UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 18th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Chhath Puja |

|
| COP28 in Dubai |

|
| Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation |

|
| Voice of Global South Summit-2023 |

|
| Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) |

|
| SATURN |

|
| Epilepsy |

|
GS-I
Chhath Puja
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
The great festival of Chhath started recently and is celebrated with great rituals and devotion.
About Chhath Puja:
- It is an important Hindu festival celebrated in states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- This festival is dedicated to God Surya and his sister Shashti Devi, often referred to as Chhathi Maiya, and it involves religious rituals.
- The most unique feature of this Chhath Puja is that there is no Murti Pujan or Idol Worshipping, unlike most of the festivals of the Hindu religion.
- The festival is celebrated in October or November, after Diwali.
- The Chhath festival begins as the Diwali festival ends.
- It is celebrated for four consecutive days and is celebrated with great reverence and dedication.
- The first day of the Chhath Puja includes taking a dip in the holy river/any water body. People also take the Ganges water to their homes to perform special offerings and rituals. Houses are thoroughly cleaned on this day.
- The second day of Chhath, also known as Kharna, involves devotees observing a day-long fast, which is broken in the late evening after performing the worship of Mother Earth. The offerings to God include rice pudding (kheer) and fruits, which is distributed among family members and friends.
- The third day of Chhath goes into the preparation of the prasad (offerings) for the evening offerings, also known as Sanjhiya Arghya. In the evening, large numbers of devotees gather on the banks of rivers and make offerings (Arghya) to the setting sun. The night of the third day witnesses a colourful event known as Kosi. A canopy is made from sugarcane sticks, and lighted earthen lamps are placed inside the canopy along with baskets filled with prasad.
- On the fourth and final day of Chhath, family members and friends go to the banks of rivers before sunrise and make offerings (Arghya) to the rising sun. After this ritual, devotees break their fast and distribute Prasad to neighbours and relatives.
Source: Times Now
COP28 in Dubai
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
The upcoming COP28, scheduled to be held in Dubai from November 30 to December 12, faces the daunting challenge of addressing the urgent climate crisis.
- Despite decades of negotiations, current global commitments to combat climate change are deemed insufficient.
- With temperatures rising at an alarming rate, the need for substantial action has never been more critical.
What is COP?
- The word ‘COP’ is an acronym for ‘Conference of the Parties. The ‘parties’ are the governments around the world that have signed the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), a treaty agreed upon in 1994.
- Every year, the COP is hosted by a different nation and the first such COP meeting – ‘COP1’ – took place in Germany in 1995.
- The conferences are attended by world leaders, negotiators, and ministers, and also by representatives from civil society, business, international organisations, and the media.
- The last COP-27 edition convened in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt with the theme “Together for Implementation” and to renew and extend the agreements reached in the historic Paris Agreement.
Climate Action So Far: Crisis and Inadequate Responses
- Rising Temperatures: 2023 is poised to become the warmest year ever recorded, with monthly warming records continually broken.
- Response Lag: Global efforts to combat climate change have not kept pace with the rapid temperature increase.
- Assessment: Recent reports indicate that current climate action plans, even in an optimistic scenario, would only achieve a 2% reduction in emissions by 2030, far from the 43% reduction recommended by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- Financial Gap: Despite increasing climate risks, financial resources allocated for adaptation measures in developing countries are insufficient, with a vast disparity between the required and actual funding.
Expectations from COP28
COP28 aims to address these pressing climate challenges and achieve significant outcomes:
(1) Tripling of Renewable Energy:
- Objective: Triple the global installed capacity of renewable energy by 2030, resulting in 70% of electricity generation from renewables.
- Potential: This initiative could reduce 7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions by 2030, making it a substantial step toward emission reduction.
- Support: The proposal has garnered endorsement from G20 countries and explicit support from 60 others.
(2) Delivery of $100 Billion:
- Background: Developed countries pledged to mobilize $100 billion annually in climate finance from 2020, a commitment that remains unfulfilled.
- Progress: Developed nations are expected to claim fulfillment of this promise at COP28, though it remains inadequate compared to the trillions required for climate action.
- Challenge: The greater challenge lies in negotiating additional funding beyond the $100 billion annually, commencing from next year.
(3) Funding for Loss and Damage:
- Fund Creation: The establishment of a loss and damage fund, designed to assist countries affected by climate change impacts, was a notable outcome of the previous climate meeting in Egypt.
