UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 13th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Delhi govt plans ‘cloud seeding’ to induce rains amid pollution
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
The Delhi government had announced that it was considering cloud seeding or ‘artificial rain’ to wash away pollutants in the air.
- The equipment, an aircraft and, more importantly, the seed are already available.
- However, the authorities are waiting for the conditions – at least the presence of clouds – to become favourable to induce rain through cloud seeding.
What is cloud seeding?
- Background
- Water vapour condenses around small particles to form the droplets that make up a cloud.
- These droplets collide and grow; as they get heavy and the cloud gets saturated, it rains.
- Cloud seeding
- Clouds are usually injected with salts like silver iodide, potassium iodide, or sodium chloride, which is the ‘seed’.
- They are dispersed into the cloud either using aircraft or through generators on the ground.
- These salts are expected to provide additional nuclei around which more cloud droplets can form.
- Clouds are usually injected with salts like silver iodide, potassium iodide, or sodium chloride, which is the ‘seed’.
- Significance of the process
- Seeding accelerates cloud microphysical processes.
- Sufficiently large droplets are needed that can reach the surface of the earth and not evaporate on the way.
- Hence, substance that is dispersed into the cloud needs to have cloud condensation nuclei and ice nuclei and these two come from two different salts.
- The cloud condensation nuclei help form cloud droplets, and ice nuclei help to form ice crystals.
- Ice crystals grow faster than drops, and they become large and fall.
- Seeding accelerates cloud microphysical processes.
Conditions required for cloud seeding
- Firstly, cloud cover and clouds of a certain type are necessary.
- Cloud seeding can only happen if there is a sufficient number of clouds and a particular depth to these clouds.
- Inside, there needs to be an adequate number of cloud droplets.
- Cloud seeding is done to increase the radius of the cloud droplets so that they will grow bigger and because of gravity, they will come down as rainfall.
- In winter, clouds form over Delhi when a western disturbance moves over the region.
- Western disturbances are storms that originate in the Caspian or Mediterranean Sea and bring non-monsoonal rainfall to northwest India.
- These disturbances bring rain to northwest India.
- In winter, when the atmosphere is stable, clouds form when a western disturbance disrupts this stability.
- In simpler terms, western disturbances are responsible for winter clouds in Delhi, even though they may not be the right type for cloud seeding.
- Additionally, factors like cloud height and water content need to be considered even if clouds are present.
Previous instances of cloud seeding in India
- During monsoon season
- Seeding has mostly been attempted during the monsoon in India, in places such as Karnataka, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- The fourth phase of the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX-IV)
- CAIPEEX-IV was conducted in drought-prone Solapur in Maharashtra in monsoon seasons of 2018 and 2019.
- It pointed to a relative enhancement of 18 per cent in rainfall.
- Experiments by IIT Kanpur
- IIT Kanpur attempted it in April and May of 2018, which are the pre-monsoon months, on their campus. It said five out of six trials resulted in rain.
Challenges
- The science of cloud microphysics is more intricate than anticipated.
- While there may be some benefits during the monsoon season if there are sufficient clouds, it is important to note that not all seeded clouds result in rain, and natural rainfall can occur without seeding.
- Overall, cloud seeding remains a complex and uncertain area of research.
Is cloud seeding expected to help with pollution levels?
- In India so far, cloud seeding has not been tried with the purpose of reducing pollution, but only been tried to deal with drought-like conditions.
- There are a few cases where China tried weather management options for reducing pollutions. However, Indian conditions are different, and we will need a dedicated study on this.
- As per experts, there should be a significant amount of rain so it washes away pollutants. It will only be temporary, but if at all it is successful, it will break the flow of pollutants.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Ben Gurion Canal Project: Joining Red Sea with Mediterranean
Subject: International Relations
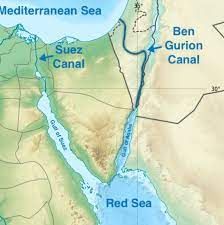
Why in News?
