cotφ−3cosecφ)2 = 49−49+9
(7cotφ−3cosecφ)2 = 9
Take square root on both sides, we get
∴ 7cotφ−3cosecφ = 3
Hence proved.
Q28: Prove that 2(sin6φ+cos6φ) 3(sin4φ+cos4φ)+1 = 0.
Ans: Given: 2(sin6φ+cos6φ) 3(sin4φ+cos4φ)+1=0
Let us take left-hand side,
2(sin6φ+cos6φ) 3(sin4φ+cos4φ)+1=2((sin2φ)3+(cos2φ)3)−3((sin2φ)2+(cos2φ)2)+1
=2[(sin2φ+cos2φ)3−3sin2φcos2φ(sin2φ+cos2φ)]−3[(sin2φ+cos2φ)2−2sin2φcos2φ]+1
=2[1−3sin2φcos2φ]−3[1−2sin2φcos2φ]+1
=2−6sin2φcos2φ−3+6sin2φcos2φ+1
=−1+1
= 0
Therefore, 2(sin6φ+cos6φ) 3(sin4φ+cos4φ)+1 = 0.
Hence proved.
Q29: If tanθ = 5/6 and θ = ϕ = 90°. What is the value of cotϕ.
Ans: Given: tanθ = 5/6 and θ = ϕ = 90°
We know that, tanθ = 1/cotθ.
cotϕ = 1/tanϕ
= 1/(5/6)
= 6/5
∴cotϕ= 6/5.
Q30: What is the Value of tanφ in terms of sinφ ?
Ans: Given: tanφ
We know that tanφ = sinφcosφ and cos²φ + sin²φ = 1
∴ tanφ = sinφ√(1 − sin²φ)
Q31: If secφ+tanφ = 4, Find the Value of sinφ, cosφ.
Ans: Given: secφ+tanφ = 4
1cosφ + sinφcosφ = 4
⇒ 1 + sinφcosφ = 4
1+sinφ = 4cosφ
Squaring on both sides.
(1+sinφ)2 = (4cosφ)2
1+2sinφ+sin2φ = 16cos2φ
1+2sinφ+sin2φ = 16(1−sin2φ)
1+2sinφ+sin2φ = 16−16sin2φ
17sin2φ+2sinφ−15 = 0
17sin2φ+17sinφ−15sinφ−15 = 0
17sinφ(sinφ+1)−15(sinφ+1) = 0
(sinφ+1)(17sinφ−15) = 0
If sinφ+1 = 0
Hence, sinφ = −1 is not possible.
Then, 17sinφ−15 = 0
∴ sinφ = 15/17
Now find cosφ
1 + sinφ = 4cosφ
Substitute the value of sinφ
1 + 1517 = 4cosφ
cosφ = 817
Conclusion:
∴ sinφ = 1517, cosφ = 817
9sec2A−9tan2A =
(1+tanθ+secθ)(1+cotθ−cosecθ) =
(secA+tanA)(1−sinA) =
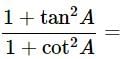
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Express the Trigonometric Ratios sinA, secA and tanA in Terms of cotA.
Ans: Find the value for sinA in terms of cotA
By using identity cosec2A−cot2A = 1
Then,
⇒ cosec2A = 1+cot2A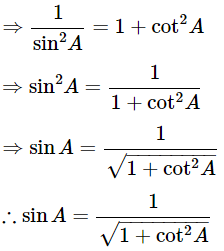
Express the value of secA in terms of cotA
By using identity sec2A−tan2A = 1
Then,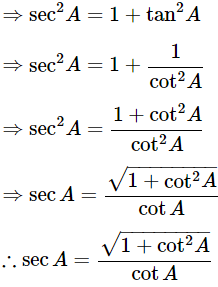
Express the value of tanA in terms of cotA
We know that, tanA = 1/cotA
∴ tanA =1/cotA.
