Body Movements Chapter Notes | Physical Education for Year 1 PDF Download
Introduction
Animals move for various reasons, such as finding food, water, escaping enemies, or returning to their shelters. Some animals, like corals, sea cucumbers, and sponges, stay in one place but can move their body parts. Additionally, some animals migrate to different places to avoid harsh seasons.
Reasons why animals move
- Find food and water: Animals move to search for food and water to survive.
- Escape from enemies: They move to avoid predators or threats.
- Return to shelters: Animals move back to their homes or safe places.
- Migrating to avoid harsh seasons: Example: Birds in cold regions fly to warmer areas during harsh winters when food is scarce.
Movement

Animals have bodies adapted to their environments to facilitate movement.
- Terrestrial Animals: These animals can walk, run, hop, jump, climb, or crawl, depending on their habitat and body structure.
- Aquatic Animals: These animals are adapted to swim in water.
- Birds: Most birds are capable of flying and walking. Birds like ducks and geese, which spend significant time in water, can also swim, walk, and fly.
Invertebrates and Their Exoskeletons
- Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column (backbone). Examples include earthworms, snails, insects, spiders, crabs, corals, and starfish.
- Some invertebrates, like insects, scorpions, crabs, and starfish, have a hard external skeleton known as an exoskeleton. This exoskeleton provides structure and protection, and the tissues responsible for movement are usually attached to it.
- Soft-bodied invertebrates, such as worms, have fluid-filled body segments or cavities that facilitate movement.
Internal Bony Skeleton of Vertebrates
- Animals like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals have an internal skeleton known as an endoskeleton, which is made of bones.
- Vertebrates are animals that possess a bony skeleton with a vertebral column (backbone).
The Human Skeleton and Its Functions
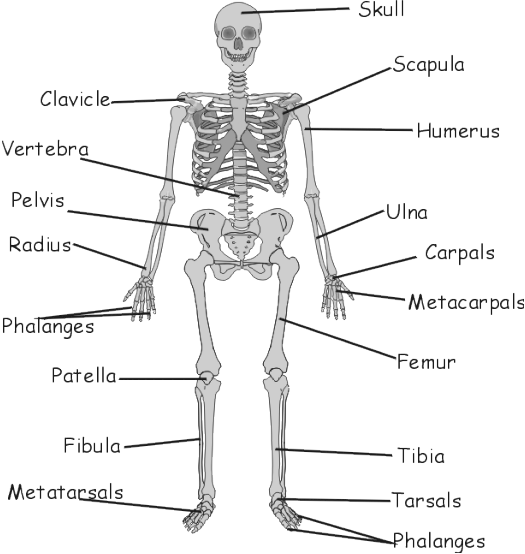
- The human skeleton comprises a framework of 206 bones, along with cartilage and ligament tissues. While bones are hard and rigid, they are also well-supplied with blood vessels and nerves, allowing them to heal quickly when damaged. Teeth are part of the skeletal system but are not classified as bones.
- The skeleton includes both movable and immovable joints. At each joint, two bones meet and are held together by strong, flexible tissues called ligaments. The ends of bones at joints are covered with cartilage, a tough, smooth, and flexible tissue that protects the bones and prevents wear at the joints.
Functions of the Human Skeleton
- Support: It provides the body's supporting structure and maintains its shape.
- Structure: The shape and size of the head and face are determined by the skull.
- Movement: The skeleton, along with its movable joints, facilitates movement.
- Protection: It safeguards vital organs such as the heart, major blood vessels, lungs, and spinal cord.
- Blood Cell Production: Long bones produce red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Parts of the Human Skeleton
The Human Skull:
- Cranium: The bony framework of the head made up of 22 bones. The cranium is formed by 8 flat, hard, and strong bones that fuse together to create immovable joints called sutures. The cranium protects the brain.
- Facial Bones: The lower jaw (mandible) is movable, allowing us to open our mouth, talk, and eat. Other facial bones, including the upper jaw (maxilla), are fixed. The skull also protects the eyes, mouth, nose, and ears.
The Vertebral Column:
- Structure: Made up of 33 bones called vertebrae, extending from the base of the skull to the hips. The last bones are fused.
- Function: Provides primary skeletal support, supports the skull, rib cage, and pelvis, and supports back muscles. The vertebral column protects the spinal cord and supports the head. It is flexible due to cartilage discs between vertebrae.
The Rib Cage:
- Structure: Composed of 12 pairs of curved bones called ribs. The top ten pairs attach to the vertebral column at the back and the sternum in front, while the last two pairs are attached only to the vertebral column.
- Function: Plays a crucial role in respiration by expanding and contracting to allow breathing. It protects the heart, major blood vessels, and lungs and supports muscles in the back.
The Bones of the Arms:
- Structure: Each arm (upper limb) has three long bones and several small bones. The upper arm contains a single long bone, the humerus, while the lower arm has two bones, the radius and ulna.
- Joints: The bones of the upper arm and lower arm join at the elbow. The wrist and hand (including the palm and fingers) have multiple small bones.
These components work together to provide structure, support, protection, and facilitate movement in the human body.
