UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 14th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Birsa Munda
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
The Prime Minister recently announced he will go to the native village of tribal icon Birsa Munda on his birth anniversary and launch a welfare scheme for the community.
About Birsa Munda:
- He was a folk hero and a tribal freedom fighter hailing from the Munda tribe.
- He spearheaded an Indian tribal mass movement that arose in the Bihar and Jharkhand belts in the early 19th century under British colonisation.
- Munda rallied the tribals to fight against the forceful land grabbing carried out by the British government, which would turn the tribals into bonded labourers and force them to abject poverty.
- He influenced his people to realise the importance of owning their land and asserting their rights over it.
- As a reaction to the introduction of the Zamindari system, or Permanent settlement in tribal areas, Birsa Munda in 1894 declared “Ulgulan”, or revolt, against the British and the Dikus – the outsiders.
- He created a faith called ‘Birsait’.
- Known as 'Dharti Abba' or the Earth Father, Birsa Munda stressed the need for the tribals to study their own religion and not forget their cultural roots.
- Birsa Munda propagated the principles of Hindu religion.
- He died on June 9, 1900, at age 25.
- His struggle against exploitation and discrimination against tribals led to a big hit against the British government in the form of the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act being passed in 1908. The act restricted the passing on of land from the tribal people to non-tribals.
- In recognition of his impact on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was created on his birth anniversary in 2000.
- November 15, the birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, was declared ‘Janjatiya Gaurav Divas by the Central Government in 2021.
Source: The Hindu
Dnieper River
Subject: Geography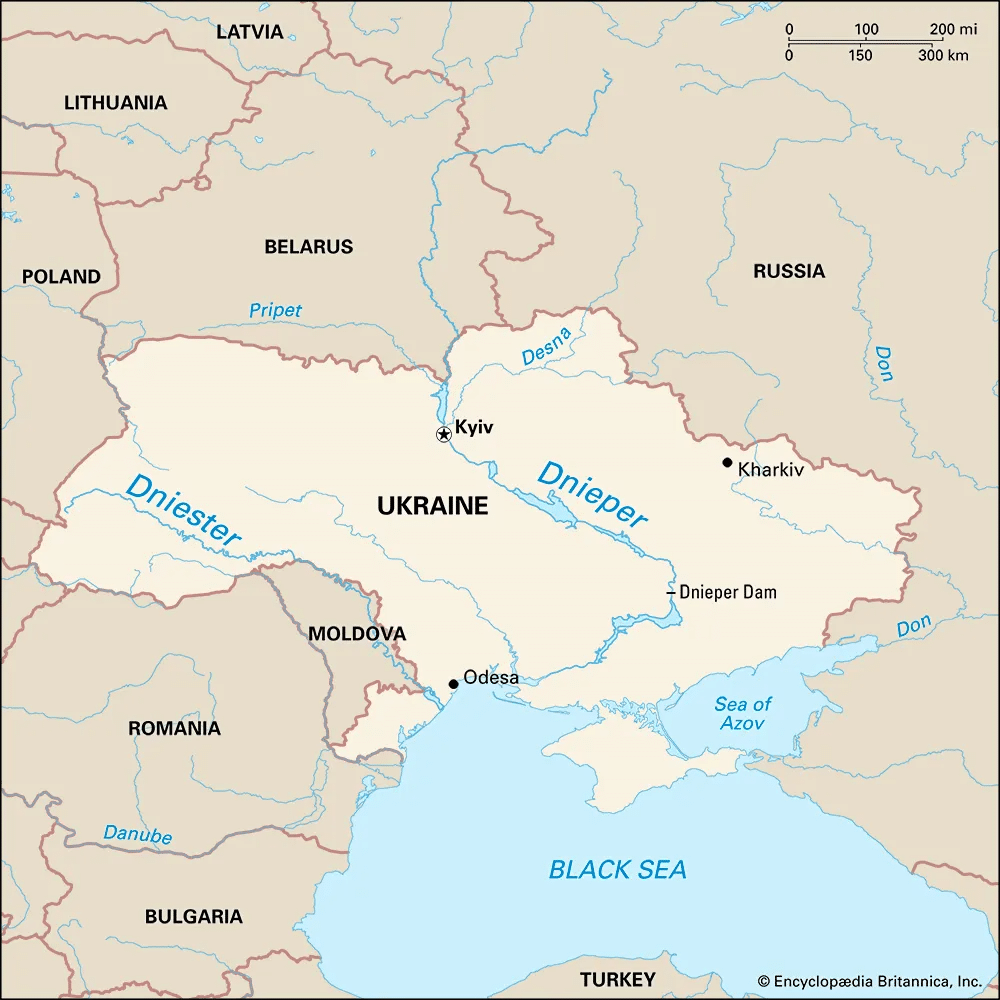
Why in News?
Russia's military recently said that its forces had thwarted a Ukrainian attempt to forge a bridgehead on the eastern bank of the Dnieper River.
About Dnieper River:
- It is the fourth-longest river in Europe (after the Volga, the Danube, and the Ural).
- In Russian, the river’s name is Dnepr. In Ukrainian, it is Dnipro, and in Belarusian, it is Dnyapro.
