Factors Affecting Crop Production and Crop Distribution | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Factors Affecting crop production
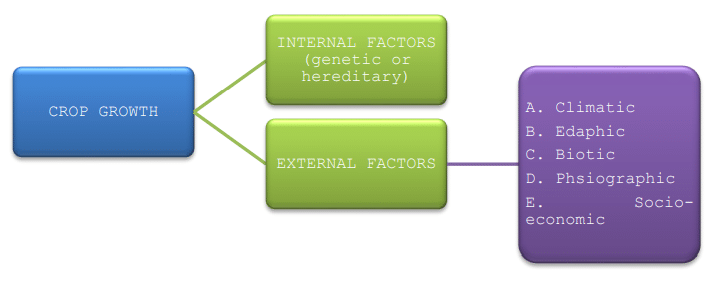
I. Genetic Factors/Internal Factors
Specific traits in crops are determined by the genetic composition of plants and are not influenced by environmental factors. For example:
- High yield capacity
- Early maturation
- Resistance to lodging
- Tolerance to drought, floods, and salinity
- Resistance to insects, pests, and diseases
- Chemical composition of grains (such as oil and protein content)
- Grain quality (fine or coarse)
- Straw quality (sweetness and juiciness)
II. External Factors
Climate factors: Approximately 50% of crop yield is determined by the impact of climatic factors. The following are the meteorological variables that affect crop production.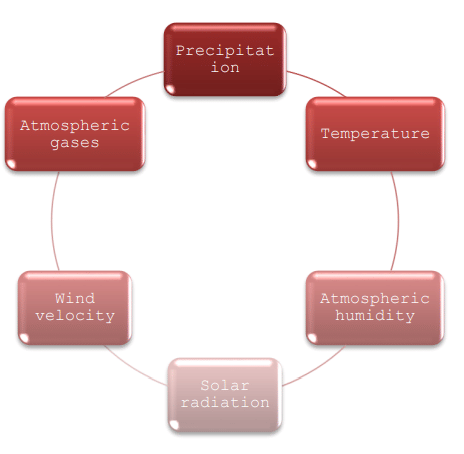
Precipitation:
- The total amount and distribution of precipitation significantly influence the selection of crops suitable for a particular region.
- For example, in regions with heavy and evenly distributed rainfall, crops like rice are cultivated in plains, while tea, coffee, and rubber are grown in the Western Ghats.
- In areas with low and uneven rainfall distribution, dryland farming is practiced, and drought-resistant crops like pearl millet, sorghum, and minor millets are cultivated.
- In desert regions, grasses and shrubs are commonly found.
- The distribution of rainfall holds greater importance than the total amount, as excessive rainfall can adversely impact crop yields.
Temperature:
- Temperature is a measurement of the level of heat energy.
- Most agricultural plants thrive within a temperature range of 15 to 40 degrees Celsius for optimal growth.
- The temperature of a location is primarily determined by its distance from the equator (latitude) and its elevation (altitude).
- Temperature plays a significant role in shaping the distribution of crop plants and vegetation.
- It also has a substantial impact on the germination, growth, and development of crops.
- The minimum, maximum (beyond which crop growth stops), and ideal temperature for a particular plant are known as its cardinal temperatures.
Atmospheric Humidity (Relative Humidity - RH):
- Relative humidity is a measure of the moisture content in the air compared to the air's capacity to hold moisture at a specific temperature.
- When relative humidity reaches 100%, it indicates that the air is saturated with water, leaving no room for soil evaporation or plant transpiration.
- For most crop plants, a relative humidity range of 40-60% is ideal.
- High relative humidity increases the risk of pest and disease outbreaks.
Solar Radiation (Essential for Life):
- Solar radiation affects crops from germination through to harvest and even post-harvest stages.
- All physical processes occurring in the soil, plants, and the environment rely on sunlight.
- Solar radiation governs temperature distribution and, consequently, the distribution of crops in a given region.
- Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR - 0.4 – 0.7μ): This encompasses light with wavelengths between 400-700 nm, which is the part of the light spectrum utilized by plants for photosynthesis. It's essential for carbohydrate production and overall biomass development.
- Photoperiodism: This refers to a plant's response to the length of daylight. It's the biological reaction to changes in the proportion of light and darkness within a 24-hour daily cycle. Based on photoperiodism, plants can be categorized as short-day, long-day, or day-neutral.

- Phototropism: This is how plants respond to the direction of light, as seen in sunflowers.
- Photosensitive: Plants are highly sensitive to light conditions, partly due to signals that activate specific photoreceptors. These light signals regulate plant growth and development by either triggering or inhibiting plant hormones. Varieties that depend on the season are influenced by the amount of light they receive.
Wind Speed:
- Wind primarily serves to transport moisture (precipitation) and heat, and it provides a fresh supply of CO2 for photosynthesis.
- Most crops thrive with wind movement at a speed of 4-6 km/hour.
- Excessive wind speed can be detrimental as it may strip leaves and twigs and harm crops like bananas and sugarcane.
- Natural wind dispersal of pollen and seeds is essential for certain crops.
- Wind can contribute to soil erosion and the spread of pests and diseases.
Atmospheric Gases:
- The composition of Earth's atmosphere includes N2 (78.09%), O2 (20.95%), Argon (0.93%), CO2 (0.03%), and other gases (0.02%).
- CO2 plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, as plants absorb it through the diffusion process from their leaves via stomata.
- CO2 is released back into the atmosphere during the decomposition of organic materials, agricultural waste, and through respiration.
- O2 is essential for the respiration of both plants and animals, with plants releasing it during photosynthesis.
- Nitrogen (N) in the atmosphere is fixed in the soil through processes like lightning, rainfall, and the activity of nitrogen-fixing microbes.
- Some gases like SO2, CO, CH4, and HF, when released into the atmosphere, can be harmful and toxic to plants.
A. Edaphic Factors (soil)
The soil factors that affect crop growth are:
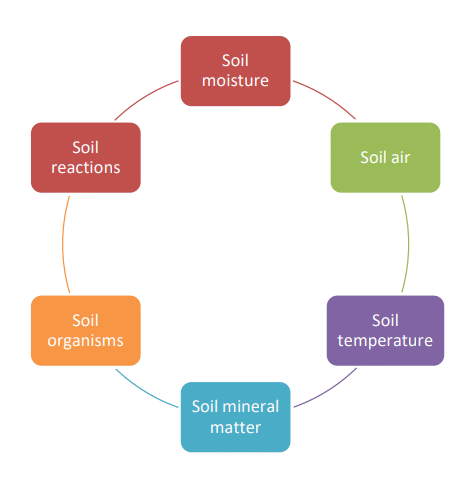
Soil Moisture:
- Plants require water for the process of photosynthesis.
- After being absorbed by the roots, water travels through a plant's stems to reach the chloroplasts in the leaves.
- Water also plays a crucial role in transporting nutrients from the soil into the plant.
- Plants can access moisture within the range between field capacity and permanent wilting point.
- Insufficient water can lead to wilting or drooping, while excess water can cause root rot.
- Clay soil generally retains more available moisture compared to sandy soil.
- Soil moisture is essential for various chemical and biological activities in the soil, including mineralization.
- It also has a significant impact on the soil environment; for instance, it helps moderate soil temperature, preventing extremes.
Soil Air:
- Adequate soil aeration is crucial for root water absorption.
- The presence of oxygen is necessary for germination to occur.
- Oxygen is essential for root and microorganism respiration.
- Soil air plays a vital role in making nutrients in the soil available to plants by converting insoluble minerals into soluble salts.
- It is also necessary for the effective decomposition of organic matter.
- Notably, certain crops like potato, tobacco, cotton, linseed, tea, and legumes have a higher oxygen requirement in the soil air.
- On the other hand, rice can tolerate low oxygen levels and even waterlogged conditions (lack of oxygen).
Note: Potato, tobacco, cotton linseed, tea and legumes need higher O2 in soil air Rice requires low level of O2 and can tolerate water logged (absence of O2) condition.
