Tips and Tricks for Syllogism | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Syllogism? |

|
| Basic Concepts and Rules |

|
| Methods to Solve Syllogism Questions |

|
| Tips and Tricks for Solving Syllogisms |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
| Conclusion |

|
What is Syllogism?
- Syllogism is a fundamental component of logical reasoning in the Common Admission Test (CAT), a premier MBA entrance exam in India.
- It involves deductive reasoning, where candidates must draw logical conclusions from two or more given statements, known as premises.
- These questions test a candidate's ability to analyse relationships between entities and deduce valid conclusions, making them a critical area for CAT aspirants to master.
- Syllogism questions are a consistent feature of the CAT exam, typically comprising 3–4 questions annually. These questions form a significant portion of the Logical Reasoning section, which includes 20 questions and accounts for approximately 30% of the weightage in the DILR section.
Basic Concepts and Rules
Types of Statements
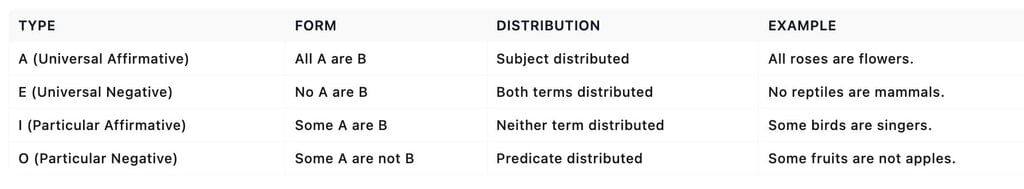
Syllogism statements are categorised into four types based on their quantifiers and polarity:
- A (Universal Positive):
All A are B.
Example: All cats are mammals. - E (Universal Negative):
No A is B.
Example: No birds are reptiles. - I (Particular Positive):
Some A are B.
Example: Some students are athletes. - O (Particular Negative):
Some A are not B.
Example: Some cars are not electric.
Rules for Drawing Conclusions
When combining two statements, the following rules determine the valid conclusions:
Validity Rules
- Middle Term: Must be distributed at least once.
- Quality: If premises include a negative statement, the conclusion must be negative.
- Quantity: The conclusion cannot be universal if a premise is particular.
Single Statement Conclusions
Certain statements imply additional conclusions when reversed:
- E reversed:
If No A is B, then No B is A (E) and Some B are not A (O) are true. - A reversed:
If All A are B, then Some B are A (I) is true. - I reversed:
If Some A are B, then Some B are A (I) is true. - O reversed:
If Some A are not B, no conclusion can be drawn.
Methods to Solve Syllogism Questions
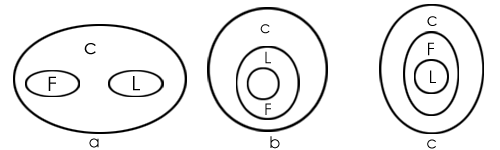
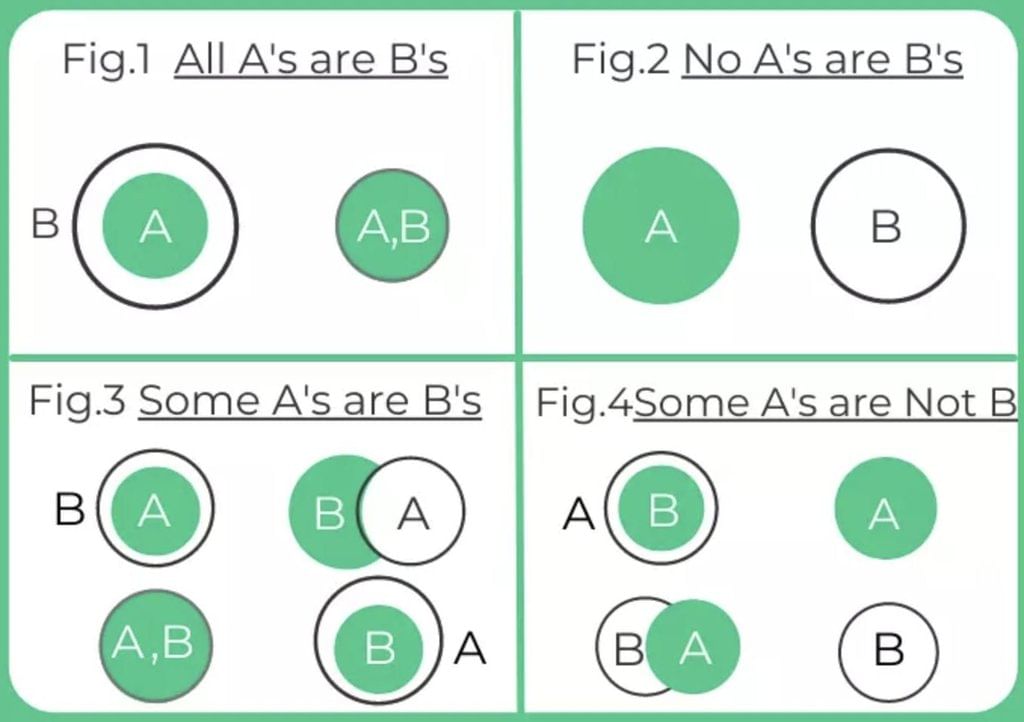
Venn Diagram Method (Preferred)
The Venn Diagram method involves representing statements as overlapping or non-overlapping circles to visualise relationships.
- Steps:
- Draw Venn diagrams for all possible scenarios based on the given statements.
- Analyse the diagrams to check if the conclusion holds true for all possible diagrams. If it does, the conclusion is valid; if it holds for only some diagrams, the conclusion is invalid.
- Advantages: This method is intuitive and helps visualise complex relationships, making it easier to deduce conclusions accurately.
Tips and Tricks for Solving Syllogisms
The following tips and tricks can help CAT aspirants solve syllogism questions efficiently and accurately:
- Practice Regularly: Solve a diverse range of syllogism questions to become familiar with various patterns and conclusions. Regular practice builds confidence and speed.
- Master Venn Diagrams: Learn to draw accurate Venn diagrams for each statement type. Practice deducing conclusions sequentially to ensure clarity.
- Memorise Key Rules: Familiarise yourself with the rules for combining statements (e.g., All + Some = No Conclusion) to solve questions quickly, especially when using the Analytical method.
- Understand Possibilities: Recognise that certain statements imply possibilities rather than definite conclusions. For example:
- If All A are B, then Some B are not A is a possibility.
- If Some A are B, then All A are B and All B are A are possibilities.