Q2: Write the Other Trigonometric Ratios of A in Terms of secA.
Ans: Express the value of sinA in terms of secA
By using identity, sin2A+cos2A = 1
⇒ sin2A = 1−cos2A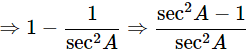
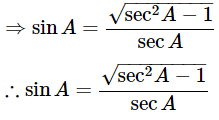
Express the value of cosA in terms of secA
We know that, cosA = 1/secA
∴ cosA = 1/secA
Express the value of tanA in terms of secA
By using identity sec2A−tan2A = 1
Then,
⇒ tan2A = sec2A−1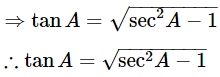
Express the value of cosecA in terms of secA
We know that, cosecA= 1sinA
Then, Substitute the value of sinA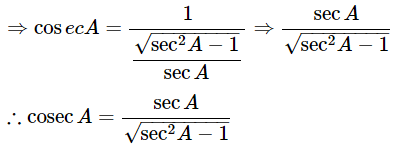
Express the value of cotA in terms of secA
We know that, 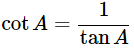
Substitute the value of tanA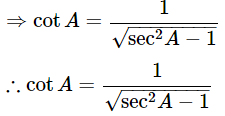
Q3: Prove the Following Identities, Where the Angles Involved are Acute Angles for Which the Expressions are Defined:
(i) (cosecθ−cotθ)2= 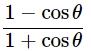
Ans: Given: (cosecθ−cotθ)2= 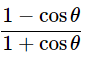
We know that, (a−b)2 = a2+b2−2ab, cosecθ = 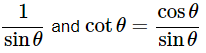
Then, let us take left-hand side
⇒ (cosecθ−cotθ)2 = cosec2θ + cot2θ − 2cosecθcotθ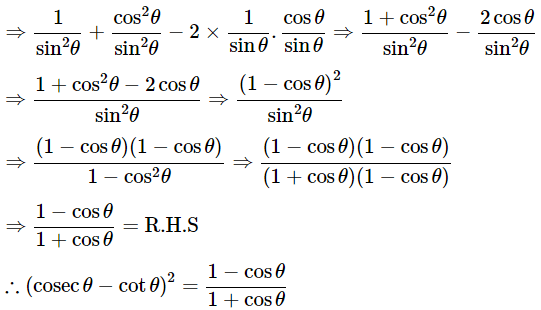
Hence proved.
(ii) 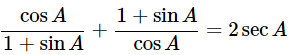
Ans: Given: 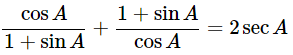
We know that, sin2θ+cos2θ = 1
Then, let us take left-hand side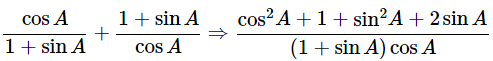
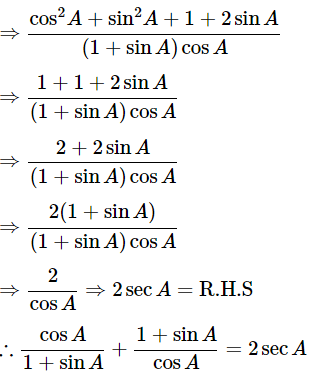
Hence proved.
