Worksheet: Federalism | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Federalism is a system of government that divides power between a central authority and ____________.
Q2: In some federal countries, there is a system of ____________ citizenship.
Q3: Federalism in Nigeria has faced challenges due to ____________ and disputes over oil resources.
Q4: The Indian Constitution divides powers into three lists: the Union List, the State List, and the ____________ List.
Q5: The Governor in India has the power to recommend the dismissal of a ____________ government.
Q6: President's rule in India can be imposed when the State government cannot function according to the provisions of the ____________.
Q7: In Indian federalism, certain States have been granted special provisions due to their unique ____________ and historical backgrounds.
Q8: Jammu and Kashmir's autonomy is granted under ____________ of the Indian Constitution.
Q9: One difference between Jammu and Kashmir and other Indian States is that no ____________ emergency can be declared without the State's concurrence.
Q10: The Constitution makers in India believed that a strong central government was necessary to address issues like ____________, illiteracy, and wealth inequality.
Match the Column
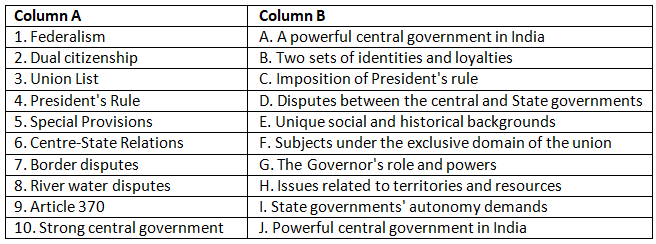
Q1: Match the terms from Column A with their corresponding descriptions in Column B.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Federalism in Nigeria faced challenges due to conflicts among different ethnic groups.
Reason: The Yoruba, Ibo, and Hausa-Fulani groups sought to expand their power into other regions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: The Indian Constitution centralizes economic and financial powers in the hands of the central government.
Reason: This centralization was considered necessary due to India's vast size, diversity, and social issues.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: President's rule can be imposed in a state without the testing of its majority.
Reason: The Constitution grants the central government the authority to dismiss a state government at its discretion.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: Special provisions in the Indian Constitution primarily apply to north-eastern states.
Reason: These states have a sizeable indigenous tribal population with distinct history and culture.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the role of a Governor in Indian federalism?
Q2: Why do border disputes between States often occur in federal systems?
Q3: What is the primary reason for President's rule in India?
Q4: Name one State in India with special provisions and explain the reason behind it.
Q5: What is the significance of the Union List in the Indian Constitution?
Q6: How does dual citizenship work in some federal countries?
Q7: What challenges has federalism in Nigeria faced?
Q8: Explain the importance of culture and ideology in the functioning of federations.
Q9: What is the significance of the Concurrent List in the Indian Constitution?
Q10: How do financial autonomy demands relate to Indian federalism?
 |
Download the notes
Worksheet: Federalism
|
Download as PDF |
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the historical background of federalism in Nigeria and its impact on the country.
Q2: Describe the division of powers between the central government and State governments in Indian federalism.
Q3: Discuss the challenges and conflicts associated with border disputes in Indian federalism.
Q4: Elaborate on the role of special provisions in the Indian Constitution and provide examples.
Q5: Analyze the power and role of Governors in Indian federalism and their impact on State governments.
Q6: What are the reasons behind demands for greater autonomy by State governments in India?
Q7: Discuss the significance of a strong central government in Indian federalism and the reasoning behind it.
Q8: Explain the concept of President's rule in India, its implications, and the controversies surrounding it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the historical background and evolution of federalism in Nigeria. How has this impacted the country's stability?
Q2: Compare and contrast the division of powers and responsibilities between the central government and State governments in Indian federalism. Highlight key differences.
Q3: Examine the issues surrounding border disputes and river water sharing in Indian federalism. How can these conflicts be effectively resolved?
Q4: Explain the concept of special provisions in the Indian Constitution, focusing on the unique status of Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370. Discuss the implications and controversies related to Article 370.
|
43 videos|223 docs|39 tests
|






















