UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
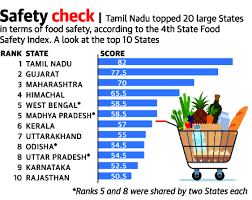
State Food Safety Index (SFSI) 2023
Subject: Social Issues
Why in News?
Four years after the FSSAI published a state-wise index - State Food Safety Index (SFSI), to spur food safety improvement, 19 out of 20 large states recorded a drop in their 2023 scores from 2019.
- After adjusting for a new parameter included in the 2023 index, 15 out of 20 states recorded lower 2023 scores compared to 2019.
What is the State Food Safety Index (SFSI)?
- FSSAI Mandate: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has a primary mandate to ensure public health through food safety.
- State Responsibility: Each state in India has its own apex food safety authority responsible for ensuring food safety.
- Annual Release of SFSI: Annually on World Food Safety Day (7th June), FSSAI publishes the State Food Safety Index (SFSI) for the upcoming financial year.
- Objective of SFSI: The SFSI is a dynamic quantitative and qualitative benchmarking model used to objectively assess food safety in all States and Union Territories (UTs).
- Inaugural Release: The first SFSI was introduced on 7th June 2019 and was based on information provided by the individual States and UTs.
Highlights of the SFSI 2023:
- The steepest fall in scores over five years was seen in Maharashtra, which scored 45 out of 100 in 2023 compared to 74 out of 100 in 2019.
- This is followed by Bihar, which scored 20.5 in 2023 compared to 46 in 2019, and Gujarat, which scored 48.5 in 2023 compared to 73 in 2019.
The SFSI 2023 - Comparing with the 1ST SFSI
Food Testing Infrastructure Parameter: This parameter assesses the presence of sufficient testing facilities and trained personnel in each state to analyze food samples. In 2023, it saw the most significant decline, with its weightage reduced to 17% from 20% in previous years. Maharashtra's score in this category dropped from 17 out of 20 in 2019 to 4 out of 17 in 2023. Gujarat and Kerala were the top performers, both scoring 13.5 out of 17, while Andhra Pradesh performed the worst.
Compliance Parameter: Given the highest weightage of 28% in 2023 (down from 30% in previous years), this parameter evaluates licensing and registration of food businesses, inspections, special initiatives, and campaigns. Jharkhand received the lowest compliance score in 2023, with 4 out of 28, while Punjab and Himachal Pradesh scored the highest with 18 points each.
Consumer Empowerment Parameter: With the second-highest weightage of 19% in 2023 (down from 20% in previous years), this parameter measures a state's involvement in consumer empowerment initiatives by FSSAI, including programs like Food Fortification, Eat Right Campus, and BHOG. Bihar's score in this category decreased from 7 out of 20 in 2019 to 1 out of 19 in 2023. Tamil Nadu led in 2023 with 17 points out of 19, followed by Kerala and Madhya Pradesh with 16 points each.
Human Resources and Institutional Data Parameter: This parameter, with the third-highest weightage of 18% in 2023 (down from 20% in previous years), assesses the availability of human resources, such as Food Safety Officers, Designated Officers, and the presence of adjudication and appellate tribunals in each state. Top performers in 2019, like Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh, received lower scores in 2023, with 10.5 and 9.5 points, respectively.
Training and Capacity Building Parameter: This parameter, with a reduced weightage of 8% in 2023 (down from 10% in previous years), recorded a significant improvement.
Improvement in SFSI Rank Parameter: This parameter, carrying a weightage of 10% in 2023, resulted in 14 out of 20 large states receiving 0 points.
Source: Indian Express
Gwalior, Kozhikode join UNESCO Creative Cities Network
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
Gwalior and Kozhikode from India are among the 55 new cities which have joined the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
- Earlier, Srinagar was designated the creative city in the field of Crafts and Folk Arts.
Inclusion in the UNESCO Creative Cities Network
Inclusion in the UNESCO Creative Cities Network
[A] Gwalior’s Musical Heritage
- Category: Gwalior, located in Madhya Pradesh, is celebrated in the 'Music' category, underscoring its rich musical legacy.
- Cultural Significance: Gwalior, renowned as the birthplace of the Gwalior Gharana and closely associated with iconic musicians like Baiju Bawra and Tansen, is recognized as a prominent destination for learning Indian classical music through the Guru-Shishya Parampara (teacher-disciple tradition).
[B] Kozhikode’s Literary Excellence
- Category: Kozhikode, situated in Kerala, has gained prominence in the 'Literature' category, shining a light on its literary accomplishments.
- Literary Legacy: Kozhikode boasts a significant literary heritage with a remarkable presence of over 500 libraries, making it a hub for literature and knowledge.