- Funding Flow: COP28 is expected to witness financial contributions to the loss and damage fund, signaling progress in addressing concerns, especially for small island nations.
(4) Global Stocktake:
- Mandate: As per the Paris Agreement (2015), COP28 will present findings from the first global stocktake exercise. This assessment evaluates countries’ progress in combating climate change and outlines necessary actions for the next five years.
- Informing Action: The stocktake findings will inform discussions and actions during the conference, providing a roadmap for more effective climate action.
(5) Phase-down of Fossil Fuels:
- Challenge: Controversial debates on the scheduled phase-down or phase-out of fossil fuels, particularly coal, persist among nations.
- Contentious Issue: Resolving the disagreement over fossil fuel reduction is expected to be a complex and unresolved matter at COP28.
Conclusion
- COP28, set to be held in Dubai, represents a critical opportunity to address the climate crisis.
- With expectations of tripling renewable energy, fulfillment of $100 billion climate finance commitments, funding for loss and damage, and global stocktake findings, the conference aims to push climate action forward.
- However, the contentious issue of fossil fuel phase-down remains a challenge for the conference.
- The world eagerly anticipates the outcomes and progress toward mitigating climate change.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation CEO Summit took place recently.
Background:-
- Speaking at the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation CEO summit in San Francisco yesterday, President Biden stressed the importance of working together with India, Japan, the Republic of Korea, and Singapore to strengthen the critical semiconductor industry.
About APEC:-
- Established: 1989
- HQ: Singapore.
- Members: 21
- Member Nations: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, Vietnam and the United States.
- India is not a Member.
- It is an inter-governmental forum that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
- It was started in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world.
- It aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.
Functions of Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):-
- APEC works to help all residents of the Asia-Pacific participate in the growing economy.
- APEC projects provide digital skills training for rural communities and help indigenous women export their products abroad.
- Recognizing the impacts of climate change, APEC members also implement initiatives to increase energy efficiency and promote sustainable management of forest and marine resources.
India and APEC:-
- India has been an important destination for APEC members’ foreign investment over the past 25 years, with three APEC economies—Singapore, Japan, and the United States—among the top five countries providing FDI inflows into India.
- India was denied APEC membership in 2007 on the grounds that its economy was not integrated into the global system.
- India is the region’s third-largest and now fastest-growing major economy.
- APEC economies, which account for 60 per cent of global GDP, are experiencing sluggish growth and must look for opportunities to bring new markets
- India is also projected to be the world’s third-largest economy by 2030 and will need well over $1 trillion of investment in infrastructure over the next decade.
Source: AIR
Voice of Global South Summit-2023
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi led the inaugural session of the second ‘Voice of Global South Summit-2023’.
About Voice of Global South Summit-2023:-
- Date: 12-13 January 2023.
- The “Voice of Global South Summit” is a platform for generating ideas from the developing world for achieving energy security, which is affordable, accessible and sustainable.
- India is hosting the Summit in a virtual format.
- The inaugural session will be followed by four parallel Ministerial sessions.
- These include the sessions by Ministers of External Affairs, Education, Finance and Environment.
- Four more parallel Ministerial sessions will be held in the afternoon.
- The theme of the inaugural Leaders’ Session: “Together, for Everyone’s Growth, with Everyone’s Trust” and that of the Concluding Leaders’ Session is “Global South: Together for One Future”.
- Akashvani correspondent reports that the Summit will focus on sharing with the countries of the Global South, the key outcomes achieved in various G20 meetings over the course of India’s Presidency.
- India hosted a two-day Voice of Global South Summit on 12-13 January 2023.
- The Summit was held in a virtual format, with 10 sessions in total.
- It saw the participation of Leaders and Ministers from 125 countries of the Global South. India convened this one-of-a-kind Summit to focus international attention on the priorities, perspectives and concerns of the developing world.
- This is particularly relevant as the world passes through a difficult period marked by challenges to health, food security, affordable access to energy, climate finance and technologies, and economic growth.
Significance:-
- This Summit is a timely reminder of what is at stake for over three-fourths of the planet’s population that is most vulnerable to the deleterious impact of the several interlinked risks we confront.
Source: AIR
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
Subject: International Relations
Why in News?
Australian naval personnel allegedly sustained minor injuries recently after “unsafe and unprofessional” conduct by a Chinese warship in international waters off Japan’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
About Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ):
- The concept of an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) was adopted through the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- EEZ, as defined under UNCLOS, is an area of the ocean extending up to 200 nautical miles (370 km) immediately offshore from a country’s land coast in which that country retains exclusive rights to the exploration and exploitation of natural resources.
- Under international law, within its defined EEZ, a coastal nation has:
- Sovereign rights for the purpose of exploring, exploiting, conserving, and managing the natural resources of the seabed, subsoil, and waters above it.
- Jurisdiction is provided for in international law with regard to the establishment and use of artificial islands, installations, and structures; marine scientific research; and the protection and preservation of the marine environment.
- Other rights and duties are provided for under international law.
- Other States have the right for their ships and aircraft to traverse the EEZ and its airspace and to lay cable and pipelines.
What is Territorial Sea?
- The territorial sea extends to a limit of 12 nautical miles from the baseline of a coastal State.
- Within this zone, the coastal State exercises full sovereignty over the air space above the sea and over the seabed and subsoil.
- A coastal State may legislate on matters concerning the safety of navigation, the preservation of the environment, and the prevention, reduction, and control of pollution without any obligation to make these rules compliant with international standards.
- Resource use within the territorial sea is strictly reserved for the coastal State.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
SATURN
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Recently, astronomers explained the possibility of the disappearance of rings around Saturn.
About Saturn:-
- Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun.
- It is the second largest planet in our solar system.
- Adorned with a dazzling system of icy rings, Saturn is unique among the planets.
- Saturn is a massive ball made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
- The farthest planet from Earth discovered by the unaided human eye, Saturn has been known since ancient times.
- The planet is named for the Roman god of agriculture and wealth, who was also the father of Jupiter.
- Saturn isn’t the only planet to have rings.
- The rings we see are made of groups of tiny ringlets that surround Saturn.
- They’re made of chunks of ice and rock.
- Saturn has a thick atmosphere.
- One day on Saturn goes by in just 7 hours.
- One year on Saturn is 29 Earth years.
- Saturn has been known since ancient times because it can be seen without advanced telescopes.
- Four robotic spacecraft have visited Saturn, including Pioneer 11, Cassini, and Voyager 1 and 2.
Source: The Hindu
Epilepsy
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
National Epilepsy Day is celebrated every year in India on November 17 to raise awareness about the brain disorder and bust myths surrounding the disease.
About Epilepsy:
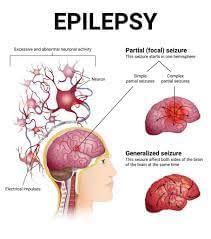
- It is a brain disease where nerve cells don’t signal properly, which causes seizures.
- A seizure is usually defined as a sudden alteration of behaviour due to a temporary change in the electrical functioning of the brain.
- Normally, the brain continuously generates tiny electrical impulses in an orderly pattern. These impulses travel along neurons—the network of nerve cells in the brain—and throughout the whole body via chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
- In epilepsy, the brain's electrical rhythms have a tendency to become imbalanced, resulting in recurrent seizures.
- In patients with seizures, the normal electrical pattern is disrupted by sudden and synchronized bursts of electrical energy that may briefly affect their consciousness, movements, or sensations.
- Seizures can be classified into two broad categories, depending on the location of abnormal brain activity.
- Seizure in one part of the brain is called a focal seizure, and it is usually accompanied by loss of consciousness, while in cases of generalised seizures, all areas of the brain are involved.
- It is a chronic, noncommunicable disease that affects people of all ages.
- Epilepsy (sometimes referred to as a seizure disorder) can have many different causes and seizure types.
- Some people may have convulsions (muscles contract repeatedly) and lose consciousness. Others may simply stop what they are doing, have a brief lapse of awareness, and stare into space for a short period of time.
- Epilepsy may develop as a result of many types of conditions that disrupt normal brain activity, known as “co-occurring conditions”. Examples of conditions that can lead to epilepsy include:
- Brain tumours
- Head trauma
- Alcoholism or alcohol withdrawal
- Alzheimer's disease
- Strokes, heart attacks, and other conditions that deprive the brain of oxygen
- Abnormal blood vessel formation (called arteriovenous malformations) or bleeding in the brain
- Brain inflammation or swelling
- Infections such as meningitis, HIV-related infections, and viral encephalitis
- Around 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, making it one of the most common neurological diseases globally.
- Nearly 80% of people with epilepsy live in low- and middle-income countries.
- The risk of premature death in people with epilepsy is up to three times higher than in the general population.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|















