Chromosome Movement | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The chromosome movement during cell division is chiefly due to the spindle apparatus.
This apparatus contains three different types of microtubules:
- Astral microtubules, radiating from centrioles (found in animal cells only);
- Continuous or inter-polar microtubules, passing from one pole to the other, account for the bulk of spindle structure, and
- Chromosomal are kinetochore microtubules which originate from the poles and reattached to the centromere (Fig. 9.9).
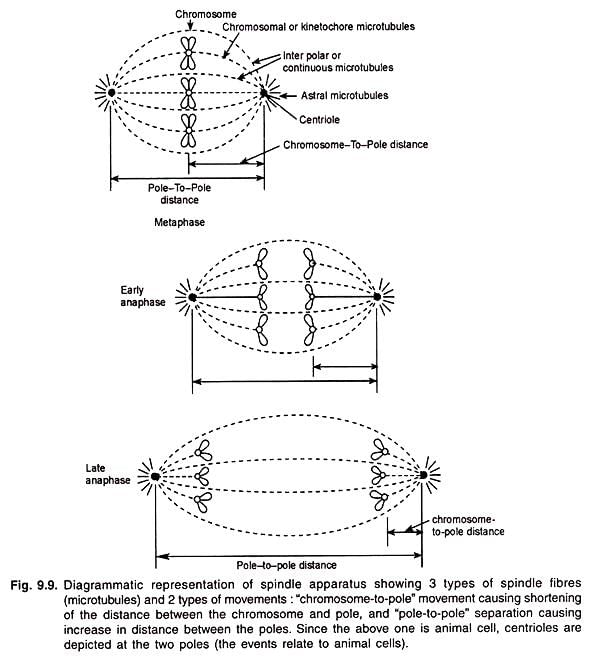
In general, the two sister chromatids of all the chromosomes in a single cell begin to separate at the same time, and move towards the two poles at about the same velocity. The pole- to-pole distances range from 10 pm to 30 pm and the movement of chromosomes is estimated to be at velocities ranging from 0.2 to 5.0 pm per minute. The forge applied per chromosome throughout the anaphase to move it from metaphase plate to the pole has been estimated as 10-8 dynes in the grasshopper spermatocytes (meiosis).
The features of chromosome movement during cell division may be summarised as follows:
- The force for movement of chromosome acts at the kinetochore and directs the chromosome towards the pole.
- The chromosomes move with approximately constant velocities.
- The initial separation of single metaphase chromosome into two anaphase chromosomes is independent of the subsequent anaphase movement.
- The forces act on each chromosome individually and independently of others moving to the same pole.
- The forces act individually on separating chromosomes, but under certain circumstances, the force on one chromosome is not independent of the partner moving to the opposite pole.
- Pairing is not a pre-requisite for coordinated movement to opposite poles during meiosis.
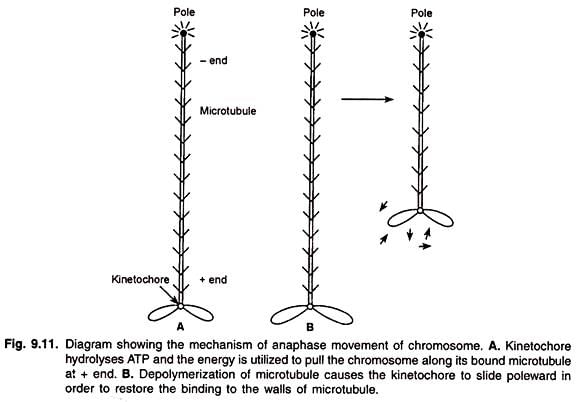
The mechanism for anaphase movement is not clear. There are two models for explanation of the mechanism of chromosome movement.
- Microtubule is attached to the kinetochore at its plus end. Kinetochore consists of microtubule-walking protein that resembles dynein or kinesin. These proteins hydrolyse ATP and the energy is utilized to pull the chromosome along its bound microtubule. The plus end of the microtubule is de-polymerised (Fig. 9.11).
- The de-polymerisation of microtubule (disassembly of microtubule) itself causes the shortening of the microtubules and generates the force to pull the chromosome towards the pole (Fig. 9.11). The addition of tubulin subunits at the polymerizing ends of microtubules elongates the interpoler microtubules.
|
181 videos|351 docs
|
FAQs on Chromosome Movement - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is chromosome movement and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How does chromosome movement occur during cell division? |  |
| 3. What are the factors that regulate chromosome movement? |  |
| 4. Can errors in chromosome movement lead to genetic disorders? |  |
| 5. How is chromosome movement studied in research? |  |





