(iii) 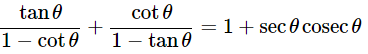
Ans: Given: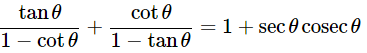
We know that, a3−b3= (a−b)(a2+b2+ab) and sin2θ+cos2θ = 1
Then, let us take L.H.S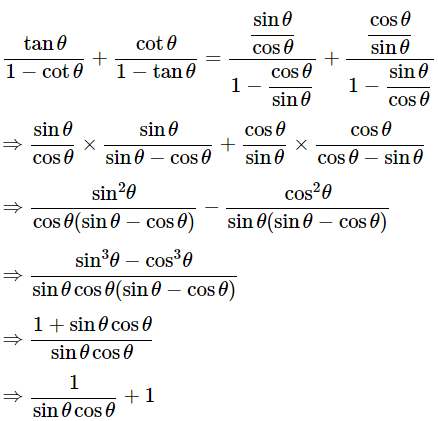
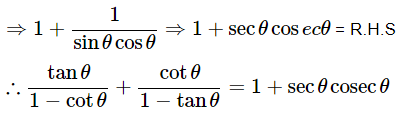
(iv) 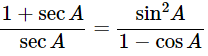
Ans: Given: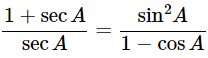
Then, let us take L.H.S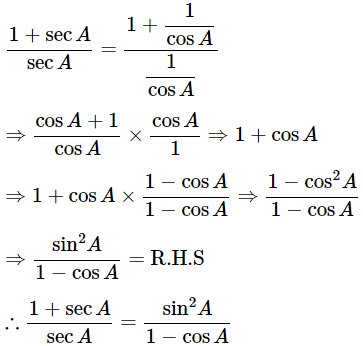
Hence proved.
(v) 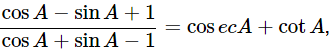 using the identity cosec2A = 1+cot2A
using the identity cosec2A = 1+cot2A
Ans: Given: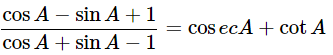
We know that, cosec2A = 1+cot2A
Then, let us take L.H.S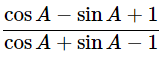
Dividing all terms by sinA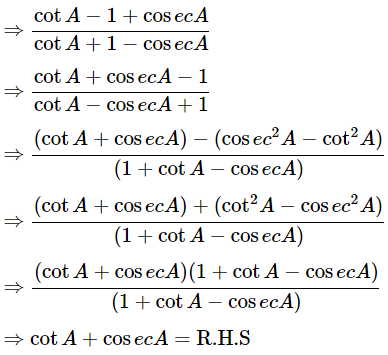
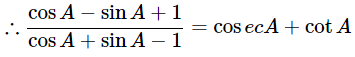
Hence proved.
(vi) 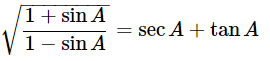
Ans: Given: 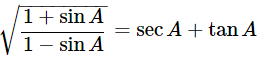
We know that, 1−sin2θ=cos2θ and (a+b)(a−b) = a2−b2
Then, let us take L.H.S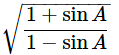
Let us take conjugate of the term. Then,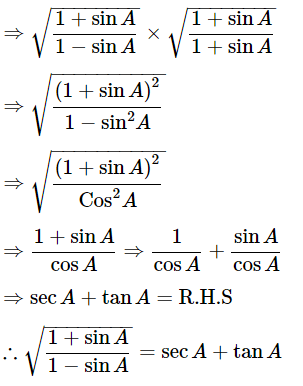
Hence proved.
(vii) 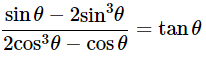
Ans: Given: 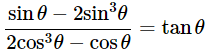
We know that, 1−sin2θ = cos2θ
Then, let us take L.H.S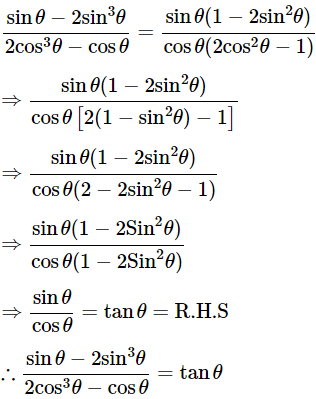
Hence proved.
