UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Amphibia: Paedomorphosis
Amphibia: Paedomorphosis | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Paedomorphosis |

|
| Evolutionary Terms for Paedomorphosis |

|
| Types of Paedomorphosis in Urodeles |

|
| Significance of Paedomorphosi |

|
Understanding Paedomorphosis
Paedomorphosis, a phenomenon observed in amphibians, refers to the attainment of sexual maturity in an arrested larval stage, also known as pre-adult stage. The term "Paedogenesis" was first introduced by Von Baer in 1866, while "Neoteny" was coined by Kollman in 1882, describing a situation where larvae become sexually mature while retaining some larval features, including gills.
Paedomorphosis and Neoteny: Different Perspectives
- Paedomorphosis Definition: Retention of ancestral juvenile characters in late developmental stages.
- Neoteny: A special case where sexual maturity occurs, but somatic development slows, allowing juvenile features to persist.
Evolutionary Terms for Paedomorphosis
- Proterogenesis: Proposed by H. Schindewolf in 1936, practically synonymous with neoteny.
- Heterochrony: Broader term used by De Beer in 1951, referring to any evolutionary changes in the relative rates of development.
Historical Perspective
- Garstang (1928) introduced the term "paedomorphosis," and in older literature, it's interchangeably known as neoteny.
Occurrence of Paedomorphosis
Paedomorphic animals are found in specific amphibian families, such as Proteidae, Cryptobranchidae, and some Ambystoma species.
Types of Paedomorphosis in Urodeles
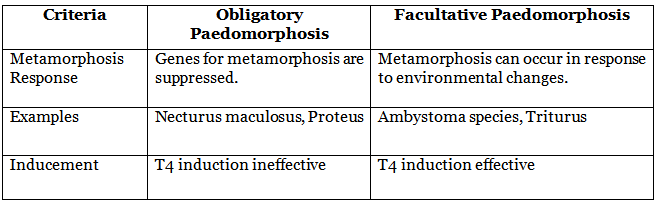
- Obligatory Paedomorphosis: Some urodeles or larval stages always remain permanently mature larval stages due to suppressed genes for metamorphosis. Examples include populations of Cryptobranchus alleganiensis and Necturus maculosus.
- Facultative Paedomorphosis: Axolotl larvae of some urodeles, like Ambystoma species, exhibit facultative paedomorphosis. They can metamorphose into adults when environmental conditions change, induced by the hormone thyroxine (T4).
Comparing Obligatory and Facultative Paedomorphosis
Recognizing Paedomorphic Forms
Paedomorphic urodeles can be identified by the presence of larval characteristics, such as the absence of eyelids, retention of external gills, and a functional lateral line system. Tooth and bone patterns also aid recognition.
Significance of Paedomorphosi
The paedomorphic axolotl provides valuable insights into understanding the role of larval characteristics in controlling or limiting the evolution of adult features. Garstang (1928) proposed that vertebrates originated from tunicate-like larvae, emphasizing the significance of paedomorphosis in evolutionary processes.
In conclusion, paedomorphosis in amphibians encompasses various types, each offering unique insights into evolutionary processes and adaptation strategies.
The document Amphibia: Paedomorphosis | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|351 docs
|
Related Searches















