UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Agriculture Optional for UPSC > What is a Cell?
What is a Cell? | Agriculture Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cell Definition |

|
| Cell |

|
| Types of Cells |

|
| Cell Structure |

|
Cell Definition
- A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.
- Cells serve as the structural, functional, and biological components of every living organism.
- These cells have the ability to replicate on their own, often referred to as the foundational elements of life.
- Within each cell, there exists a fluid known as cytoplasm, enclosed by a membrane.
- The cytoplasm houses various biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
- Cellular components known as cell organelles are suspended within the cytoplasm.
Cell
- A cell is the fundamental and structural unit of life.
- The field of Cell Biology encompasses the study of cells, delving into their fundamental structure and the functions of each cell organelle.
- It was Robert Hooke, a biologist, who made the initial discovery of cells.
- All living organisms are composed of cells, which can exist as single cells (unicellular) or as collections of many cells (multicellular).
- Mycoplasmas are recognized as the smallest known cells.
- Essentially, cells serve as the foundational components of all living entities.
- They provide the structural framework for organisms and are responsible for converting nutrients from food into energy.
- Cells possess intricate structures, and each component within them serves specific functions within an organism.
- Cells exhibit a variety of shapes and sizes, much like the bricks used in constructing buildings.
- The human body is composed of cells of diverse shapes and sizes.
- Cells represent the most basic level of organization in every life form.
- The number of cells varies from one organism to another, with humans, for instance, having a greater number of cells compared to bacteria.
- Cells are equipped with numerous cell organelles, each having distinct functions that contribute to life processes.
- These organelles exhibit specific structures.
- Additionally, the genetic material of organisms is housed within cells.
Types of Cells
Cells can be likened to factories where different workers and departments collaborate to achieve a common goal.
There are two primary types of cells based on their cellular structure:
Prokaryotic Cells
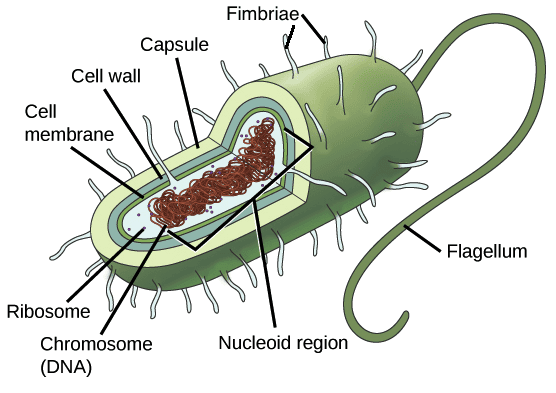
- Prokaryotic cells lack a distinct nucleus. Instead, in some prokaryotes, such as bacteria, the genetic material is freely suspended in a region within the cell known as the nucleoid.
- Prokaryotic cells are typically single-celled microorganisms. Examples include archaea, bacteria, and cyanobacteria.
- The size of prokaryotic cells typically ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 µm in diameter.
- The hereditary material in prokaryotes can be either DNA or RNA.
- Prokaryotes generally reproduce through binary fission, a form of asexual reproduction. They can also engage in conjugation, which is often considered analogous to sexual reproduction in prokaryotes, although it is not strictly sexual reproduction.
Eukaryotic Cells
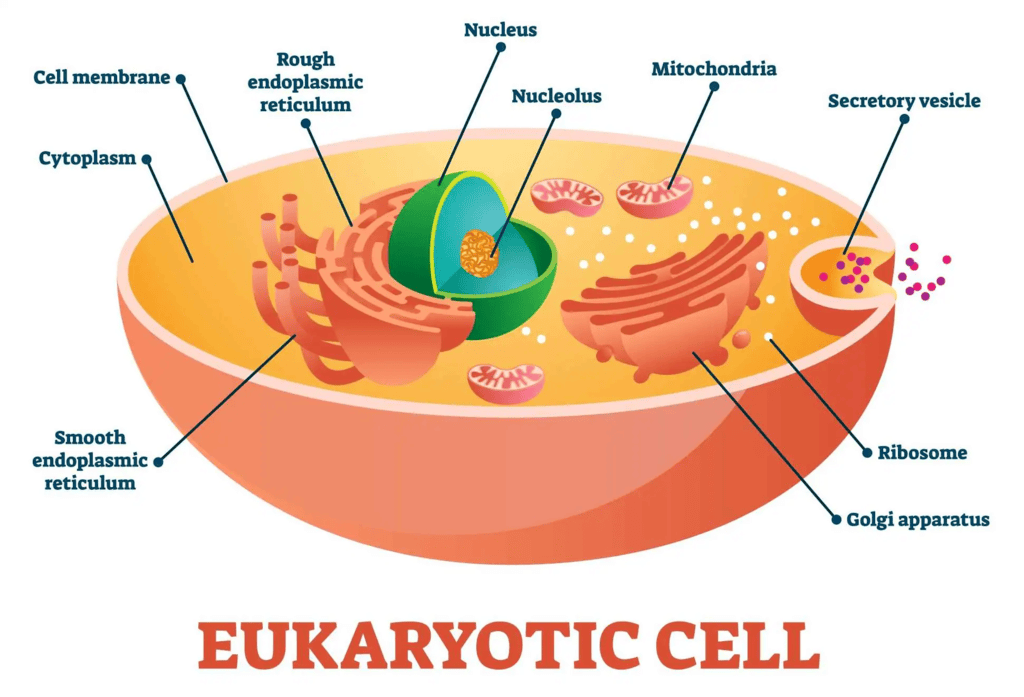
- Eukaryotic cells are characterized by the presence of a true nucleus.
- These cells are larger, with sizes ranging from 10–100 µm in diameter.
- Eukaryotes encompass a wide range of life forms, including plants, fungi, protozoans, and animals.
- The plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells plays a crucial role in regulating the transport of nutrients and electrolytes in and out of the cells. It also facilitates cell-to-cell communication.
- Eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- There are distinctions between plant and animal cells. For instance, plant cells contain chloroplasts, central vacuoles, and other plastids, which animal cells do not possess.
Question for What is a Cell?Try yourself: Which type of cells lack a distinct nucleus?View Solution
Cell Structure