(viii) (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2 = 7+tan2A+cot2A
Ans: Given: (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2=7+tan2A+cot2A
We know that, cosec2θ =1+cot2θ and sec2θ = 1+tan2θ
Then, let us take L.H.S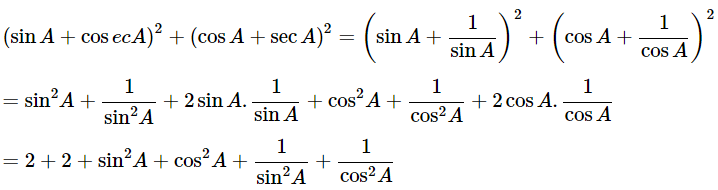
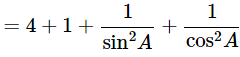
= 5+cosec2A+sec2A
= 5+1+cot2A+1+tan2A
= 7+tan2A+cot2A = R.H.S
∴ (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2=7+tan2A+cot2A
Hence proved.
(ix) (cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA)= 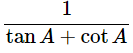
Ans: Given: (cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA) = 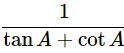
We know that, sin2θ+cos2θ = 1
Then, let us take L.H.S
(cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA) = 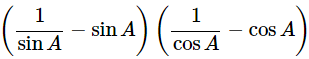
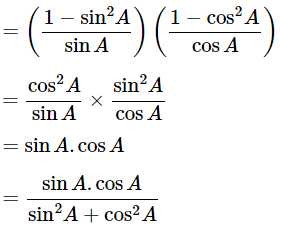
Dividing all the terms by sinA.cosA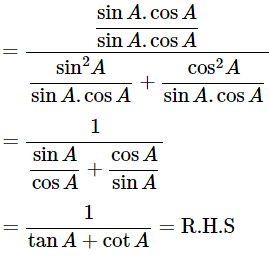
∴ (cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA) = 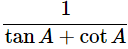
Hence proved.
(x) 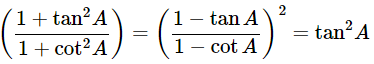
Ans: Given: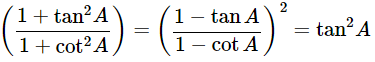
We know that, 1+tan2θ = sec2θ and 1+cot2θ = cosec2A
Then, let us take L.H.S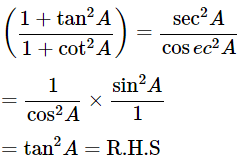
Now, prove the Middle side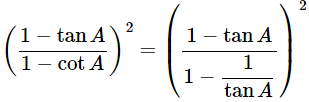
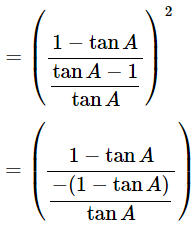
= (−tanA)2
= tan2A = R.H.S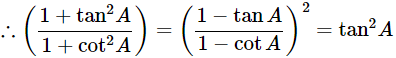
Hence proved.
Q4: Evaluate the Following Equations:
i. sin60°cos30°+sin30°cos60°
Ans: Given: sin60°cos30°+sin30°cos60°
We know that, 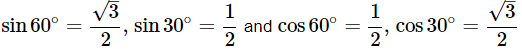
Then, sin60°cos30°+sin30°cos60°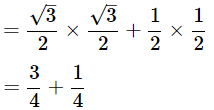
= 4/4 = 1