Israel’s aspirations to gain full control over the Gaza Strip and eliminate Hamas may be linked to an ambitious economic opportunity—the creation of the Ben Gurion Canal Project.
Ben Gurion Canal Project
- Vision: Named after Israel’s founding father, David Ben-Gurion, the Ben Gurion Canal Project remains an ambitious infrastructure proposal.
- Route: It envisions cutting a canal through the Negev Desert to connect the Gulf of Aqaba with the Eastern Mediterranean, challenging Egypt’s dominance over the Suez Canal.
- History: A declassified 1963 US government memorandum explored the idea of using nuclear explosives for digging the canal.
- Need: It would offer an alternative route to connect Europe and Asia, bypassing the Suez Canal.
- Transformational Impact: If realized, this project could reshape global trade dynamics by breaking Egypt’s monopoly over the shortest trade route.
Bypassing the Suez
- Historical Significance: The Suez Canal, opened in 1869, revolutionized global maritime trade by reducing travel distances between Europe and Asia.
- Congestion Issues: Despite expansion efforts, the Suez Canal remains congested, causing significant delays and economic losses.
- Political Conflicts: Egypt’s control over the canal has led to conflicts and wars, impacting global geopolitics.
Logistical and Political Challenges
- Complexity and Cost: Building the Ben Gurion Canal is a massive and costly endeavour, potentially exceeding $100 billion.
- Route Length: The proposed canal route is over 100 km longer than the Suez Canal, primarily due to terrain limitations.
- Security Concerns: Constant military threats, such as Hamas rockets or Israeli attacks, would pose a significant challenge to the canal’s operation.
Source: Indian Express
The Indian Institute of Management (Amendment) Act 2023
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
The 3 grounds for dissolution of an IIM Board are expected to be spelt out in the amended Rules (under the revised IIM Act) being finalised now by the Union Ministry of Education (MoE).
What is the IIM (Amendment) Act 2023?
- The Act amends the Indian Institutes of Management Act, 2017.
- The 2017 Act declares Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) as institutes of national importance and regulates their functioning.
- IIMs provide post-graduate education in the field of management and allied areas.
Salient Provisions of the IIM (Amendment) Act 2023:
- Visitor: The Act designates the President of India as Visitor of every Institute covered by the Act.
- Appointment of the IIM Directors:
- Under the 2017 Act, the Director of an IIM is appointed by the Board of Governors, based on the recommendations of a Search-cum-Selection Committee.
- The 2023 Act mandates the Board to obtain the prior approval of the Visitor before appointing an Institute Director.
- The procedure for selecting the Director will be prescribed by the central government.
- Composition of the Search-cum-Selection Committee:
- Under the 2017 Act, the Search Committee comprises the Chairperson of the Board, and 3 members from amongst eminent administrators, industrialists, educationists.
- The 2023 Act reduces these 3 members to 2, and adds another member to be nominated by the Visitor.
- Removal of the IIM Director:
- Under the 2017 Act, the Board may remove the Director from office on grounds such as: (i) insolvency, (ii) mental and physical incapacity, (iii) conflict of interest.
- The 2023 Act adds that the Board will require prior approval of the Visitor before removing a Director.
- It also grants the Visitor the authority to terminate the services of the Director, as may be prescribed.
- Appointment of the Chairperson of the Board of Governors:
- Under the 2017 Act, the Chairperson of the Board of Governors of each Institute is appointed by the Board.
- The 2023 Act amends this to provide that the Chairperson of the Board will be nominated by the Visitor.
- Inquiries against IIMs:
- The 2017 Act empowers the Board to initiate an inquiry against an Institute if it has not been functioning in accordance with the Act. A retired HC judge conducts such inquiries and based on its findings the Board may take action.
- The 2023 Act confers the power of inquiry upon the Visitor. The Visitor may appoint persons to review the work of any Institute and hold inquiries into its affairs.
