Gene | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- The genetic blueprint contained in the nucleotide sequence can determine the phenotype of an individual.The hereditary units, which are transmitted from one generation to the next generation are called genes.
- Mendel was the first scientist who proposed genes as particulate units and called them hereditary elements or factors.
Modern Concept of Gene
- A gene can be described as a polynucleotide chain, which is a segment of DNA. It is a functional unit controlling a particular trait such as eye colour.
- Beadle and Tatum concluded by various experiments that gene is a segment of DNA that codes for one enzyme. They proposed one gene-one enzyme hypothesis. But as some genes code for proteins that are not enzymes, the definition of gene was changed to one gene-one protein hypothesis.
Protein Hypothesis
- The concept of gene has undergone further changes as the new facts came to light. Since proteins are polypeptide chains of amino acids translated by mRNA, gene was defined as one gene-one polypeptide relationship.
- Some proteins have two or more different kinds of polypeptide chains, each with a different amino acid sequence. They are products of different genes. Thus, gene is defined as one gene-one polypeptide relationship.
Structural and Regulatory Genes
- Even the one gene-one polypeptide definition is not complete as it does not include gene which codes for rRNA and tRNA. Only mRNA is translated into proteins. Therefore genes which code for polypeptides and RNAs are called structural genes.
- In addition to structural genes, DNA also contains some sequences that have only regulatory function. These regulatory genes constitute signals, which “turn on” and “turn off” the transcription of structural genes and perform various other regulatory functions. In this way the definition of gene includes structural genes as well as regulatory genes.
Molecular Definition of a Gene
- According to Lodish and others, gene is defined as the entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional gene product, which may be polypeptide or any type of RNA. In addition to structural genes (coding genes) it also includes all the control sequences and non-coding introns.
- Most prokaryotic genes transcribe polycistronic mRNA and most eukaryotic genes transcribe monocistronic mRNA.
Number of Genes on a Single Chromosome
- Total number of genes on a single chromosome is different in different organisms.
- Bacteriophage virus R17 consists of only three genes, SV40 consists of 5-10 genes. E. coli bacteria have more than 3000 genes on single 1 mm long chromosome.
Size of a Gene
- In E. coli there are more than four million pairs of nucleotides (4638858 base pairs). It has been estimated that there are about 3000 genes in E. coli.
- The minimum size of a gene that encodes a protein can be directly estimated. Each amino acid of a polypeptide chain is encoded by a sequence of three consecutive nucleotides in a single strand of DNA. Therefore by measuring the size of the polypeptide chain, the size of a gene can be directly measured.
- The average polypeptide chain has about 450 amino acids, which are encoded by 1350 nucleotides. Therefore, in E. coli the number of genes will be around 3000 (4000000/1350=3000). Human genome contains about 30000 genes, (Source: International Human genome sequencing consortium led in the United States by National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) have estimated the number of human protein coding genes to be less than 30000. Simple round worm C. elegans has about 20000 genes).
- A single copy of chromosome is composed of more than 3 billion base pairs. Coding regions of these genes take up only 3% of the genome.
Fine Structure of a Gene
- A gene is present only in one strand of DNA, which is a double stranded helix. A gene consists of several different regions. The main region is the coding sequence which carries information regarding amino acid sequence of polypeptides. The region on the left side of coding sequence (upstream or minus region) and on the right side (downstream or plus region) consists of fairly fixed regulatory sequences.
- Regulatory sequences consist of promoters which are different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Types of Genes
1. Simple Genes:
Simple genes have a coding sequence of bases in one DNA strand. Upstream the coding region, the promoter is present. Downstream, the termination region is present.
2. Split Genes:
- In most of eukaryotes, many non-coding sequences are present between coding sequences. The coding sequences of DNA of the genes are called exons. In between exons are present non-coding sequences called introns. Exons alternate with introns. Normally introns do not possess any genetic information and are not translated. Such genes are called split genes or interrupted genes.
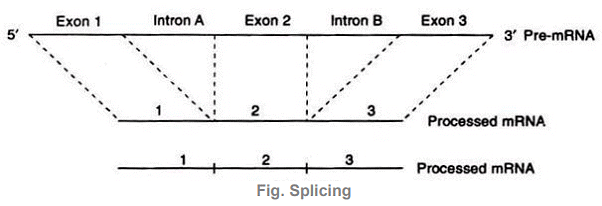
- The mRNA transcribed from this DNA is called precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) and contains exons as well as introns. The introns are removed by excision and discarded. This process is known as splicing. The remaining segments or exons are joined together to form the mature mRNA which takes part in translation. The mature mRNA is much smaller than the pre-mRNA for example α-globin has two introns, ovalbumin has seven introns and α-collagen has 52 introns.
3. Overlapping Genes:
Most genes consist of DNA sequences that code for one protein. But there are some sequences that code for more than one protein. Overlapping genes are common in many viruses. Here the small length of viral DNA is exploited for synthesising different proteins.
4. Jumping Genes or Transposons:
Earlier it was thought that genes are static and have definite and fixed locus. However, recently it has been discovered that segments of DNA can jump to new locations in the same or different chromosome. These mobile genes are called transposable elements or transposons. They can jump within the genome, thus affecting the gene expression. Transposable elements are components of moderately repetitive class of DNA.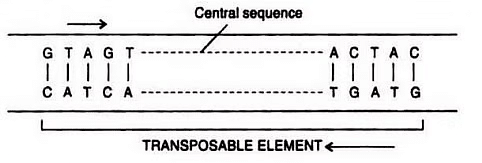
5. Variable Genes:
Certain polypeptides are coded not by one gene but they are coded by more than one gene present on the same or different chromosomes.
Open Reading Frame
- A gene is a segment of genome which is transcribed into RNA. If the RNA is a transcript of a protein coding gene then it is called messenger RNA or mRNA. This is translated into protein. If the RNA is non-coding as ribosomal RNA (rRNA) or transfer RNA (tRNA) it is not translated.
- The part of the protein coding gene which is translated into protein is called open reading frame. It has triplet nucleotide codons. Open reading frame starts with an initiation codon and ends with a termination codon. The region of DNA before a gene is called upstream region denoted with a minus (-) sign while region after the gene is called downstream denoted with a plus (+) sign. Many genes are split between exons and introns. The introns are removed by splicing to produce a functional RNA before translation.
|
181 videos|351 docs
|
FAQs on Gene - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the modern concept of a gene? |  |
| 2. What is the protein hypothesis of gene function? |  |
| 3. What is the molecular definition of a gene? |  |
| 4. How many genes can be found on a single chromosome? |  |
| 5. What is the fine structure of a gene? |  |















