UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Evolution of Man
Evolution of Man | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Human evolution is a complex interplay of biological and cultural developments, setting humans apart from other animals. Unique attributes empower humanity, allowing individuals to shape their destiny, control their environment, remember the past, envision the future, and communicate effectively for collective progress.
Biological Evolution
A. Man's Place in the Animal Kingdom
- Classification:
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Genus: Homo
- Species: sapiens
- Order Primates:
- Encompasses lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys, and apes, with humans at the pinnacle.
B. Place and Time of Human Evolution
- Geographical Origin:
- Fossils suggest East Africa as the cradle of human evolution.
- Chronology:
- Initiated 15 million years ago, but Homo sapiens emerged approximately 3 million years ago.
C. Ancestry and Salient Features
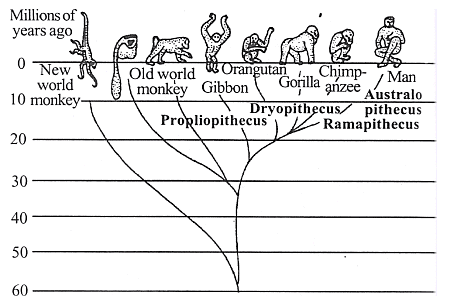
- Ancestor:
- Apes were ancestral to humans; modern apes (gibbons, orangutans, chimpanzees, and gorillas) are evolutionary cousins.
- Apes' Features:
- Arboreal nature
- Tailless
- Narrow-nostriled
- Two premolar teeth
- Canal connecting external and middle ear
- Posterior occipital condyles
- Large incisors and canines
- Narrow and elongated pelvis
 Apes
Apes
D. Salient Features of Humans
- Unique Traits:
- Bipedal gait
- Erect walk
- Dextrous hands for tool use
- Large cranium
- Prominent brow
- Expanded pelvis
- Distinct chin
- Enlarged breasts
- Hairlessness
- Speech and cultural behaviors
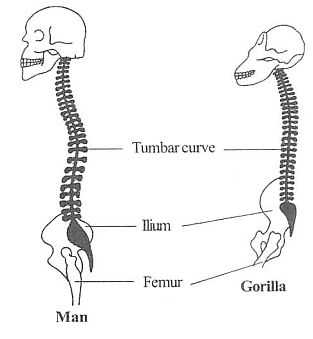 Vertebral column of man and gorilla
Vertebral column of man and gorilla
E. Causes for Human Evolution
- Transition to Terrestrial Life:
- Ancestors transitioned from trees to the ground due to factors like constant food supply, shrinking forests, protection for offspring, competition, and behavioral changes from genetic recombination.
Cultural Evolution
A. Evolution as Seen in the Fossil Record
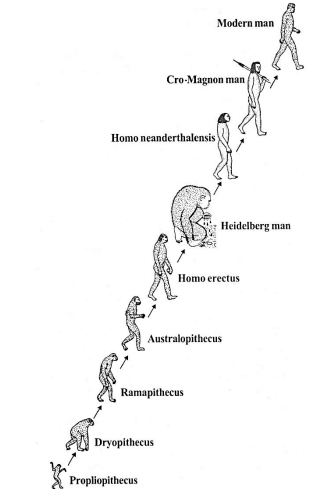 Evolution of man as seen in the fossil record
Evolution of man as seen in the fossil record
- Darwinian View:
- Supports gradual evolution of humans.
- Geographical Origin:
- East Africa as the starting point.
- Major Evolutionary Changes:
- Transition from arboreal to terrestrial life
- Opposability of great toes
- Development of erect posture
- Bipedal locomotion
- Basin-like pelvis
- Chin development
- Increase in brain size and intelligence
- Use of forelimbs for non-locomotory functions
B. Stages in the Origin of Man
- Chronological Evolution: a. Apes:
- Ancestral phase b. Ape-men:
- Transitional phase c. Primitive Men:
- Early Homo species d. Modern Men:
- Homo sapiens
Cultural Evolution of Man: Unveiling the Tapestry of Human Advancement
A. Definition of Cultural Evolution
- Intellectual Development:
- Cultural evolution signifies the intellectual progress in human beings.