- Based on the report of such inquiries, the Visitor may issue directions which will be binding on the Institute.
- Dissolution of the Board:
- The 2023 Act provides that the central government may prescribe the conditions and procedure for dissolving or suspending an Institute’s Board.
- If a Board is suspended or dissolved, the central government will constitute an interim board for six months or until a new Board is constituted.
Amended Rules under the Revised IIM Act:
- The grounds under which the Government of India will get to invoke powers to dissolve the board of any IIM are likely to be: i) persistent disobeying of its orders, ii) public interest and iii) inability of the board to perform its duties.
- While the amendment to the IIM Act granted the President the authority to remove the director of an IIM, the Rules are expected to explicitly state that the institute’s Board is obligated to follow the decision of the Visitor in this regard.
- The Rules are also expected to firmly establish the educational qualifications of an IIM Director.
- The amended Rules are also expected to specify that any candidate or applicant for the position of an IIM Director should possess a first-class degree at both the Bachelor’s and Master’s levels, in addition to a Ph.D/ an equivalent qualification.
- Currently, under the unamended Rules, an IIM Director’s academic credentials are described as “a distinguished academic with a PhD or equivalent”.
What Necessitated Changes in the Rules?
- The amendment of the Rules under the IIM Act has been necessitated by recent changes to the law.
- In a surprising move, the MoE had introduced an amendment Bill for the IIM Act during the monsoon session this year, significantly diluting the absolute autonomy granted to the 20 IIMs five years ago in 2018.
- The changes were made to entrust the management accountability of the IIMs with the President, which were vested in the IIM Board earlier.
- The provision on educational qualifications comes in the wake of the IIM Rohtak case, where the incumbent Director had misrepresented his academic credentials during his initial appointment.
How are the Powers of the Board of Governors Curtailed?
- The Board of Governors is the highest decision-making body in an IIM.
- Earlier, only the Board of Governors in an IIM had the powers to audit the functioning of the institute and remove or appoint directors. The Union government had little say in the matter.
- This changed 3 months ago when the MoE amended the IIM Act to assert more authority over the business schools, including giving itself powers to dissolve an IIM Board.
- The changes to the IIM Act clearly stated that henceforth the President (in her capacity as the Visitor of all IIMs) is empowered to dissolve the Board.
- While the Ministry appoints an interim Board in its place, the extent of this power is now being defined under the Rules of the amended IIM Act.
Source: AIR
I&B Ministry introduces draft Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
The Information & Broadcasting Ministry recently unveiled the draft Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023, a transformative legislation designed to modernize and streamline the broadcasting sector in India.
- This bill presents a unified regulatory framework encompassing traditional broadcasting, OTT content, digital news, and current affairs.
Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023
| Description | |
| What is it about? | – Replaces outdated laws, including the 1995 Cable Television Networks (Regulation) Act. – Extends regulatory oversight to emerging broadcasting technologies (OTT, Digital Media, DTH, IPTV). |
| Structure and Definitions | – Comprises six chapters, 48 sections, and three schedules. – Provides clear definitions for modern broadcasting terms and formally defines technical terms. |
| Self-Regulation and Advisory Bodies | – Introduces “Content evaluation committees” for self-regulation within the broadcasting industry. – Establishes the Broadcast Advisory Council to advise the government on program and advertisement code violations. |
| Penalties and Fairness | – Operators and broadcasters may face penalties such as advisory warnings, censure, or monetary fines based on the seriousness of offenses. – Imprisonment and fines are reserved for severe violations and are commensurate with the entity’s financial capacity. |
| Inclusivity for Disabilities | – Promotes broadcasting accessibility for individuals with disabilities through subtitles, audio descriptors, and sign language. – Provides for the appointment of a “Disability Grievance Officer” to address disabled individuals’ concerns. |
| Infrastructure Sharing and Dispute Resolution | – Facilitates infrastructure sharing among broadcasting network operators. – Streamlines the “Right of Way” section, improving efficiency in addressing relocation and alterations. – Establishes a structured dispute resolution mechanism. |
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
500-Years of Aldrovandi’s Herbarium
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Researchers have found a 500-year-old herbarium from Italy, particularly Bologna in the north.
