Life Processes- 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 5
Assertion Reason Type Questions
Q1: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: Kidneys perform a dual function in our body.
Reason: Selective reabsorption occurs in the glomerulus.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion is true that kidneys perform a dual function in our body. They not only remove waste products and excess substances via urine, but also regulate the levels of electrolytes, blood pressure and red blood cell production. However, the reason is false. Selective reabsorption doesn't occur in the glomerulus, but in the renal tubules. So, the answer is C.
Q2: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: Tracheal cartilage is present in the throat.
Reason: The larynx plays an important role in human speech.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (b)
Assertion is true, tracheal cartilage is indeed present in the throat. It provides support and keeps the trachea open during breathing. The reason is also true, the larynx plays a crucial role in human speech as it houses the vocal cords. However, these two facts are not related, thus the answer is B.
Q3: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: Veins have valves.
Reason: The pressure for the flow is far lesser compared to arteries.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Assertion and reason are both true and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion. Veins have valves to prevent the backflow of blood as the pressure for the flow is far lesser compared to arteries. So, the answer is A.
Q4: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells.
Reason: Stomatal pores are the site for exchange of gases by diffusion.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (b)
ssertion is true that the opening and closing of the stomatal pore is a function of the guard cells. However, the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. While it's true that stomatal pores are the site for exchange of gases by diffusion, this is not related to the function of the guard cells. Hence, the answer is B.
Q5: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: Respiration is opposite of Photosynthesis.
Reason: In Photosynthesis food is made from energy and in Respiration food is converted to energy.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Respiration is indeed the opposite of photosynthesis as in photosynthesis, plants convert light energy into food, while in respiration, this food is converted back into energy. So, the answer is A.
Q6: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: Kidneys purify blood.
Reason: Renal vein has more Oxygen than renal artery.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (c)
Assertion is true that kidneys purify blood by filtering out waste products and excess substances. However, the reason is false. The renal vein does not have more oxygen than the renal artery. The renal artery brings oxygenated blood to the kidneys and the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys. Hence, the answer is C.
Q7: Following questions consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion: In plants gaseous exchange takes place by the opening and closing of guard cells.
Reason: The exchange of gases occurs across the surface of stem, roots and leaves.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Ans: (b)
The assertion is true that in plants, gaseous exchange takes place due to the opening and closing of the stomata by the guard cells. However, the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. While gaseous exchange does occur across the surface of the stem, roots and leaves, it primarily occurs through the stomata. Hence, the answer is B.
CCT Questions
Our body needs to remove the wastes that build up from cell activities and from digestion. If these wastes are not removed, then our cells can stop working and we can get very sick. The organs of excretory system consist of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethr(a) Each kidney is made up of nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephrons. The formation of urine involves various processes that take place in the different parts of the nephrons. Each nephron consists of a cup- shaped upper end called Bowman’s capsule containing a bunch of capillaries called glomerulus. Bowman’s capsule leads to tubular structure, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule which ultimately join the collecting tubule.
Q1: The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form.
(a) Urea
(b) Uric acid
(c) Ammonia
(d) All of these
Ans: The least toxic excretory product in animals is urea (A). This is because urea, which is a nitrogenous waste product, is less concentrated and requires less water to be excreted from the body than uric acid and ammonia. Ammonia is the most toxic waste product and needs to be converted to urea or uric acid before being excreted.
Q2: Glomerular filtrate is first collected by
(a) Distal convoluted tubule
(b) proximal convoluted tubule
(c) Bowman’s capsule space
(d) loop of Henle
Ans: The glomerular filtrate, which is a fluid containing water, glucose, salts and urea that has been filtered out from the blood in the kidneys, is first collected by the Bowman’s capsule space (C). The Bowman's capsule surrounds the glomerulus and is the site where filtration of blood occurs, making it the first stop for the filtrate.
Q3: The outline of principal events of urination is given below in random order.
I) stretch receptors on the wall of urinary bladder send signals to the CNS.
II) The bladder fills with urine and become distended.
III) Micturition (voiding out urine)
IV) CNS passes on motor messages to initiate the contraction of smooth muscles of bladder and simultaneous relaxation of urethral sphincter.