About UNESCO Creative Cities Network
| Purpose | To promote cooperation among cities for cultural and creative industries development |
| Initiation | Established by UNESCO in 2004 |
| Seven Categories | Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, Music, and Crafts & Folk Art |
| Member Cities | Over 250 cities from around the world |
| Objectives | Foster innovation, cultural diversity, and sustainable urban development |
| Activities | Collaborative projects, cultural events, and initiatives |
| Selection Process | Cities apply and are designated by UNESCO based on criteria related to creativity |
| Network Coordination | UNESCO provides coordination and support |
| Impact | Enhances cities’ cultural identity, economy, and international visibility |
| Other Indian Cities in UCCN |
|
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
Rafah border crossing between Gaza and Egypt partially opens
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
The Rafah border crossing between the Gaza Strip and Egypt has opened for the first time since the Israel-Hamas war broke out in early October.
- At least seven injured people from Gaza entered Egypt in ambulances for treatment.
What is the Rafah border crossing?
Location: The crossing is the primary entry and exit point for the small Palestinian enclave, connecting it to Egypt. It is under the control of Egypt.
Geographical Placement: This crossing is situated at the southernmost point of exit from Gaza, bordering Egypt's Sinai Peninsula.
Other Crossings in Gaza:
- Erez Crossing: Located in northern Gaza, this crossing is designated for the movement of people into Israel.
- Kerem Shalom Crossing: This is a junction for exclusively handling commercial goods with Israel, located in southern Gaza.
Status of Crossings: As of now, both Erez and Kerem Shalom crossings are closed, limiting movement in and out of the Gaza Strip.
What is the current situation at the crossing?
Diplomatic Agreement: Following weeks of diplomatic negotiations, a Qatar-mediated deal has been reached involving Egypt, Israel, and Hamas.
Rafah Border Crossing: The agreement entails a partial opening of the Rafah border crossing.
Egypt's Role: Egypt will permit the entry of 88 critically injured Palestinians and approximately 500 foreign nationals.
Israel's Involvement: Israel and Egypt have collaboratively established a list of individuals holding foreign passports who are allowed to exit Gaza.
Why is the Rafah border crossing important in the conflict?
- In response to the cross-border infiltration by Hamas fighters on October 7 that killed more than 1,400 Israelis, Israel imposed a total blockade of Gaza.
- The Jewish state shut down Erez and Kerem Shalom until further notice, leaving the Rafah border as the only way into and out of the Strip for people seeking to flee.
- It is also the only crossing point for humanitarian aid.
Why is access across Rafah restricted by Egypt?
- Egypt is worried about safety near its border with Gaza in northeastern Sinai.
- In this region, the country faced an Islamist insurgency that peaked after 2013 and has now largely been suppressed.
- Since Hamas took control in Gaza in 2007, Egypt has helped enforce a blockade of the enclave and heavily restricted the flow of people and goods.
- In 2008, tens of thousands of Palestinians crossed into Sinai after Hamas blasted holes in border fortifications, prompting Egypt to build a stone and cement wall.
- Egypt has acted as a mediator between Israel and Palestinian factions during past conflicts.
- But in those situations, it has also locked down the border, allowing aid to enter and medical evacuees to leave but preventing any large-scale movement of people.
Why are Arab states so reluctant to take in Palestinians?
- Arab countries have deep-rooted fears that Israel’s latest war with Hamas in Gaza could spark a new wave of permanent displacements.
- Egypt, the only Arab state to share a border with Gaza, and Jordan, which flanks the Israeli-occupied West Bank, have both warned against Palestinians being forced off their land.
- For Palestinians, the thought of being forced to leave the land where they hope to establish their own country reminds them of the "Nakba," which means "catastrophe" in Arabic.
- This term refers to the time in 1948 when many Palestinians had to flee or were driven away from their homes during the war that happened when Israel was established.
Source: The Hindu
Isthmus of Kra Land Bridge Project
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Thailand, with its distinctive geography resembling a plume of smoke rising from the sea, is considering a bold and historic project – the creation of an Isthmus of Kra Land Bridge.
- This project aims to revolutionize global trade routes and significantly impact Thailand’s economy.
About the Isthmus of Kra
| Details | |
| Location | Southern Thailand, separating the Malay Peninsula |
| Width | Approximately 44 km |
| Geographic Features | Connects Andaman Sea (west) to South China Sea (east) |
| Strategic Importance | Historical trade route; potential shortcut for maritime trade |
The Land Bridge Project: A Historical Dream
- Centuries-Old Idea: The dream of connecting Thailand’s two coasts across the Isthmus of Kra dates back to King Narai the Great of the Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1677.
- Early Efforts: British and French colonial interests led to surveys and studies in the 19th century to create a maritime channel through the isthmus.
- Modern Proposal: In 2021, Thailand introduced a new proposal, envisioning a land bridge instead of a canal.
Current Vision
- Reducing Shipping Distance: Thai PM envisions a 90-kmland bridge with road and rail networks, connecting deep-sea ports on both coasts.
