UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 23rd November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Vanuatu Islands
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
A Magnitude 6.7 Earthquake Jolted the Vanuatu Islands Near Australia recently.
About Vanuatu Islands:-
- Vanuatu, a country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
- It consists of a chain of 13 principal and many smaller islands located about 500 miles (800 km) west of Fiji and 1,100 miles (1,770 km) east of Australia.
- Vanuatu (officially, the Republic of Vanuatu) is divided into 6 provinces.
- These provinces are Malampa, Penama, Sanma, Shefa, Tafea and Torba.
- These provinces are further subdivided into municipalities.
- The indigenous population, called ni-Vanuatu, is overwhelmingly Melanesian, though some of the outlying islands have Polynesian populations.
- Subsistence agriculture has traditionally been the economic base of Vanuatu, together with an elaborate exchange network within and between islands.
- Since independence, Vanuatu’s tourism and offshore financial services have emerged as the largest earners of foreign income.
- The Lapita sites became Vanuatu’s first UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2008.
About Earthquake:-
- An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth’s surface.
- It is caused by the seismic waves or earthquake waves that are generated due to a sudden movement (sudden release of energy) in the earth’s crust (shallow-focus earthquakes) or upper mantle (some shallow-focus and all intermediate and deep-focus earthquakes).
- A seismograph, or seismometer, is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes.
- Hypocentre/Focus: The point where the energy is released.
- Epicentre: The point on the surface directly above the focus.
- Isoseismic line: A line connecting all points on the surface where the intensity is the same.
Source: Times Now
Sant Mirabai
Subject: Art and Culture

Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Mathura in Uttar Pradesh today to take part in Sant Mirabai Janmotsav.
Background:-
- The programme is being organized to mark the 525th Birth Anniversary of Sant Mirabai. During the event, the Prime Minister will also release a commemorative stamp and a coin in honour of Sant Mira Bai.
About Sant Mirabai:-
- Mirabai was born into a Rajput royal family in Kudki, Rajasthan’s Pali region, and spent her youth in Merta.
- By around 1600 CE, she was referenced in Bhaktamal, indicating that she was a well-known and revered figure in the Bhakti movement.
- Mirabai was a Rajput princess who married a prince from the royal family.
- She became a follower of Ravidas, a saint who was said to be untouchable.
- She committed her life to Lord Krishna’s devotion.
- She was the first to introduce the Giridhara Gopala cult of Brindavan and also the first to introduce Bhajan in the Bhakti movement
- Her bhajans were composed in the language of Vraj Bhasha.
- Meerabai’s five teachings are:-
- She did not believe in the caste hierarchy and instead attacked higher caste standards.
- She fled the kingdom because of her great devotion to Lord Krishna.
- She was not a follower of kingly traditions.
- She preached love while avoiding hatred.
- Despite being from the royal family, she became a follower of Ravidas, who was considered untouchable.
Source: AIR
GS-II
ISRAEL-PALESTINE CONFLICT
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi welcomed the agreement for the ongoing ISRAEL-PALESTINE CONFLICT.
Background:-
- Israel and the Palestinian terror group Hamas agreed to the release of 50 hostages held in Gaza and a temporary pause in fighting.
- In his remarks at the virtual G20 Leaders Summit last evening, Mr Modi expressed hope that all the hostages will be released soon.
About ISRAEL-PALESTINE CONFLICT:-
- Both Israelis and Palestinians have been in a struggle for self-determination and sovereignty over the territory, developing respective movements for their causes.
- Both Palestinians and Israelis see the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea as their own, and Christians, Jews, and Muslims all hold parts of the land as sacred.
- The past seven decades have brought war and uprisings.
Historic Timeline:-
- Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire had controlled that part of the Middle East from the early 16th century until control of most of the region was granted to the British after World War I.
- In 1916: the Sykes-Picot Agreement secretly negotiated between Britain and France planned to carve up the Middle East into spheres of influence, and determined that the land in question was to be internationalized.
- In 1917: Britain’s foreign secretary, Lord Arthur Balfour, expressed his government’s support for “the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people.
1947: UN resolution
- 1947: After World War II, nearing the end of the British Mandate for Palestine, the United Nations General Assembly in 1947 passed Resolution 181, urging the partition of the land into two independent states — one Arab and one Jewish.
- Religiously significant Jerusalem is to be under special international administration.
- The plan is not implemented after the Arab side rejects it, arguing that it is unfavourable to their majority population.
- Violence in the regional conflict grows.
1948: Israel declares independence.
- Israel declared independence in May 1948.
- The next day, a coalition of Arab states, allied with Palestinian factions, attacked Israeli forces in what became the first of several Arab-Israeli wars.