- Located in Eastern Europe, the Dnieper River and its tributaries drain much of Belarus and Ukraine.
- Historically, the river was an important barrier dividing Ukraine into right and left banks.
- Course:
- It originates in Russia, in the low Valday Hills west of Moscow.
- It runs a total length of 1,368 miles through western Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine before emptying into the Black Sea.
- Approximately 300 miles of the waterway is located in Russia, 430 miles are in Belarus, and 680 miles are within Ukraine.
- It passes through numerous urban centers such as the Russian cities of Smolensk and Dorogobuzh, as well as Mogilev in Belarus and Kiev, Cherkasy, Dnipro, and Zaporizhia in Ukraine.
- Tributaries: It has as many as 32,000 tributaries, including the Sozh, Desna, Trubizh, Bilozerka, Drut, Berezina, and Prypiat Rivers.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Aurora
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Recently, NASA recently shared an incredible picture of an aurora captured from the International Space Station.
Background:-
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on Tuesday shared a remarkably beautiful image of an aurora taken from the International Space Station as it flew above the American state of Utah.
About Aurora:-
- Auroras are a space weather phenomenon that occurs when electrically charged electrons and protons collide with neutral atoms in the upper atmosphere.
- An Aurora is a display of light in the sky predominantly seen in the high-latitude regions (Arctic and Antarctic).
- It is also known as a Polar light.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the phenomenon is called the northern lights (aurora borealis), while in the Southern Hemisphere; it’s called the southern lights (aurora australis).
- Auroras result from emissions of photons in the Earth’s upper atmosphere (above 80 km), from ionized nitrogen atoms regaining an electron, and from electrons from oxygen and nitrogen atoms returning from an excited state to the ground state.
- The solar wind coming from the sun is the origin of the charged protons and electrons that excite oxygen and nitrogen and cause auroras.
- The aurora’s colour depends on the type of atom that is excited and how its electrons return from those excited states to the ground state.
- High-energy electrons cause oxygen to emit green light (the most familiar colour of the aurora), while low-energy electrons cause red light.
- Nitrogen generally gives off a blue light.
- The blending of these colours can also lead to purples, pinks, and whites.
- The oxygen and nitrogen also emit ultraviolet light, which can be detected by special cameras on satellites.
- Auroras are not just something that happens on Earth.
- If a planet has an atmosphere and magnetic field, they probably have auroras.
- Discrete Auroras on Mars: Unlike auroras on Earth, which are seen only near the north and south poles, Discrete Auroras (DA) on Mars are seen all around the planet at night time.
- Auroras have been observed on Saturn and Jupiter.
Source: Indian Express
India’s 2+2 Ministerial Dialogues: Partnerships and Objectives
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Indian Defence Minister and External Affairs Minister recently hosted their US counterparts for the fifth annual 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue in New Delhi.
Understanding 2+2 Dialogues
- Purpose: 2+2 dialogues involve the participation of high-level representatives, typically the Ministers of Foreign Affairs and Defence, from two nations. This format aims to expand the scope of dialogue and collaboration between these countries.
- Rationale: Such dialogues enable comprehensive discussions on strategic concerns, mutual sensitivities, and political factors. They facilitate a deeper understanding of each other’s geopolitical perspectives and contribute to the development of stronger, more integrated strategic relationships in an ever-changing global environment.
India’s 2+2 Partners
- United States: The United States is India’s foremost and oldest partner in the 2+2 format. The inaugural 2+2 dialogue took place in September 2018 during the Trump Administration.
- Australia: India engages in 2+2 meetings with Australia, further enhancing bilateral security and defence cooperation.
- Japan: The 2+2 talks with Japan commenced in 2019, with the objective of bolstering strategic depth in security and defence cooperation.
- United Kingdom: In October 2023, India initiated its first 2+2 dialogue with the United Kingdom, signifying the growing importance of this partnership.
- Russia: India and Russia also engage in 2+2 dialogues, fostering a mutually beneficial understanding on various regional and international issues.
Significance of 2+2 Dialogues
- Defence and Strategic Agreements: These dialogues have led to significant bilateral agreements and partnerships. India and the United States, for instance, have signed Troika Pacts like:
- Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA)
- Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA)
- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA) for deep military cooperation.
- Addressing Regional Concerns: In the face of common regional concerns, such as China’s increasing assertiveness, 2+2 dialogues have become vital mechanisms for India and its partners to align their strategic interests. This includes cooperation within the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) forum with Japan, Australia, and the United States.
- Expanding Traditional Alliances: India also values its 2+2 dialogues with Russia, acknowledging shared worldviews and goals in promoting a multipolar world order.
Conclusion
- India’s participation in 2+2 Ministerial Dialogues with key global partners underscores its commitment to fostering robust and multifaceted strategic relationships.
- These dialogues are pivotal in addressing regional and global challenges, strengthening military cooperation, and promoting shared interests in a dynamic world order.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Paintbrush swift butterfly
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Recently, a Paintbrush swift butterfly was photographed for the first time in Himachal Pradesh.