∴ sin60°cos30°+sin30°cos60° = 1
(ii) 2tan245°+cos230°−sin260°
Ans: Given: 2tan245°+cos230°−sin260°
We know that, tan45° = 1, sin60° = √3/2 and cos30° = √3/2
Then, 2tan245°+cos230°−sin260°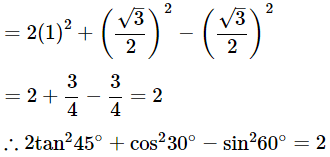
(iii) 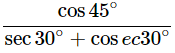
Ans: Given: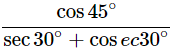
We know that, 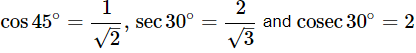
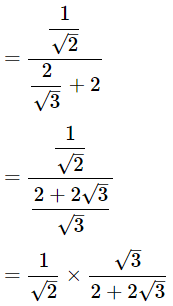
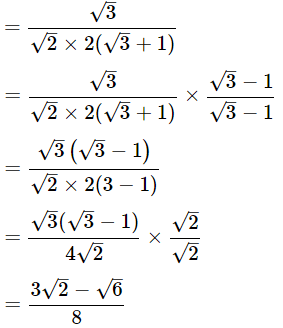
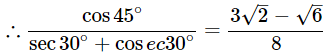
(iv) 
Ans: Given: 
We know that, 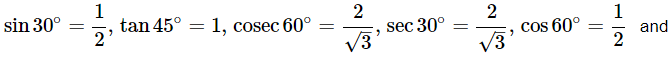
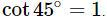
Then, 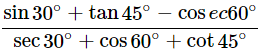
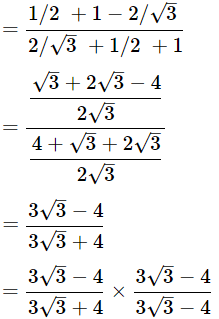
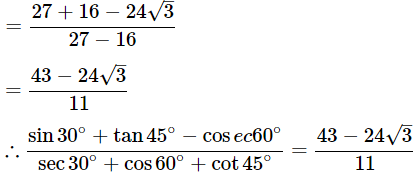
(v) 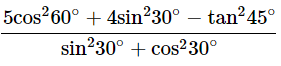
Ans: Given: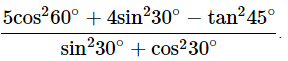 Then,
Then,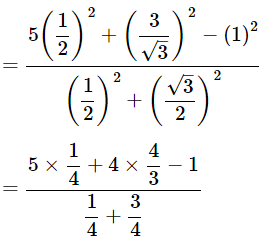
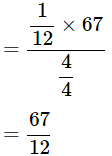
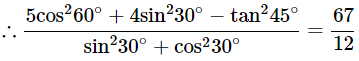
Q5: Prove the Following Identities, Where the Angles Involved are Acute Angles for Which the Expressions are Defined:
(i) (cosecθ−cotθ)2=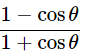
Ans: Given: (cosecθ−cotθ)2=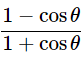
We know that, (a−b)2= a2+b2−2ab, cosecθ = 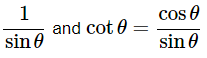
Then, let us take left-hand side
⇒(cosecθ−cotθ)2=cosec2θ+cot2θ−2cosecθcotθ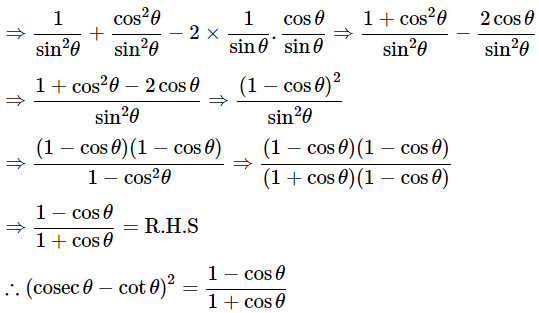
Hence proved.
(ii) 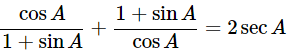
Ans: Given: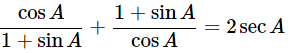
We know that, sin2θ+cos2θ =1
Then, let us take left-hand side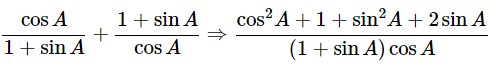
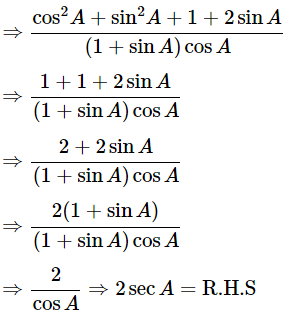
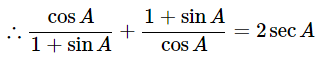
Hence proved.