- In the end, Israel gains control of an even larger portion of territory — not including the areas of the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
1967: the Six-Day War
- In June of 1967, a war known as the “Six-Day War” or the 1967 Arab-Israeli War broke out amid lingering conflicts, including Egypt’s continued blockade of shipping into the Gulf of Aqaba.
- Israel ultimately takes control of the Gaza Strip, Sinai, the West Bank, the Golan Heights, and predominantly Palestinian East Jerusalem.
- The Arab armies suffered massive losses.
1987: First intifada
- A Palestinian uprising, or intifada, brings largely spontaneous clashes, protests, and civil disobedience against Israeli occupation in the West Bank, Gaza, and Israel, leading to harsh Israeli military crackdowns.
- Unrest continues for years, with many killed or injured on both sides.
1993: Oslo Accords
- The first of two pacts, known as the Oslo Accords, was signed between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- It set out a peace process based on previous U.N. resolutions.
- It charted out the expansion of a limited Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- A follow-up accord was signed in 1995.
- However, key issues such as Israeli settlements in the West Bank and the status of Jerusalem, were left unresolved.
2006: Hamas elected in Gaza
- Israel withdrew its troops from Gaza in 2005.
- The Palestinian militant group Hamas wins legislative elections the next year, leading to political strains with the more moderate Fatah party controlling the West Bank.
2017: U.S. recognizes Jerusalem as capital
- The Donald Trump administration recognizes Jerusalem as the capital of Israel and announces that it plans to shift the U.S. Embassy from Tel Aviv, stirring outrage from Palestinians.
2022: Netanyahu sworn in for sixth term
- Benjamin Netanyahu is sworn in again as Israeli prime minister, after winning an election that gives him his sixth term and elevates a once-fringe bloc of far-right politicians into powerful seats.
2023: Recent events:-
- January 2023: Israeli forces raid the Palestinian city of Jenin, killing nine people in a shootout.
- Summer 2023: Retaliatory attacks flare
- Israel launches surprise airstrikes across the Gaza Strip in May.
- October 2023: Israel is attacked by Hamas.
- Prime Minister of Israel, Netanyahu formally declared war on Hamas on Oct. 8 following a surprise assault by Hamas militants that came a day after the 50th anniversary of the start of the 1973 Yom Kippur War.
Source: AIR
Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE)
Subject: Government Schemes

Why in News?
Recently, AIM, NITI Aayog launched a new accelerator called Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) to support Australian and Indian circular economy startups.
About Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE):
- The India Australia RISE Accelerator is delivered in partnership between CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency, and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), the Government of India’s flagship initiative to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- This initiative focuses on startups and small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India and Australia working on circular economy technologies and solutions.
- Focus Themes: With a focus on Environment and Climate Technology, the program will be tailored to accelerate start-ups working on a range of areas:
- Climate Smart Agriculture
- Clean Energy
- Circular Economy and Waste Management
- Climate Smart Mobility
- Over the nine months, the RISE Accelerator program will help startups navigate early steps in a new region, fast-track connections to the right partners, customers, and talent, and build credibility to succeed in international markets.
- The accelerator, in its first round, will focus on supporting startups and SMEs working on technologies and solutions for the waste and circular economy
- Participating startups may also be eligible for up to INR 40,00,000 in non-equity grants.
- The future rounds of the accelerator will focus on climate-smart agriculture, clean energy and climate smart mobility.
What is the circular economy?
- A circular economy means products are designed in such a way that they can be used again, or even multiple times, to maximise their value
Source: PIB
How Racism overshadowed India-Taiwan Co-operation
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Recent reports of India and Taiwan considering a MoU to facilitate Indian workers’ employment in Taiwan have revealed underlying issues of racism and stereotypes.
- These negative perceptions have implications for both countries and the need for addressing such biases is paramount.
Racism in Taiwan and Stereotypes
- MoU Announcement: Reports of a MoU between India and Taiwan sparked racism in Taiwan towards Indian men.
- Negative Stereotypes: Taiwanese netizens labeled Indian men as dirty, uneducated, and even used derogatory terms like ‘rapists.’
- China-Backed Media: China-backed media amplified stereotypes, perpetuating narratives about women’s safety in India.
- Taiwan’s Response: Taiwan clarified that the news of Indian workers’ arrival was ‘inaccurate’ but acknowledged ongoing talks with India.
Reality of Indian Workers Globally
- Worldwide Presence: Indian workers, both blue-collar and white-collar, are present globally, contributing significantly to economies.
- Remittances: According to a World Bank report, Indian laborers remittances abroad reached a record USD 100 billion in 2021, highlighting their global acceptance.
Misconceptions and Global Gender Issues
- Misplaced Blame: Associating crimes and issues with specific nationalities hinders cooperation.