Soil Temperature:
- Soil temperature has a bearing on the physical and chemical activities taking place in the soil and impacts the speed at which water and nutrients are absorbed.
- It plays a role in the germination of seeds and the growth rate of underground parts of crops such as tapioca and sweet potatoes.
- Soil temperature regulates microbial activity and processes related to nutrient availability.
- Cold soils are generally unfavorable for the rapid growth of most agricultural crops.
Soil Mineral Matter:
- Soil mineral content results from the breakdown of rocks.
- These minerals serve as sources of essential plant nutrients, including calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), and potassium (K), among others.
Soil Organic Matter:
- It serves as a source of all the primary, secondary, and micronutrients required by crops.
- Soil organic matter enhances soil texture, making it more conducive for plant growth.
- It increases the soil's capacity to retain water.
- Organic matter acts as a food source for the majority of microorganisms in the soil.
- During the decomposition of organic matter, organic acids are released, promoting mineralization and thereby releasing previously unavailable plant nutrients.
Soil Organisms:
- Various microorganisms in the soil decompose raw organic matter, making plant nutrients available.
- Soil microbes, through symbiotic (Rhizobium) or non-symbiotic (Azospirillum) associations, fix atmospheric nitrogen and make it accessible to crop plants.
Soil pH (Soil Reaction):
- Soil pH, which is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, has a significant impact on crop growth. A neutral soil with a pH of 7.0 is most suitable for the growth of most crops.
- Soils can be categorized as acidic (pH < 7.0), neutral (pH = 7.0), saline, or alkaline (pH > 7.0).
- Soils with a low pH are detrimental to plants due to the high toxicity of iron (Fe) and aluminum (Al), and low pH can also hinder the availability of other essential plant nutrients.
B. Biotic Factors
- Plants: Interaction between field crops can be both competitive and mutually beneficial.
- Competition among plants arises when there is a limited supply of nutrients, moisture, and sunlight, especially in densely planted conditions.
- When different types of crops like cereals and legumes are grown together, it can lead to mutual benefits and increased yields (synergistic effect).
- There can also be competition between crop plants and parasitic weeds, such as the Striga parasite on sugarcane crops.
- Animals:
- Soil-dwelling creatures like protozoa, nematodes, snails, and insects play a role in decomposing organic matter and use it as a source of sustenance.
- Some insects and nematodes can be harmful to crop yields, causing damage.
- Beneficial organisms like honey bees and wasps aid in cross-pollination, enhancing yields.
- Earthworms that burrow into the soil improve aeration and drainage, as they ingest organic and mineral materials, continuously mixing them in the soil.
- Larger animals, such as cattle and goats, can harm crop plants through grazing activities.
C. Physiographic Factors: Topography refers to the surface characteristics of the Earth, which can be level or sloped. These topographic features indirectly impact crop growth.
- Altitude: As altitude increases, it leads to a drop in temperature and an increase in precipitation and wind velocity. This effect can be observed in both hilly and plain regions.
- Slope Steepness: Steeper slopes result in rainwater runoff and the loss of nutrient-rich topsoil.
- Light and Wind Exposure: Areas with low-intensity light and strong, dry winds, such as coastal regions and interior pockets, can lead to poor crop yields.
D. Socio-Economic Factors:
- Society's inclination toward agriculture and the availability of individuals for farming activities.
- The selection of crops by people to meet the food and fodder needs of their households.
- Human innovation in breeding crop varieties for improved yield or resistance to pests and diseases.
- The economic status of farmers significantly influences their ability to gather resources and inputs. This can vary among marginal, small, medium, and large-scale farmers.
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on Factors Affecting Crop Production and Crop Distribution - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the main factors that affect crop production? |  |
| 2. How does climate affect crop production? |  |
| 3. What role does soil fertility play in crop production? |  |
| 4. How does water availability impact crop production? |  |
| 5. How do pests and diseases affect crop production? |  |
