(iii) 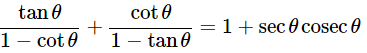
Ans: Given: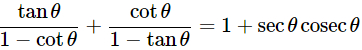
We know that, a3−b3=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab) and sin2θ+cos2θ=1
Then, let us take L.H.S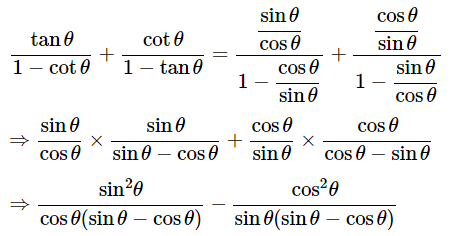
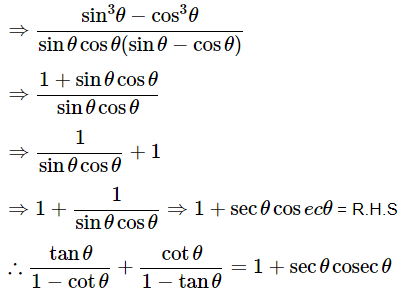
Hence proved.
(iv) 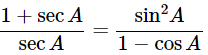
Ans: Given: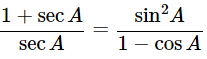
Then, let us take L.H.S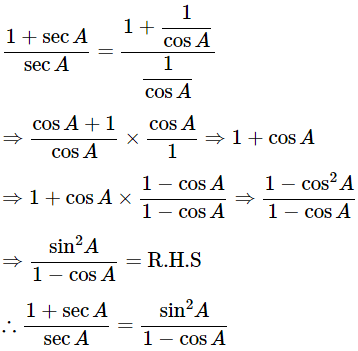
Hence proved.
(v) 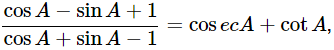 using the identity cosec2A=1+cot2A
using the identity cosec2A=1+cot2A
Ans: Given: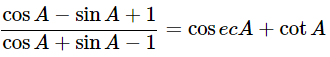
We know that, cosec2A=1+cot2A
Then, let us take L.H.S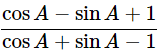
Dividing all terms by sinA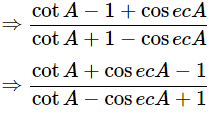
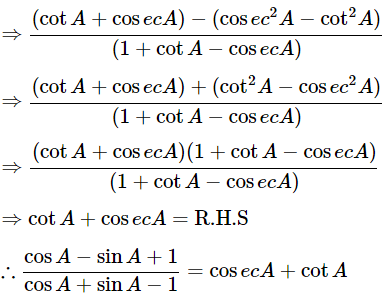
Hence proved.
(vi) 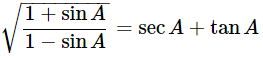
Ans: Given: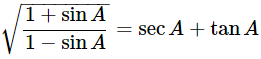
We know that, 1−sin2θ=cos2θ and (a+b)(a−b)=a2−b2
Then, let us take L.H.S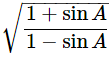
Let us take conjugate of the term. Then,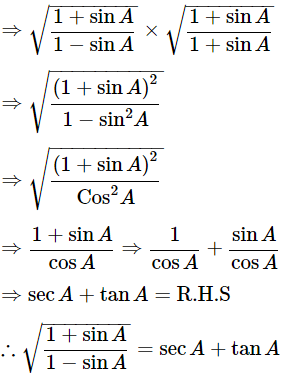
Hence proved.
(vii) 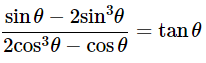
Ans: Given: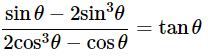
We know that, 1−sin2θ=cos2θ
Then, let us take L.H.S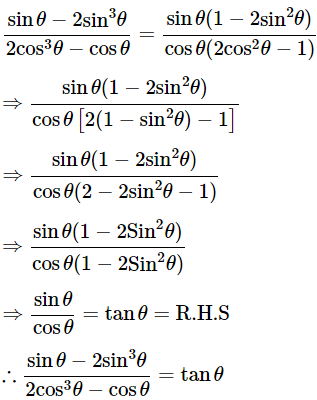
Hence proved.