The Pectoral Girdle
- Function: The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, connects the upper limbs to the torso. It includes the clavicles (collarbones) and the scapulae (shoulder blades). The pectoral girdle supports the arms and allows for a wide range of motion.
The Bones of the Legs
- Structure: Each leg (lower limb) is made up of three long bones and several small bones.
- Upper Leg: Contains the femur (thigh bone), which is the single long bone in the upper leg.
- Lower Leg: Includes two bones, the tibia (shinbone) and fibula, which join the femur at the knee.
- Ankle and Feet: Comprise multiple small bones that form the ankle and foot structure.
- Characteristics: The long bones in the arms and legs are hollow and tube-like, which makes them strong enough to support weight and endure pressure, facilitating activities like walking and lifting.
The Pelvic Girdle
- Structure: Formed by the two hip bones (coxal bones) that join with the end portion of the vertebral column. The pelvic girdle forms a basin-like structure.
- Function:
- Support: Bears the weight of the upper body when standing or sitting.
- Protection: Encases the pelvic cavity, which houses and protects the reproductive organs and some excretory organs.
- Movement: The bones of the legs attach to the pelvic girdle at movable joints, allowing for leg movement and flexibility.
These components work together to provide structural support, protect vital organs, and enable movement in the human body.
Joints of the human skeletal system
- When two bones come together, they form what is called a joint.
- The human body has many different types of joints, most of which allow movement.
- These mobile joints are crucial for the body's motion and flexibility.
Movable Joints
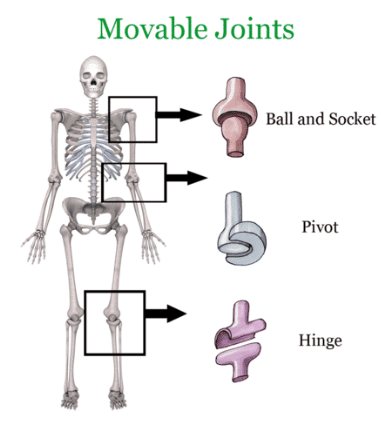
- Movable joints are surrounded by a thick fluid known as synovial fluid.
- This fluid acts like oil, helping to lubricate the joints.
- Cartilage and synovial fluid work together to make the surfaces of bones at joints resistant to wear and tear.
- Effects on Aging:
- Elderly individuals often experience knee issues primarily because of cartilage damage.
- Cartilage repair is slow due to the lack of direct blood supply to this tissue.
Types of Movable Joints
Movable joints in our body enable various movements in different body parts like toes, ankles, knees, hips, neck, shoulders, elbows, wrists, and fingers. These joints come in various types, each facilitating specific kinds of movements. Let's break down and simplify the information about the types of movable joints in the human body.
- Ball-and-socket joint:
- In this type of joint, one bone has a spherical ball-like end that fits into a hollow, cup-like depression in another bone. It allows for movement in multiple directions.
- Example: The hip joints and shoulder joints are ball-and-socket joints, enabling a wide range of motion.
- Hinge joint:
- Similar to a door hinge, this joint permits movement in only one direction.
- Example: Knees and elbows are equipped with hinge joints, allowing bending and straightening movements.
- Pivot joint:
- This joint allows rotation, such as the movement of the neck from side to side and bending forward and backward.
- Example: The joint between the skull and the vertebral column acts as a pivot joint, enabling the movement of the head.
- Gliding joint:
- Found in wrists and ankles, these joints have flat bones that slide against each other, allowing sideways and back-and-forth movements.
- Example: The wrists and ankles possess gliding joints, facilitating smooth movements in different directions.
Movement on Land
- Animals on land use their limbs to lift their bodies from the ground to move around.
- Limbs are essential as they support the animal's weight and help in generating motion.
- Most vertebrates possess a tail that aids in maintaining balance while they are in motion.
- When animals jump, their hindlimbs are pushed backward forcefully, resulting in an upward motion in the forward direction.
- During walking, the limbs are pushed backward to provide a forward thrust, propelling the body forward.
Movement in some animals
Certain animals, such as earthworms, snails, and snakes, do not have limbs. They move by pushing their bodies against the ground to propel themselves forward.
How does an earthworm move?
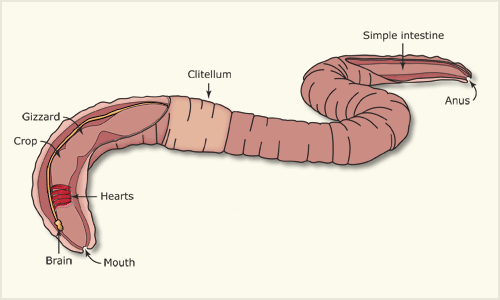
- An earthworm moves using its muscles and tiny, stiff hair-like structures called bristles, located on the lower surface of its body. These bristles can extend and retract to grip the ground.
- By anchoring itself to the moist soil with its bristles, the earthworm stretches its muscles to move forward. Similarly, it can move backward by contracting its muscles. However, this method allows it to cover only a short distance with each movement.
How do snails move?