The correct sequence of the events is
(a) I → II → III→ IV
(b) IV → III → II→ I
(c) II → I→ IV → III
(d) III → II→ I→ IV
Ans: The correct sequence of the principal events of urination is II → I→ IV → III (C). This sequence describes how the bladder fills up with urine (II), stretch receptors in the bladder wall send signals to the central nervous system (CNS) when it is full (I), the CNS then initiates the contraction of bladder muscles and relaxation of the urethral sphincter (IV), and finally, urine is voided out (III).
Q4: Urine formation occurs through
(a) Ultrafiltration, reabsorption, secretion.
(b) Secretion, osmosis, ultrafiltration and reabsorption.
(c) Only filtration and absorption.
(d) Only osmosis and secretion.
Ans: Urine formation occurs through ultrafiltration, reabsorption, and secretion (A). Ultrafiltration is the process where blood is filtered in the kidneys to remove waste products, reabsorption is where useful substances like glucose and salts are reabsorbed back into the blood, and secretion is the final process where any remaining waste products are secreted into the urine for excretion.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Name the respiratory pigments of human beings.
Ans: Haemoglobin
Q2: In which form is food stored in plants and in animals?
Ans: Starch in plants and glycogen in animals
Q3: Why are heterotrophs called consumers?
Ans: They obtain food from other sources.
Q4: Name the watery substance released in our mouth during eating.
Ans: Saliva
Q5: What does saliva contain?
Ans: Mucin and salivary amylase
Q6: Name the structure which prevents food from entering the passage to the lungs.
Ans: Epiglottis
Q7: Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem of plants?
Ans:
- Xylem transports water and minerals to the plant body. The roots of a plant have hair called root hairs. The root hairs are directly in contact with the film of water in between the soil particles. Water and minerals get into the root hair by the process of diffusion. The water and minerals absorbed by the root hair form the soil pass from cell to cell by osmosis through the epidermis root cortex, endodermis and reaches the root xylem. The xylem vessels of the root the plant are connected to the xylem vessels into stem.
- Therefore, the water containing dissolved minerals enter the root xylem vessels into stem xylem vessels.
- The xylem vessels of the stem branch into thleaves of the e leaves of the plants. So the water & minerals carried by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves through the branched xylem vessels which enter from the petiole into the each part of the leaf. Thus the water and minerals form the soil reach through the root and stem to the leaves of the plants.
- Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a suction which pulls water form the xylem cells of roots. The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plants is known as transpiration.
Q8: What is the role of following in human digestive system –
(a) mucous
(b) Bicarbonate
(c) Trypsin
Ans: (a) Mucus – It protects the inner living of stomach from HCl.
(b) Bricarbonate – It makes the acidic food alkaline so that pancreatic enzymes act on it.
(c) Trypsin – It digest proteins into amino acids.
Q9: (a)What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants?
(b)Where do the substances in plants reach as a result of translocation?
Ans: (a)Translocation is the process of movement of materials from leaves to all other parts of the plant body.
(b)As a result of translocation, the substances in plants reach to the storage organs of roots, fruits and seeds and to growing organs.
Q10: What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Ans: Outside raw materials used for by an organism includes:
(a) Food
(b) Water
(c) Oxygen
Q11: What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Ans: The processes essential for maintaining life are:
(a) Nutrition
(b) Respiration
(c) Transportation
(d) Excretion
Q12: Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Ans:
- Carbon dioxide from atmosphere.
- Light from Sun
- Water from Soil
- Chlorophyll from chloroplast of green plants.
Q13: In artificial kidney, which substance passes from the blood to the dialysis fluid?
(a) Urea
(b) Heart
(c) Uric acid
(d) Creatinine
Ans: (a)
Q14: What is the role of the acids in our stomach?
Ans:
HCl plays following role in our stomach:
- Make the medium acidic for action of enzyme pepsin.
- Kills the harmful bacteria present in food
- Prevents fermentation of food
Q15: How is small intestine deigned to absorb digested
Ans: The inner lining of small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which transport the absorbed food to each and every cells of the body. Where, it is utilized to obtaining energy and repair of old tissues.
Q16: What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: The rate of breathing is slower in terrestrial organisms as compared to aquatic organisms. This is due to the fact that in water, the amount of oxygen is less as compared to air while in aquatic organisms the rate of breathing is faster.