- Global Gender Inequality: Issues such as unequal pay, workplace harassment, and unfair work burdens affect women worldwide.
India-Taiwan Cooperation: Mutual Benefits
- Taiwan’s Aging Population: Taiwan faces an impending ‘super-aged’ society by 2025 and requires a younger workforce.
- India’s Labor Force: India can provide a youthful and skilled workforce to fill Taiwan’s labor gap.
- Economic Benefits: Such cooperation benefits both countries by addressing unemployment and boosting foreign remittances for India and supporting Taiwan’s economy.
Taiwan’s Focus on India
- Historical Perspective: Taiwan has traditionally focused on Europe and the US for economic growth, trade, and funding.
- Need for Attention: India, as an economic and strategic partner, deserves more attention for stronger ties.
Taiwan’s Racism Problem
- Past Instances: Taiwan has faced criticism for discriminatory policies against Southeast Asian workers during the COVID-19 outbreak.
- Exploitative Practices: Some foreign workers in Taiwan experience exploitative practices bordering on forced labor.
Taiwan’s Reputation and India’s Support
- Positive Image: Taiwan’s democratic credentials and resistance to China’s influence have earned it a positive image among Indians.
- India’s Support: India’s support for Taiwan enhances its international standing and challenges China’s efforts to isolate it.
Conclusion
- Addressing racism, stereotypes, and discriminatory policies is essential for nurturing the growing strategic and economic ties between India and Taiwan.
- Both nations must work towards fostering a friendly and inclusive environment to protect the investment made in their relationship and counteract divisive narratives.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Ozone
Subject: Environment and Ecology
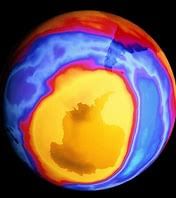
Why in News?
Recent reports suggest that the ozone Hole May Not Be Recovering After all.
Background:-
- The hole in the Antarctic ozone layer has been getting deeper in mid-spring over the last two decades, despite a global ban on chemicals that deplete Earth’s shield from deadly solar radiation, new research suggested.
About Ozone:-
- Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen.
- It is both a natural and a man-made product.
- It occurs in the Earth’s Stratosphere and the Troposphere.
- Stratospheric ozone is formed naturally through the interaction of solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation with molecular oxygen (O2).
- Ozone is produced naturally in the stratosphere.
- But this ozone is gradually being destroyed by man-made chemicals referred to as ozone-depleting substances (ODS), including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), halons, methyl bromide, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform.
Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion:-
- Humans may have severe health problems as a result, including skin conditions, cancer, sunburns, cataracts, rapid ageing, and weakened immune systems.
- Animals that are directly exposed to UV light develop skin and eye cancer.
- Strong UV radiation may prevent plants from growing, blooming, or performing photosynthesis.
- Planktons are greatly affected by exposure to harmful ultraviolet rays.
Efforts taken to control ground-level ozone pollution:-
- Adoption of BS-VI standards
- The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) for Delhi was prepared by the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEFCC) after the order of the Supreme Court in December 2016.
- The Environmental Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA) is responsible for its implementation.
- It aims to prevent the worsening of the Air Quality of Delhi-NCR including Ozone pollution.
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): The government launched this campaign to reduce air pollution in 102 non-attainment cities including Ozone pollution.
Source: Science Alert
Gujarat declares ‘Ghol’ as State Fish
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
The Gujarat government’s decision to declare the ‘Ghol’ as the state fish highlights its uniqueness and economic value.
About Ghol Fish
- The Ghol fish or the Blackspotted Croaker, is a significant species in marine fisheries.
- It belongs to the family Sciaenidae and is scientifically known as Protonibea diacanthus.
- It is commonly found in the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the Persian Gulf to Indonesia and north to Japan.
- The Ghol fish is characterized by its robust body, brownish color, and the presence of black spots on its sides.
- It has a large mouth and a slightly protruding lower jaw.
- This species can grow quite large, with some individuals reaching up to 1 meter in length and weighing around 25 kilograms.
Economic Value of Ghol
- The Ghol fish is highly valued, especially for its fish maw (dried swim bladder), which is a delicacy and used in traditional medicines, particularly in East Asian markets.
- The fish maw is believed to have various health benefits and is often used in soups and stews.
- It can fetch high prices in the market, sometimes as much as Rs 25,000 per kilogram.
Source: Indian Express
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 23rd November 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of Vanuatu Islands? |  |
| 2. Who is Sant Mirabai and what is her contribution? |  |
| 3. What is the Israel-Palestine conflict? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE)? |  |
| 5. How did racism overshadow India-Taiwan cooperation? |  |
















