Nemathelminthes: Overview | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Characteristics of Phylum Nematoda |

|
| Basic Classification of Nematodes |

|
| Economic Significance of Phylum Nematoda |

|
| Phylum Nematoda Examples |

|
Characteristics of Phylum Nematoda
- Habitat Diversity: Nematodes exhibit a wide range of habitats, including aquatic and terrestrial environments. They can be free-living or parasitic.
- Body Shape: The body of nematodes is elongated, cylindrical, and unsegmented, resembling a worm-like structure.
- Bilateral Symmetry: Nematodes display bilateral symmetry, with a tapered body at both ends.
- Organ-System Grade Organization: They are triploblastic animals with organ-system grade organization, indicating distinct organ systems.
- Unique Body Wall: The body wall of nematodes consists of a thick cuticle, as well as cellular and longitudinal muscle cells arranged in four bands.
- Pseudocoelom: Nematodes lack a true coelom. Instead, they have a pseudocoel or blastocoel, which is not lined by mesoderm and is often filled with parenchyma.
- Nervous System: Nematodes possess a less developed nervous system, including a circumcenter ring and anterior and posterior nerves.
- Absence of Circulatory and Respiratory Systems: Nematodes lack circulatory and respiratory systems, relying on respiration through their body surface. Free-living forms respire aerobically, while parasitic forms use anaerobic respiration.
- Internal Cephalization: Internal cephalization is present, though there is minimal external differentiation between the anterior and posterior regions. Nematodes lack a distinct head but have a mouth in the anterior region.
- Complete Digestive System: Nematodes have a complete digestive system with a mouth and anus. The muscular pharynx and the inner gut lining lack cilia. Extracellular digestion occurs, and the mouth is surrounded by six lips.
- Excretory System: They possess an excretory system devoid of flame cells and nephridia.
- Sense Organs: Sense organs are relatively underdeveloped and consist of papillae, including the amphid (located near the mouth) and plasmid (near the anus).
- Sexual Reproduction: Nematodes exhibit separate sexes (gonochoristic), with males typically smaller than females. Tubular gonads are present, and the male and female genital ducts have separate openings.
- Sperm Characteristics: Sperm cells in nematodes are amoeboid in shape.
- Reproduction and Development: Nematodes do not undergo asexual reproduction, and fertilization can be either internal, cross-fertilization, or self-fertilization. Their development may be direct or involve intermediate hosts, making their life cycle diverse.
Basic Classification of Nematodes
Classification by Presence of Phasmids (Caudal Sensory Organs):
Class 1: Aphasmidia
- Phasmids (caudal sensory organs) are absent.
- Pore-like amphids (anterior sense organs) may be present.
- The excretory system is either absent or poorly developed.
- Well-developed mesenterial tissue.
- Caudal adhesive glands are present.
Class 2: Phasmidia
- Phasmids are present.
- Pore-like amphids are present.
- Well-developed excretory system.
- Less developed mesenterial tissue.
- Absence of caudal adhesive glands.
Further Classification of Aphasmidia (Class 1) into Orders: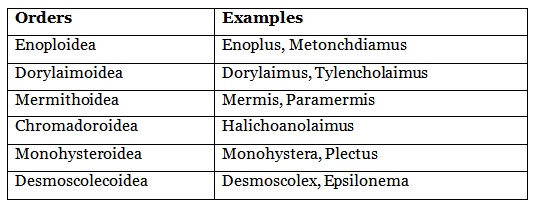
Further Classification of Phasmidia (Class 2) into Orders: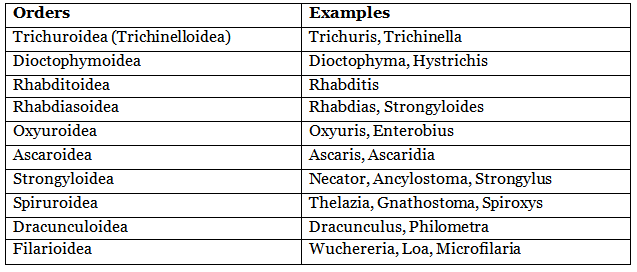
This classification provides a systematic way to categorize nematodes based on the presence or absence of caudal sensory organs (phasmids) and their characteristics within each class.
Economic Significance of Phylum Nematoda
Phylum Nematoda, comprising roundworms, holds significant economic importance in various aspects:
Soil Aeration and Nutrient Distribution:
- Nematodes play a crucial role in aerating the soil and distributing organic materials and minerals. Their activities enhance soil structure and nutrient availability for plant growth.
Crop, Livestock, and Human Health Impact:
- Some nematode species can infest crops, livestock, and humans, leading to various diseases. For instance, hookworms and trichinosis are common diseases caused by parasitic nematodes, resulting in economic losses and healthcare costs.
Contribution to Nutrient Cycling:
- Nematodes are microbivores, feeding on microorganisms such as fungi, protozoans, bacteria, and even other nematodes. Their involvement in nutrient cycling processes is essential as they release nutrients from organic matter, benefiting plant growth.
Natural Pest Control:
- Nematodes can act as biocontrol agents by preying on insects, thereby contributing to natural pest control in agriculture. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides and promotes sustainable farming practices.
Key Players in Ecosystems:
- Nematodes serve as primary producers in their ecosystems, contributing to the decomposition of organic matter. They play a vital role in breaking down complex organic compounds and releasing nutrients back into the environment.
Phylum Nematoda Examples
Some of the examples of the phylum Nematoda are as follows:
1. Ascaris
Classification of Ascaris–
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Nematoda
- Class: Chromadorea
- Order: Ascaridida
- Family: Ascarididae
- Genus: Ascaris
 Ascaris
Ascaris
2. Adenophorea
Classification of Adenophorea–
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Nematoda
- Class: Adenophorea
- Genus: Adenophorea
 Adenophorea
Adenophorea
3. Enoplea
Classification of Enoplea–
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Nematoda
- Class: Enoplea
- Genus: Enoplea
 Enoplea
Enoplea
In summary, Phylum Nematoda has a multifaceted economic impact, ranging from positive effects on soil health and pest control to negative consequences in agriculture, livestock, and human health due to parasitic infections. Understanding and managing nematode populations are essential for maintaining a balanced ecosystem and sustainable economic activities.
|
198 videos|351 docs
|




