- Strait of Malacca Alternative: This project could offer a shorter, safer, and cost-effective route, saving approximately 1,200 km and 2 to 3 days of travel compared to the congested Strait of Malacca.
- Economic Benefits: It aims to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and reduce transport time, benefiting Thailand’s economy and its position in Southeast Asia.
Challenges and Considerations
- Financial Hurdles: The estimated cost of the project is around $27.44 billion, posing a significant financial challenge. Thailand may seek investment from China.
- Geopolitical Implications: Closer ties with China could impact Thailand’s relationships with the United States, Japan, and India.
- Viability Concerns: Past China-backed infrastructure projects have faced viability issues, environmental concerns, and potential impacts on marine ecology and tourism.
Conclusion
- Thailand’s proposal to create an Isthmus of Kra Land Bridge reflects its ambition to redefine global trade routes, boost its economy, and strengthen its role in Southeast Asia.
- While financial, geopolitical, and environmental challenges loom large, this project symbolizes Thailand’s determination to shape its future on the world stage.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
NexCAR19: India’s own CAR-T Cell Therapy
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
India has achieved a significant milestone in the field of cancer treatment with the approval of NexCAR19, its first indigenous CAR-T Cell Therapy, by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- Developed by ImmunoACT, an incubated company of IIT Bombay, NexCAR19 is set to transform cancer treatment in India and make it more affordable.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
- Revolutionary Approach: CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying T-cells, a type of white blood cell, into potent cancer-fighting cells.
- Targeting Cancer: These genetically enhanced cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they identify and eliminate cancer cells, particularly effective against blood cancers like leukemia and lymphomas.
- Game-Changer: Unlike chemotherapy or immunotherapy, CAR-T therapy offers the potential for a cure and lifelong benefits, making it a transformative treatment option.
NexCAR19: India’s Indigenously Developed CAR-T Therapy
- NexCAR19 is designed to target cancer cells carrying the CD19 protein, a marker on cancer cells, enhancing precision in treatment.
- India joins a select group of nations with its own CAR-T and gene therapy platform, reducing dependence on imports.
- Initially approved for patients aged 15 and above with B-cell lymphomas who did not respond to standard treatments, leading to relapse or recurrence.
Effectiveness and Unique Features
- Approximately 70% of patients respond to NexCAR19 treatment, with some achieving complete remission.
- Lab and animal studies indicate lower drug-related toxicities, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
- Trials for paediatric patients are underway at Tata Memorial Hospital, ensuring broader applicability.
Availability and Affordability
- ImmunoACT is in the process of securing licenses and partnering with hospitals, including Tata Memorial, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, across multiple cities.
- CAR-T therapy is expected to be available in a matter of weeks to a few months, pending final government approvals.
- Initially priced at Rs 30-40 lakh, ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
- Approval by regulatory agencies like CDSCO should lead to insurance coverage, but the extent may vary, and discussions with insurers and the government are ongoing.
Source: The Hindu
Centre to depute national level monitors to oversee livestock schemes
Subject: Economics

Why in News?
The Centre has decided to deploy National Level Monitors (NLM) to oversee the implementation of its livestock schemes including National Livestock Mission and Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
National Livestock Mission
- National Livestock Mission (NLM) was launched in the fiscal year 2014-15.
- Objective: Its primary goal is to enhance both the quantity and quality of livestock production systems and to provide capacity building for all involved parties.
- Realignment: In 2021-22, the scheme underwent a realignment.
- Entrepreneurial Focus: The core concept of the NLM Scheme is to foster entrepreneurship. This is done with the aim of establishing connections between the unorganized sector and the organized sector for the available produce.
- Aims of the Revised Scheme:
- Job creation
- Promotion of entrepreneurship
- Boosting per-animal productivity, leading to increased production of meat, goat milk, eggs, and wool.
- Implementing Agency: The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying has been overseeing the implementation of the scheme since the financial year 2014-15.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM)
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) has been in operation since December 2014, with a focus on the development and preservation of indigenous bovine breeds.
- Framework: It falls under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development (NPBBD) and is administered by the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- Objectives:
- Improve bovine productivity and sustainable milk production through advanced technologies.
- Promote the use of high-quality bulls for breeding.
- Expand Artificial Insemination coverage by strengthening breeding networks and providing services at farmers' doorsteps.
- Advocate for the scientific and comprehensive rearing and conservation of indigenous cattle and buffalo.
- Significance:
- Vital for augmenting milk production and bovine productivity to meet rising milk demands.
- Aims to make dairy farming more financially rewarding for rural farmers.
- Expected to lead to increased productivity and widespread benefits, particularly for small and marginal farmers across India.
- Notably, this program is expected to be particularly advantageous for women, as they undertake over 70% of the work involved in livestock farming.
