Irrigation Projects - 1 | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
In India, the primary utilization of water has historically been for irrigation purposes. Irrigation projects encompass a variety of engineering or hydraulic structures designed to gather, transport, and supply water to agricultural areas. These projects can vary widely in size, ranging from small-scale systems that serve individual farms, which might include a simple diversion weir or an affordable pumping facility along with small channels and minor control features, to extensive projects that cover millions of hectares. Large-scale irrigation projects typically comprise substantial components such as sizeable storage reservoirs, massive dams, extensive networks of canals, branches, and distributaries, as well as various control structures and associated infrastructure (Asawa, 2005).
Irrigation Projects Classification
In the Indian context, irrigation projects are typically categorized in the following ways:
Based on Cultural Command Area (CCA)
- Major Irrigation Projects: These projects are designed to irrigate areas exceeding 10,000 hectares (CCA>10,000 ha). They typically include large storage reservoirs, flow diversion structures, and an extensive network of canals. Major projects often serve multiple purposes, such as flood control and hydroelectric power generation.
- Medium Irrigation Projects: Projects with a CCA of less than 10,000 hectares but more than 2,000 hectares fall into this category. They are also multi-purpose surface water projects and primarily involve medium-sized storage, diversion, and distribution structures.
- Minor Irrigation Projects: These projects cover areas with a CCA of less than or equal to 2,000 hectares. They rely on sources like tanks, small reservoirs, and groundwater pumping. Minor irrigation projects may exist independently within the command area of major or medium irrigation projects.
Major and Medium Irrigation (MMI) projects are further divided into two types based on the irrigation method employed:
- Direct Irrigation Method: This approach involves diverting water directly from a river into canals through the construction of a diversion structure like a weir or barrage across the stream. It is typically used in areas with a consistent and perennial water supply, often in regions with flat terrain, such as deltaic tracts.
- Indirect or Storage Irrigation Method: In this system, water is stored in a reservoir during the monsoon season by constructing a dam across a river. The stored water is then distributed to fields through a network of canals during the dry period. Indirect irrigation is adopted when the river is not perennial, or the flow in the river is insufficient during the lean periods.
Based on the Way of Water Application
Based on the method of water application, irrigation schemes are categorized into two types:
- Gravity/Flow Irrigation Scheme: This irrigation system involves storing water at a higher elevation to allow for the natural flow of water to the land by gravity. These schemes typically include headworks constructed across rivers to store water and a network of canals for distributing the water.
Gravity irrigation schemes can be further divided into:
a. Perennial Irrigation Scheme: This type of scheme ensures a consistent and guaranteed water supply to the command area throughout the entire crop period to meet the irrigation needs of the crops.
b. Non-Perennial Irrigation (Restricted Irrigation) Scheme: Canal water supply is generally accessible during non-monsoon periods from the stored water. - Lift Irrigation Scheme: These irrigation systems involve pumping water to the fields or canal network from lower elevations, as the natural flow of water by gravity is not feasible in this case.
Some of the Major Irrigation Projects
Since gaining independence, India has undertaken the development of numerous significant irrigation projects. A list of some of these major irrigation projects is presented in Table 3.1 and visualized in Figure 3.1.
Table 3.1. Major irrigation projects of India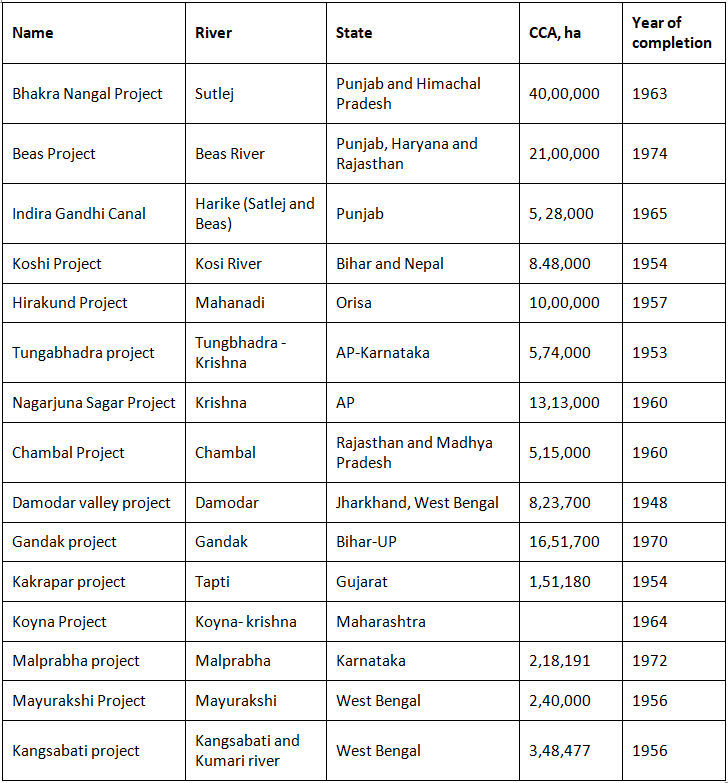
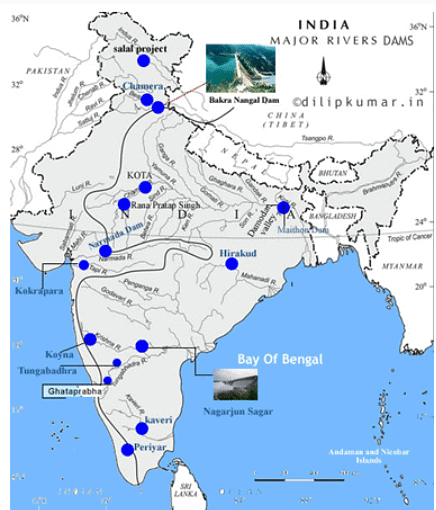 Fig. 3.1. Major Irrigation Projects of India
Fig. 3.1. Major Irrigation Projects of India
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
