- Scope of Culture:
- Encompasses skills, ways of life, transmitted through interpersonal communication and tradition rather than genetics.
- Includes knowledge, language, religion, beliefs, laws, customs, rituals, arts, tools, food, utensils, science, technology, agriculture, medicine, human society, and livelihood means.
B. Acquisition of Culture
- Essential Feature:
- Culture is acquired through interpersonal interactions, not genetic transmission.
- Acquired from peers, not passed through gametes.
- Biological Evolution Link:
- Cultural evolution is a consequence of man's biological evolution.
Speed of Cultural Evolution
A. Rapid Progress
- Comparative Timeframes:
- Stone Age to modern civilization transition occurred rapidly compared to biological evolution.
- Human evolution progressed faster than other organisms.
- Significant acceleration in the last 25,000 years.
Culture of Early Man
A. Characteristics
- Nomadic Lifestyle:
- Early humans were nomadic.
- Habitat:
- Inhabited caves.
- Population Size:
- Small groups.
- Clothing:
- Wore clothing made from leaves.
- Food Procurement:
- Hunted game, gathered wild fruits, seeds, nuts, and roots.
- Tools:
- Manufactured tools from stones and bones.
- Protection Measures:
- Faced threats from wild animals and environmental changes.
- Beliefs:
- Belief in afterlife and supernatural power.
- Communication:
- Communicated through speech.
- Cultural Expressions:
- Elaborate religious ceremonies, cave paintings, and arts.
- Environmental Challenges:
- Suffered from floods, storms, drought, famine, and volcanoes.
Milestones of Cultural Evolution
A. Tools
- Transition to Tool Usage:
- Tools crafted as hands were freed from locomotory functions.
- Early tools made from stones and bones.
B. Cannibalism
- Evidence from Choukoutien Caves:
- Skulls of Homo erectus suggesting cannibalistic practices.
C. Fire
- Capture and Use:
- Man obtained and tended fires, possibly from natural occurrences.
- Stone disc with a hole used as the first fire-making instrument, dating back 30,000 years.
D. Hunting and Food Gathering
- Primitive Techniques:
- Ancient people hunted game and gathered fruits using stone tools.
- Utilized fire for cooking and manipulating animal movements.
E. Burials
- Cultural Advance:
- Burial practices evolved, with added ornaments, beads, and tools around 25,000 years ago.
- Suggests belief in an afterlife.
F. Carvings and Art
- Cave Art and Statues:
- Carvings on cave walls and statues depict animals and human figures.
- Oldest statue, mammoth ivory carving, dates back 25,000-30,000 years.
G. Agriculture
- Emergence:
- Plant and animal cultivation began around 7,000 to 10,000 years ago.
- Connected with settled life, fishing, and gradual development of cultivation practices.
H. Clothing
- Evolution of Attire:
- Early Europeans used animal skins stitched with rawhide.
- Later innovations included weaving with flax, wool, and cotton fabrics.
I. Writing
- Late Emergence:
- Invention of writing occurred after settlements.
- Sumerians produced the first tablets about 5,500 B.P.
J. Speech
- Distinctive Human Ability:
- Speech involves formulating and articulating abstract ideas.
- Differentiates humans from other animals.
K. Family
- Social Structure:
- Most societies featured a single male with exclusive sexual rights and leadership roles.
- Headman or chief demonstrated skill and intelligence, often with multiple wives.
In summary, the cultural evolution of man paints a vivid picture of progress, from nomadic cave dwellers to the architects of civilizations, with each milestone revealing the intricate layers of human advancement.
The document Evolution of Man | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|351 docs
|
Related Searches





















