Worksheet: Citizenship | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Citizenship is granted to an individual by __________.
Q2: Full and equal membership in a political community defines __________.
Q3: What are the three types of rights typically included in democratic countries?
Q4: The struggle for securing citizens' rights in European countries, like the French Revolution in 1789, was sometimes __________.
Q5: In South Africa, black Africans waged a prolonged struggle against the ruling white minority for equal citizenship until the __________.
Q6: Freedom of movement is a right granted to __________ in many countries.
Q7: The right to protest is guaranteed under the Constitution as long as it does not cause harm to __________.
Q8: Equal rights and opportunities for all citizens can be challenging because different groups may have varying __________.
Q9: The concept of universal citizenship is supported, but each state sets its own criteria for granting citizenship in their __________.
Q10: Statelessness is a major issue facing the world today, and the United Nations has appointed a High Commissioner for __________.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the concepts on the left with their descriptions on the right.
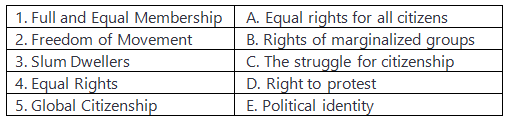
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Citizenship extends beyond the relationship between states and their members.
Reason: Citizenship is only about political identity and rights.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: Full and equal membership in a political community is a fundamental aspect of citizenship.
Reason: Citizenship only applies to democratic countries.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Global citizenship is the same as national citizenship.
Reason: People already feel connected to each other beyond national boundaries.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: In India, the state should not discriminate against citizens on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth, or any of them.
Reason: India defines itself as a secular, democratic nation-state.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the three types of rights typically included in democratic countries?
Q2: Give an example of a violent struggle for equal citizenship.
Q3: What is the significance of freedom of movement for workers?
Q4: How does the Constitution guarantee the right to protest?
Q5: What challenges do governments face regarding tribal people and forest dwellers?
Q6: What is the problem of statelessness?
Q7: Provide an example of India providing refuge to persecuted individuals.
Q8: Why is global citizenship important in the modern world?
Q9: What is the main focus of a democratic state's national identity?
Q10: How does the Indian Constitution protect against discrimination based on religion, race, and caste?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of global citizenship and its significance in today's world.
Q2: Discuss the challenges governments face in providing equal rights and opportunities to all citizens, considering diverse needs.
Q3: Describe the idea of a nation-state and its role in defining national identity.
Q4: Explain the criteria for granting citizenship in India.
Q5: What are some of the struggles and controversies despite inclusive provisions in the Indian Constitution?
Q6: What is the problem of statelessness, and why is it a significant issue globally?
Q7: How has India provided refuge to persecuted individuals, and why is this significant?
Q8: Discuss the importance of global citizenship in addressing issues that transcend national boundaries.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define and elaborate on the concept of universal citizenship, considering the criteria for granting citizenship and the challenges it poses for states.
Q2: Discuss the relationship between citizens and the nation-state, with a focus on how democratic states aim to define their national identity.
Q3: Explain the provisions of the Indian Constitution related to citizenship and how they aim to protect against discrimination.
Q4: Analyze the idea that national citizenship should be complemented with global citizenship, emphasizing the need for collaboration and interconnectedness beyond national borders.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
44 videos|373 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Citizenship - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the importance of citizenship in a democratic society? |  |
| 2. How can one acquire citizenship in a country? |  |
| 3. What are the rights and duties of a citizen? |  |
| 4. What role does citizenship education play in schools? |  |
| 5. How does global citizenship differ from national citizenship? |  |