(viii) (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2=7+tan2A+cot2A
Ans: Given: (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2=7+tan2A+cot2A
We know that, cosec2θ=1+cot2θ and sec2θ=1+tan2θ
Then, let us take L.H.S
(sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2= 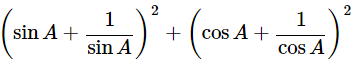
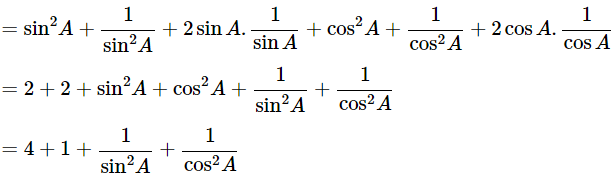
= 5+cosec2A+sec2A
= 5+1+cot2A+1+tan2A
= 7+tan2A+cot2A = R.H.S
∴ (sinA+cosecA)2+(cosA+secA)2=7+tan2A+cot2A
Hence proved.
(ix) (cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA) =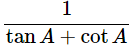
Ans: Given: (cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA)=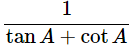
We know that, sin2θ+cos2θ = 1
Then, let us take L.H.S
(cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA)= 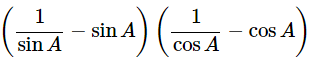
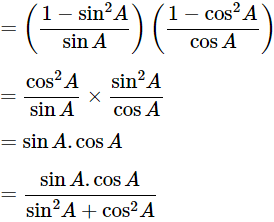
Dividing all the terms by sinA.cosA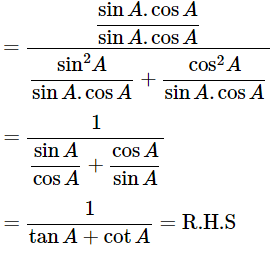
∴(cosecA−sinA)(secA−cosA) = 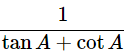
Hence proved.
(x) 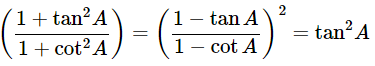
Ans: Given: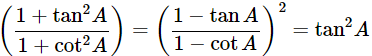
We know that, 1+tan2θ=sec2θ and 1+cot2θ=cosec2A
Then, let us take L.H.S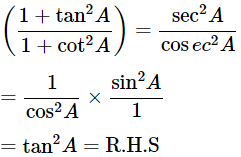
Now, prove the Middle side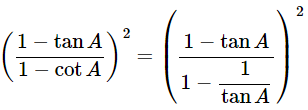
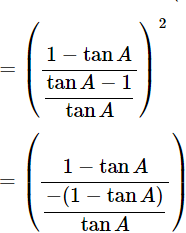
= (−tanA)2
= tan2A = R.H.S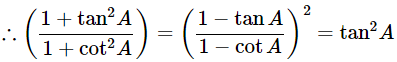
Hence proved.
(i) 9sec2A−9tan2A=
(i) (1+tanθ+secθ)(1+cotθ−cosecθ) =
(secA+tanA)(1−sinA) =
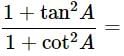
|
127 videos|550 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Important Question Answers - Introduction to Trigonometry
| 1. What are the basic trigonometric ratios? |  |
| 2. How do you remember the trigonometric ratios? |  |
| 3. What are the values of trigonometric ratios for special angles like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°? |  |
| 4. How do you find the height of a triangle using trigonometry? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between the trigonometric functions and the unit circle? |  |









