The structure of a cell is composed of distinct components, each with its own unique functions that are crucial for executing life's processes. These components encompass the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various cell organelles. Continue reading to gain a deeper understanding of the structure and functions of cells.
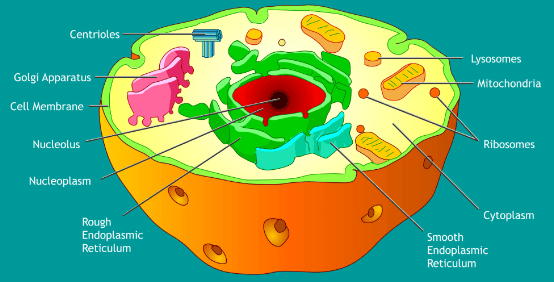
Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane plays a vital role in providing support and protection to the cell.
- The cell membrane is crucial for regulating the passage of substances into and out of the cell.
- The cell membrane is a barrier that separates the cell from its external environment.
- The cell membrane is commonly known as the plasma membrane.
- The cell membrane is a porous membrane containing openings for selective substances.
- The cell membrane protects internal components and prevents leakage of cellular contents.
- The cell membrane acts as a boundary-like structure creating separation between cells and surroundings.
- The cell membrane is crucial for fortifying plant defenses against external factors.
- Plants use an additional defense mechanism in the form of the cell wall to reinforce resilience.
Cell Wall
- The most prominent component of a plant's cell structure is the cell wall.
- It consists of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.
- The cell wall is unique to plant cells and serves the purpose of safeguarding the plasma membrane and other cellular constituents.
- This rigid and inflexible structure forms the outermost layer of plant cells.
- Its primary functions include providing structural integrity and support to the cells, along with protection against mechanical trauma and damage.
Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm is a dense, transparent, gel-like substance located inside the cell membrane.
- Most of the chemical reactions within the cell occur in the cytoplasm.
- Within this cytoplasm, various cell organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, mitochondria, and ribosomes, are suspended.
Nucleus
- The nucleus houses the cell's hereditary material, the DNA.
- It transmits signals to the cells for growth, maturation, division, and apoptosis.
- The nucleus is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, which separates the DNA from the remainder of the cell.
- It serves the critical role of safeguarding the DNA and is an integral component of the plant cell's structure.
Question for What is a Cell?Try yourself: What is the function of the cell membrane in a plant cell?View Solution
The document What is a Cell? | Agriculture Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Agriculture Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
52 videos|224 docs
|
FAQs on What is a Cell? - Agriculture Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the basic definition of a cell? |  |
Ans. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms, capable of carrying out various biochemical processes essential for life.
| 2. What are the different types of cells found in living organisms? |  |
Ans. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, and eukaryotic cells, which have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
| 3. Can you explain the structure of a typical cell? |  |
Ans. A typical cell is composed of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes, as well as genetic material in the form of DNA.
| 4. How do cells function in the human body? |  |
Ans. Cells in the human body perform various functions such as carrying out metabolism, producing energy, synthesizing proteins, maintaining homeostasis, and enabling communication between different cells and tissues.
| 5. What role do cells play in the growth and development of organisms? |  |
Ans. Cells are responsible for the growth and development of organisms by undergoing cell division, differentiation, and specialization to form tissues, organs, and systems necessary for the overall functioning of the organism.
Related Searches




