- This collection, meticulously crafted by Italian naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi between 1551 and 1586, offered a window into the past.
Aldrovandi’s Herbarium
- Floristic Changes: The herbarium, containing 5,000 specimens, unveiled a tapestry of historical changes in Italy’s flora over five centuries.
- Human Impact: Clues of human disturbance, habitat loss, transformation, and the invasion of alien species emerged from the pressed and preserved plant specimens.
- Climate Change: The collection allowed insights into the impact of climate change on Italy’s botanical landscape.
- Demographic Trends: European demographic shifts, excluding the European part of the former USSR, were reflected in the herbarium.
- Extinct and Unknown Species: The herbarium hinted at species, both native and alien, that have vanished or remain undiscovered in contemporary times.
Legacy of Transformation
- New World Influence: Aldrovandi’s herbarium holds the memory of Europe’s first encounters with species from the Americas, which later invaded the continent.
- Transforming Flora: It documents the initial signs of a profound transformation in European flora and habitats, paving the way for the introduction of new species and ecological shifts.
Source: The Hindu
Insights into White Holes, Time, and the Universe
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
In a discussion with a theoretical physicist, we explore the intriguing concepts of white holes, the nature of time, and their profound implications for our comprehension of the cosmos.
- We delve into theories, from the transition of black holes to white holes to the fundamental granularity of space-time, providing a glimpse into the forefront of contemporary physics.
White Holes and Their Significance
- Reverse of Black Holes: White holes are essentially the opposite of black holes, with objects entering them behaving like a reversed movie.
- Simplicity in Behavior: White holes exhibit a straightforward behaviour: objects fall in, rebound, and ascend along the same path with reduced velocity.
- Quantum Mechanics Role: Quantum mechanics introduces the concept of a bounce within black holes, resulting in the formation of white holes.
- Altering Space-Time: White holes challenge conventional notions of space-time, suggesting that it undergoes quantum leaps and is not uniform or local.
Universe Emerging from a White Hole
- Analogous to a Bouncing Ball: The transition from a black hole to a white hole shares similarities with a ball bouncing back from the ground, albeit with reduced energy.
- Energy Dissipation: Energy dissipates as heat during this transition, a concept pioneered by Stephen Hawking known as Hawking radiation.
- Black Hole to Big Bang: The theory posits that a universe entering a black hole could bounce and generate an event akin to the Big Bang, potentially leading to the creation of our universe.
Understanding Time
- Relativity of Time: Time does not progress uniformly for all observers; it varies based on factors such as velocity.
- Einstein’s Insight: Albert Einstein introduced the idea that time is not a fixed entity like a clock but rather a flexible concept, akin to a stretchable rubber band.
- The Time Field: Einstein envisioned time as an integral component of a gravitational field, influenced by mass and gravity.
- Granular Space-Time: Combining quantum mechanics and gravity suggests that space-time is granular, consisting of discrete “time-steps,” challenging the notion of continuous space-time.
Source: Indian Express
Loss and Damage Fund
Subject: Indian Economy

Why in News?
In light of the escalating climate crisis, the 'Loss and Damage' (L&D) fund and adaptation have recently come into focus.
What is the Loss and Damage Fund?
- About:
- The 'Loss and Damage' (L&D) fund is a financial mechanism designed to address the irreversible consequences of climate change that cannot be avoided or mitigated through adaptation efforts.
- Adaptation is the proactive response to climate change, the art of survival using which communities and countries make deliberate choices to prepare for and cope with climate-related challenges.
- This fund recognizes and aims to compensate for the real losses incurred by communities, countries, and ecosystems due to the impacts of climate change.
- These losses extend beyond monetary value and cut to the core of human rights, well-being, and environmental sustainability.
