Linkage and Cross-Over and their Significance in Recombination Breeding | Agriculture Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Recombination |

|
| Differences between Linkage and Recombination |

|
| Morgan’s Experiment |

|
| Types of Linkages |

|
| Types of Recombination |

|
Introduction
Linkage refers to the strong association of genes or other DNA sequences located on the same chromosome. The proximity of two genes on a chromosome directly influences the probability of their joint inheritance from one generation to the next.
The closer genes are situated on a chromosome, the greater the likelihood that they will be inherited together through multiple generations, spanning from grandparents to parents and offspring. This is due to the fact that when genes are in close proximity, there are fewer instances of recombination occurring between these genes during the process of meiosis.
Recombination
Recombination is the process of breaking apart and then recombining segments of DNA to create novel combinations of alleles. This recombination process is responsible for generating genetic diversity at the level of individual genes and contributes to variations in DNA sequences among different species.
When examining the progeny resulting from a test cross, it's essential to note that the recombination frequency will never exceed 50%. Consequently, in cases where two genes are entirely linked, the likelihood of recombination occurring is almost nonexistent.
Differences and Types
There are two primary types of linkages:
- Complete Linkage
- Complete linkage occurs when genes situated on the same chromosome do not undergo any crossing over during reproduction. As a result, these genes are inherited together across multiple generations. This phenomenon allows for the inheritance of specific combinations of parental traits. While it is relatively rare, complete linkage has been observed in certain species, including male Drosophila and other organisms with different sex chromosomes.
- Incomplete Linkage
- Incomplete linkage, on the other hand, arises from the process of crossing over, where genes located on the same chromosome have a tendency to separate. This separation leads to the creation of recombinant offspring with traits that differ from those of the parents.
- During independent assortment, it's common for the number of recombinant individuals to be lower than expected. In such cases, there is a 25% probability of each of the four types (two parental types and two recombinant types) being selected during independent assortment.
- In situations involving linkage, the two parental types are each represented by a percentage greater than 25%, while the two recombinant types each have a percentage that is less than 25%.
Types of Genetic Recombination
There exist three categories of recombination:
- Homologous Recombination: Homologous recombination occurs when DNA molecules possess similar sequences, as suggested by its name. This process is widespread during meiosis, the cellular division responsible for genetic recombination.
- Nonhomologous Recombination: Nonhomologous recombination, on the other hand, involves interactions between DNA molecules that are not necessarily closely related. While there may be some level of sequence similarity, it is typically not as evident as in homologous recombination.
- Site-specific Recombination: Site-specific recombination is characterized by interactions between specific, very short sequences that are often quite similar to each other.
Differences between Linkage and Recombination
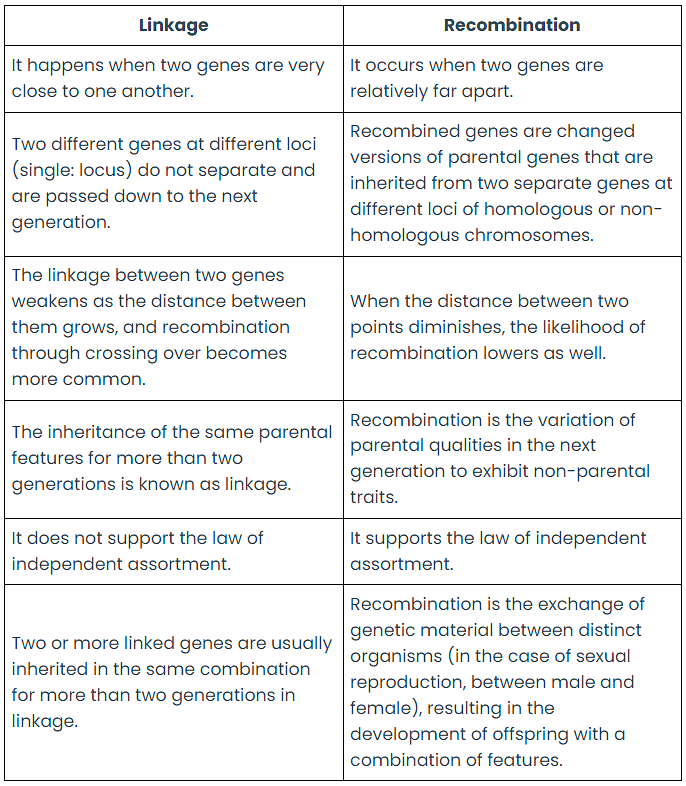
More About Linkage and Recombination
Linkage and recombination play crucial roles in the inheritance of genes and traits. Linkage refers to the situation where two DNA segments are inherited together on the same chromosome for multiple generations. Recombination, on the other hand, is a phenomenon that leads to the creation of offspring with combined traits through the separation of genetic material during the process of crossing over, which occurs during meiosis.
Defining these concepts is just the beginning because linkage and recombination are complex topics in the field of genetic inheritance. To gain a deeper understanding, it's important to explore the distinctions between linkage and crossing over in genetics.
Morgan’s Experiment
- In 1910, Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted an experiment at Columbia University to demonstrate the role of sexual reproduction in producing variations in offspring. His experiment involved breeding fruit flies, specifically Drosophila. During his research, Morgan made a significant observation: among a large population of red-eyed fruit flies, there was a solitary white-eyed male fly. After numerous observations, Morgan concluded that:
- Eye color and sex were determined by the same chromosome, indicating that chromosomes carry the genes responsible for inheriting parental traits in offspring.
- Morgan's groundbreaking experiment was documented in an article titled "Sex Limited Inheritance in Drosophila."
- Fruit flies were chosen as the ideal subjects for Morgan's study for several reasons:
- Easy differentiation between males and females.
- Short lifespan, approximately two weeks.
- High reproductive rate, allowing for the generation of many offspring from a single mating.
- Simple cultivation process.
- Morgan's experiment also revealed that the white eye color trait was exclusive to males because it was located on their X-chromosome. This finding illustrated that the inheritance of traits could vary between sexes. Females did not display white eyes because this trait was present on only one of their X-chromosomes. In essence, Morgan's experiment provided a comprehensive explanation of the concepts of linkage and crossing over.
Types of Linkages
There are two primary types of linkages:
- Complete Linkage: Complete linkage is a type of genetic linkage where two or more traits are inherited together and can be observed in subsequent generations. In this type of linkage, these linked traits are located on the same chromosome.
- Incomplete Linkages: Incomplete linkages result in the formation of some non-parental combinations. These types of linkages occur when linked traits are positioned at a distance from each other on a chromosome. During the process of crossing over, there is occasional exchange or breaking of chromosomal segments between these traits, leading to the creation of non-parental combinations.
Types of Recombination
There are three primary types of recombination:
- Homologous Recombination: Homologous recombination is a type of recombination in which nucleotide sequences are swapped between two identical nucleic acids, whether it's DNA or RNA.
- Non-Homologous Recombination: Non-homologous recombination is a recombination process that occurs when double-strand breaks in the DNA of somatic cells are repaired.
- Site-Specific Recombination: Site-specific recombination is a type of recombination where DNA strands exchange genetic material among segments that share a specific degree of homology.
Recombination of Linked Genes
This is the last topic we'll explore in this discussion. We'll delve into the recombination of linked genes using an example.
Blonde hair and patchy skin characteristics manifest in an individual because these traits are located on the same chromosome. In cases of homologous recombination, these two genes occasionally undergo separation.
The likelihood of inheriting both of these mentioned traits is quite slim during homologous recombination. Consequently, most of these traits are typically inherited together.
|
52 videos|224 docs
|