- A snail carries a shell made of calcium carbonate on its back, which it drags along as it moves using its sticky foot. The snail’s foot muscles contract and expand, allowing it to move forward.
- The snail also produces a slimy mucus from a gland, which hardens when exposed to air, creating a protective layer on the path the snail takes. This hardened mucus enables the snail to move even on rough surfaces, often leaving behind silvery tracks in gardens.
How do snakes move?

- Snakes move by sliding their bodies along the ground. Different types of snakes have unique movement patterns that leave distinct marks on the soil, sometimes allowing identification of the species from these marks.
- The underside of a snake’s body is covered with scales, which help it grip the ground and move forward.
How do birds and bats fly?

- Insects, birds, bats, and flying fish are the only animals that can fly. In birds, the entire body is adapted for flight. Their skeletons are made of lightweight, porous, and hollow bones, reducing their body weight. Birds have a streamlined body shape designed for flying.
- They use wings covered in feathers, which provide a large surface area for flight, and tail feathers to maintain balance. Legs also play a role in flying, as birds with injured legs may struggle to fly. Birds fly by either flapping their wings or gliding. Bats, the only mammals capable of flight, do not have feathers but have hair on their bodies. Their wings are composed of elongated fingers connected by flaps of skin.
How do insects move?

- Insects walk and climb using their three pairs of legs. Most insects also have wings, made of a thin layer of cuticle, which help them fly. The wings and legs are attached to the thorax region with muscles.
- Insects possess a hard external skeleton, known as an exoskeleton, to which the tissues of their legs are connected, enabling them to walk.
How do fish swim?
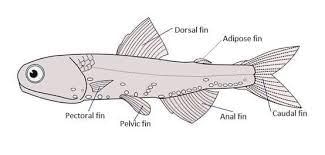
- Water-dwelling animals are adept swimmers, with bodies adapted for swimming. Fish have streamlined bodies that help them move quickly through water. They use fins, supported by cartilage and attached to muscles, to swim.
- By bending their bodies and tails in rapid succession, fish create a zigzag motion that propels them forward. The tail moves side to side, guiding the fish, while the fins help maintain balance and change direction. Ducks' webbed feet, penguins' flipper-like wings, and turtles' large flipper-like front limbs also aid in swimming.
FAQs on Body Movements Chapter Notes - Physical Education for Year 1
| 1. What are invertebrates and how do their exoskeletons help with movement? |  |
| 2. What is the internal bony skeleton of vertebrates and how does it aid in movement? |  |
| 3. What are the functions of the human skeleton? |  |
| 4. How do movable joints aid in movement? |  |
| 5. How do animals move on land? |  |





