Key highlights
- NLMs to oversee the implementation of different livestock schemes
- Apart from the NLM and RGM, the Department of Animal Husbandry also implements the National Programme for Dairy Development and Livestock Health and Disease Control programme.
- These programmes will also be monitored by the NLMs.
- Two types of monitoring by NLMs
- Two types of monitoring will be conducted by NLMs — regular and special.
- The objectives of this monitoring include ascertaining:
- whether the programmes of the Ministry are implemented according to guidelines prescribed by the Ministry; and
- if prescribed implementation processes are being followed.
- This monitoring will also determine:
- villagers’ views on the programmes,
- consider their suggestions for improvement, and
- whether the selection of beneficiaries under a programme has been transparent, unbiased and fair.
- Nature of NLMs
- The NLMs will be third-party independent monitors — individuals and institutions deployed by the government.
- Individual NLMs will be selected from among retired Civil/Defence Services Officers, and academia.
- Significance
- The Centre’s focus on monitoring the implementation of its schemes in the Animal Husbandry and Dairying sector is significant given this sector’s rising contribution to the economy.
- Involving the NLMs will ensure its schemes’ monitoring is unbiased and objective.
Contribution of livestock sector in agriculture
- The contribution of livestock sector in agriculture in terms of output, has increased from 24.32 per cent (2014-2015) to 30.87 per cent (2020-21).
- The Livestock sector has been growing at a compounded annual growth rate of 7.93 per cent (at constant prices) from 2014-15 to 2020-21.
- Value of output of livestock sector is Rs 14.49 lakh crore at current price during 2020-21 (as per National Account Statistics 2022).
- Value of output of milk is more than Rs 9.31 lakh crore which is the highest of the agriculture produce and even more than the combined value of Paddy and Wheat.
Source: The Hindu
Haemoglobin isn’t used only in Blood: Scientists
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
A groundbreaking study published in Nature has unveiled an unexpected revelation: haemoglobin is not exclusive to RBCs.
- Scientists from China have discovered that chondrocytes, the cells responsible for cartilage production, also produce haemoglobin, which appears vital for their survival.
- For decades, textbooks have taught that haemoglobin resides solely in red blood cells (RBCs), responsible for making blood red and transporting oxygen.
About Haemoglobin
| Fact | Description |
| Definition | A protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs. |
| Molecular Structure | Composed of four subunits: two alpha-globin chains and two beta-globin chains. |
| Iron-Binding | Each subunit contains an iron atom that binds to oxygen, forming oxy-hemoglobin. |
| Oxygen Transport | Carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and releases oxygen for cellular respiration. |
| Color | Gives red blood cells their red color when oxygenated and appears bluish when deoxygenated. |
| Carbon Dioxide Transport | Aids in transporting carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions from tissues back to the lungs for exhalation. |
| Hemoglobin Variants | Different types of hemoglobin, with HbA being the most common. Variants can result from genetic mutations. |
| Hemoglobin Levels | Vary by individual and are measured in grams per deciliter (g/dL). Normal levels range from 12 to 18 g/dL. |
| Hemoglobin Disorders | Genetic disorders like sickle cell disease and thalassemia are characterized by abnormal hemoglobin production. |
| Iron Metabolism | Adequate iron levels are essential for hemoglobin synthesis. Iron is a key component of heme in hemoglobin. |
| Fetal Hemoglobin | Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) has a higher oxygen affinity and aids in oxygen transfer from mother to fetus. |
| Hemoglobin Tests | Used for diagnosing anemia, assessing health, and monitoring medical conditions. |
| Oxygen Saturation | Measured as the percentage of hemoglobin molecules bound to oxygen, often using a pulse oximeter. |
New Breakthrough: Haemoglobin Bodies (Hedy)
- Pathologists in China researching bone development, stumbled upon spherical structures resembling RBCs within chondrocytes.
- These structures, termed “haemoglobin bodies” or Hedy, contained haemoglobin and formed large, membraneless blobs, akin to phase separation in oil and water.
Functionality of Hedy
- Essential for Survival: Experiments on genetically modified mice revealed that chondrocytes without haemoglobin experienced cell death, emphasizing Hedy’s vital role.
- Oxygen Transport: Similar to RBCs, haemoglobin in chondrocytes likely serves as an oxygen store and supplier, preventing hypoxic stress (low-oxygen conditions) in cartilage cells.
Haemoglobin’s Broader Implications
- New Research Avenues: The discovery bridges gaps between haematology and skeletal biology, paving the way for further exploration into the relationship between haemoglobin and stem cell fate in growth plates.
- Potential for Joint Disease Insights: Functional haemoglobin in cartilage raises possibilities of its involvement in joint diseases and bone deformities, offering fresh insights into disease mechanisms.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