Background:-
- The State is home to 25% of the butterfly species found in India; 120 species of butterflies have been documented by the Wild Bhattiyat Project initiated by the State Forest Department in 2022
About Paintbrush Swift Butterfly:-
- Its scientific name is Baoris Farri.
- It is from the Hesperiidae family.
- The species’ larvae feed on bamboo and some other grass species.
- Its habitat is distributed in northeast, central and south India.
- It is identified based on two separated spots in the upper forewing cell.
- The species’ larvae feed on bamboo and some other grass species.
- Habitat loss and scarcity of larval host plants are major causes of the decline in the butterfly population.
- Conservation status:-
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- The paintbrush swift (Baoris farri), a butterfly species of the Hesperiidae family, was sighted and photographed during a field survey conducted under the Wild Bhattiyat Project initiated by the Bhattiyat Forest Range of the Dalhousie Forest Division of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department in 2022.
Source: The Hindu
Euclid Space Telescope unveils mysteries of Dark Universe
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
European astronomers have unveiled the first images captured by the newly launched Euclid space telescope.
- These groundbreaking images offer a glimpse into Euclid’s extraordinary capabilities, demonstrating its capacity to observe billions of galaxies situated up to 10 billion light years away.
What is Euclid Mission?
- Euclid’s mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA) in partnership with NASA, aims to unravel the enigmatic forces of dark matter and dark energy, which together constitute 95% of the universe.
- The Euclid Space Telescope is equipped with a 1.2-meter primary mirror, allowing it to capture detailed observations of galaxies.
- It carries two main scientific instruments: the visible-wavelength camera (VIS) and the near-infrared camera and spectrometer (NISP).
- By mapping the distribution and evolution of galaxies, Euclid aims to shed light on the fundamental forces shaping the cosmos.
(1) Mission Scope and Duration
- Euclid is a space-based mission, equipped with a sophisticated telescope and state-of-the-art scientific instruments.
- The mission is expected to have a nominal operational lifetime of 6 years, during which it will conduct an extensive survey of the sky.
(2) Launch and Spacecraft
- Euclid was launched on July 1, 2023, from Cape Canaveral in Florida using a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- The spacecraft carries the Euclid Space Telescope, which is designed to observe galaxies across a wide range of wavelengths.
(3) Investigating Dark Energy and Dark Matter
- Dark energy, discovered in 1998, explains the unexpected acceleration of the universe’s expansion.
- Euclid’s mission aims to provide a more precise measurement of this acceleration, potentially uncovering variations throughout cosmic history.
- Dark matter, inferred through the gravitational effects it exerts on galaxies and clusters, plays a vital role in preserving their integrity.
Unraveling the Dark Universe
- 5% Visible, 95% Dark: The mission emphasizes that our understanding of the universe is limited to merely 5%—the matter we can see. The rest of the universe remains “dark” because it does not emit electromagnetic radiation, but its effects on visible matter are evident.
- Dark Matter’s Role: Dark matter is suspected to influence galaxies’ rotation, galaxy clusters’ cohesion, and the formation of cosmic structures, further validating its existence.
- Dark Energy’s Mystery: Dark energy, an even more enigmatic force, was proposed in the 1990s when the universe’s accelerated expansion was discovered. This mysterious energy was awarded a Nobel Prize in 2011.
Mission Ahead
- Creating a 3D Map: Following its initial commissioning and overcoming technical challenges, Euclid will construct a 3D map covering approximately one-third of the sky. This map will reveal subtle variations attributable to the dark universe.
- Cosmic Web Exploration: By gaining insights into dark energy and dark matter, scientists aim to understand the formation and distribution of galaxies within the cosmic web, a network of cosmic structures that make up the universe.
Source: Hindustan Times
Inflation
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
The Retail inflation eased to 4.87% in October 2023 compared to 5.02 % in September 2023.
Background:-
- Retail inflation, based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), eased to 4.87 per cent in October compared to 5.02 per cent in September this year.
About Inflation:-
- Inflation refers to a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
- It is the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
- Inflation measures the average price change in a basket of commodities and services over time.
- The opposite and rare fall in the price index of this basket of items is called ‘deflation’.
- Inflation is indicative of the decrease in the purchasing power of a unit of a country’s currency.
- This is measured in percentage.
Measures of Inflation in India:-
- In India, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation measures inflation.
- There are two main sets of inflation indices for measuring price level changes in India
- the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- GDP deflator is also used to measure inflation.
Impacts of inflation:-
- Reduces people’s purchasing power
- Reduces overall demand
- Harms savers and helps borrowers
- Helps the government meet debt obligations: In the short term, the government, which is the single largest borrower in the economy, benefits from high inflation.
- In the short term, corporates, especially the large and dominant ones, could enjoy higher profitability because they might be in a position to pass on the prices to consumers.
- Worsens the exchange rate.
Source: AIR
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 14th November 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. Who is Birsa Munda? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Dnieper River? |  |
| 3. What is Aurora? |  |
| 4. What are India's 2+2 Ministerial Dialogues? |  |
| 5. What is the Euclid Space Telescope and its role in unveiling mysteries of the Dark Universe? |  |
