- Genesis and Evolution of the L&D Fund:
- Historical Accountability and Inception:
- Over 30 years, there has been a persistent call for affluent nations to acknowledge their role in historic pollution, which has elevated the world’s average surface temperature by more than 1 degree Celsius.
- This historic pollution is currently causing significant damage worldwide, especially in the poorest nations.
- COP 19 (2013):
- The formal agreement at the 19th Conference of the Parties (COP 19) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Warsaw, Poland, in 2013, led to the establishment of the L&D fund.
- This fund was specifically created to provide financial and technical assistance to economically developing nations that were incurring Loss and Damage due to climate change.
- Subsequent Developments and Challenges:
- COP 25:
- Following COP 19, the Santiago Network for L&D was established at COP 25. However, at this point, countries did not commit any funds to support the initiative.
- COP 26:
- 2021 COP26 climate summit in Glasgow, aimed to continue discussions over the next three years regarding the operationalization of the fund.
- COP 27 (November 2022):
- After intense negotiations at COP 27, representatives of the UNFCCC’s member states agreed to set up the L&D fund. Additionally, a Transitional Committee (TC) was established to figure out how the new funding mechanisms under the fund would operate.
- The TC was tasked with preparing recommendations for countries to consider, deliberate on, and potentially adopt by COP 28.
- COP 25:
- Stalemate at TC4 and TC5:
- TC4 Meeting:
- The fourth meeting of the TC4 concluded with no clear consensus on operationalizing the L&D fund.
- The key points of contention included the hosting of the fund at the World Bank, the foundational principle of common but differentiated responsibilities (CBDR), issues related to climate reparations, and the eligibility of all developing nations for the funds.
- TC5 Meeting:
- Recommendations from TC5 have been drafted and forwarded to COP 28.
- TC4 Meeting:
What are the Challenges Regarding the Loss and Damage Fund?
- Developed Nations' Reluctance:
- Developed nations, particularly the US, have remained non-committal about being primary donors to the fund. Their support is voluntary, raising concerns about the commitment to the fund's objectives.
- The unwillingness of wealthy nations to fulfill their intended commitments undermines faith in global climate negotiations and hampers the cooperative spirit necessary to address climate change.
- Uncertainty Surrounding the Fund:
- There is currently no indication of the size of the L&D fund, and any attempt to specify the fund's size was quashed under pressure from the U.K. and Australia.
- The current draft merely urges and invites developed nations to provide money, without a clear commitment or framework.
- Diplomatic Breakdown and Global Consequences:
- Developing nations express discontent, perceiving that their concerns and needs are not adequately addressed by the international community.
- This complicates the path to climate action and raises doubts about addressing other global issues effectively.
- Beyond immediate diplomatic and trust-related repercussions, the watering down of the L&D fund has far-reaching implications. It threatens climate justice and exacerbates the suffering of vulnerable communities in developing nations, who have contributed minimally to global emissions but bear the brunt of climate change.
- Security Implications of Climate-Change-Induced Instability:
- Climate-change-induced instability can have security implications as conflicts and tensions emerge in vulnerable nations.
- These conflicts threaten to spill across borders, creating security challenges.
- Beyond the immediate consequences, the absence of support for vulnerable communities can lead to an increase in humanitarian crises, including food shortages, people displacement, and conflicts.
- This forces communities to cope independently with a worsening climate and its consequences.
Way Forward
- Global Commitment: Urge developed nations to actively contribute as primary donors to the L&D fund, ensuring a strong financial commitment.
- Transparency and Structure: Advocate for transparent discussions to define the fund's size, operational guidelines, and allocation mechanisms, providing clarity and accountability.
- Inclusive Diplomacy: Foster open diplomatic dialogues that address the concerns of developing nations, promoting collaboration for effective climate action and global issue resolution.
- Security Mitigation: Proactively address security implications of climate-induced instability, implementing measures to tackle humanitarian crises and supporting vulnerable communities.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