Q17: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide,water and energy takes place in
(a) cytoplasm
(b) mitochondria
(c) chloroplast
(d) nucleus
Ans: Correct option (b)
Q18: What are different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Ans: The pathways of break-down of glucose in various organisms are as below:
Q19: How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Ans: In human beings, a pigment hemoglobin is present in RBC which has high affinity for oxygen, takes up the oxygen from the air in the lungs and carry it to tissues which are defficient in oxygen. Some oxygen is carried in dissolved state in blood plasm(a) Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen is mostly transported in the dissolved form in our bloo(d)
Q20: (i) Draw a diagram of an excretory unit of a human kidney and label the following:
Bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus, Collecting duct, renal artery
(ii)Write the important function of the structural and functional unit of kidney.
(iii)Write any one function of an artificial kidney.
Ans: (i)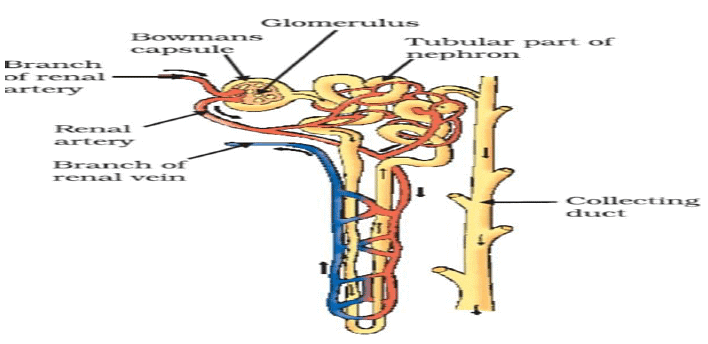
(ii) Function of nephron is filtration, re-absorption and secretion.
(iii) Function of artificial kidney: Help to remove harmful wastes, extra salts and water. It controls blood pressure. Maintain the balance of sodium, potassium salts in a patient whose kidneys have failed.
Q21: What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Ans: The components of human transport system include:
- Heart- receives and pumps the bloo(d)
- Arteries- carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to various organs.
- Veins- Bring back blood to heart.
- Capillaries- exchange of various materials and gases between blood and tissues.
Q22: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Ans:
- The separation of the right and left side of heart is useful to prevent oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood from mixing. Such separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- This is useful in animals that have high energy needs, such as birds and mammals that constantly use the energy to maintain their body temperature.
Q23: The doctor measured Ravi’s blood pressure and said it is normal now. The range of Ravi’s blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) is likely to be-
(a)120/80mm of Hg
(b)160/80mm of Hg
(c)120/60mm of Hg
(d)180/80mm of Hg
Ans: (a)
Q24: What are the components of transport system in highly organized plants?
Ans: The transport system of higher plants consists of xylem and phloem. Xylems have vessels and trachieds to transport water and minerals from root to other part of the plants. Phloem, which consists of sieve tubes and companion cells, transport food from leaves to storage organs and other parts of plant.
Q25: How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans:
- Water and minerals are transported in plants through xylem which consists of trachieds and vessels.
- Water and minerals absorbed by root hairs present in root by osmosis is passed to xylem tissues of root.
- From root xylem it passes to stem xylem and thus water reaches to leaves.
Q26: The function of the lymph fluid is to
(a) Drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood
(b) Carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine
(c) Circulates around the body and help in clotting of blood
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans: (d)
Q27: How is food transported in plants?
Ans: Food is transported in plants through phloem which consists of sieve tubes, sieve cells and companion cells. The food prepared in leaves in soluble form transported to leaves phloem. Active transport of food passes to all other parts of plants.
Q28: In birds and mammals the left and right side of the heart is separate(d) Give reasons.
Ans: The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Q29: What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Ans:
- Plant produces carbon dioxide as wastes during respiration and oxygen as waste during photosynthesis.
- Excess of water is removed through transpiration.
- Some waste products like gums and resins are stored in older xylem tissue.
Q30: List two types of the transport system in human being and write the functions of any one of these.
Ans: (i) Function of blood circulatory
- Transport of oxygen
- Transport of digested food
- Transport of carbon dioxide
- Transport of nitrogenous waste
- Transport of salts
(ii) Functions of lymphatic system
- Carries digested and absorbed fat.
- Drains extra fluid from tissue back into the blood.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Life Processes- 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 5
| 1. What are the main life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do plants carry out photosynthesis, and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What role does respiration play in living organisms? |  |
| 4. Why is excretion necessary for living organisms? |  |
| 5. How does reproduction contribute to the continuity of life? |  |

