- Avoid Assumptions: Base conclusions solely on the given premises. Do not introduce external information or assumptions.
- Manage Time Effectively: Syllogism questions can be time-consuming. Practice solving them quickly, and if stuck, move on and return later if time permits.
- Check for Reversals: Be cautious with reversed statements. For example, All A are B implies Some B are A, but not All B are A.
- Use Shortcut Tricks: Leverage shortcuts to save time:
- All ↔ Some: If All A are B, then Some B are A is true.
- Some ↔ Some: If Some A are B, then Some B are A is true.
- No ↔ No: If No A is B, then No B is A is true.
- Prioritise Easier Questions: In the exam, identify and solve simpler syllogism questions first to secure marks quickly.
- Double-Check Conclusions: Verify conclusions against the original statements to avoid errors.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Which of the two conclusions can be concluded on the basis of given statements?
Statements:
- Some parrots are scissors.
- Some scissors are not combs.
Conclusions:
- Some scissors are parrots.
- Some combs are parrots.
Sol:
Now, in this case, the possible conclusion is:
Some scissors are parrots (I to I), as the universal principal no. 4 says, that with two particular statements only I to I is possible.
Therefore, only 1 conclusion is possible. Nothing else is possible.
Example 2 : Which of the two conclusions can be concluded on the basis of given statements?
Statements:
- All flowers are candles.
- All lanterns are candles.
Conclusions:
- Some flowers are lanterns.
- Some candles are lanterns.
Sol: Three possible diagrams is show in the above for the given statements.
Conclusion I follows from last two possible solutions, but does not follow from the first possible solution. Therefore, this conclusion is false.
Conclusion II follows from all the three possible solutions.
Therefore, conclusion II is true.
Example 3: Which of the two conclusions can be concluded on the basis of given statements?
Statements:
- All prisoners are men.
- No man is educated.
Conclusions:
- All prisoners are uneducated.
- Some men are prisoners.
Sol: So their are two possible diagrams is show in below for the given statements.
Conclusion I follows from both the possibilities, so conclusion I is true.
Conclusion II also follows from both the possibilities, so conclusion II is also true.
Therefore, both conclusions are true.
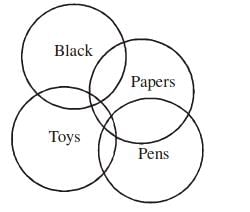
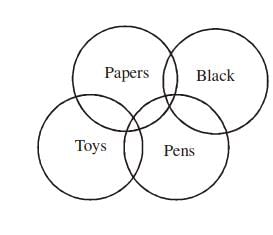
Example 4: Question below has a three statement, followed by four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV. You have to consider every given statement as true, even if it does not conform to the well known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the conclusions can be logically derived.
Statements:
I. Some toys are pens.
II. Some pens are papers.
III. Some papers are black.
Conclusions:
I. Some toys are black.
II. No pen is black.
III. No toy is black.
IV. Some pens are black.
(a) None follows
(b) Either II or IV
(c) Either I or III and either II or IV
(d) Either I or IV
(e) All of the above
Sol:
From the statements
The possibilities are :
orFrom the above two possibilities
we can say Either I or III and either II or IV follows
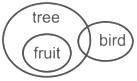
Example 5: Consider the given statements to be true and decide which of the conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements.
Statement:
- All fruits are trees. Some trees are birds.
Conclusions:
- Some birds are trees.
- Some trees are fruits.
(a) Only conclusion 1 follows.
(b) Both conclusions 1 and 2 follow.
(c) Either conclusion 1 or 2 follows.
(d) Only conclusion 2 follows.
(e) None of the above
Sol:
As per the given information,
Conclusion 1: Some birds are trees → As some trees are birds, some birds will be trees, hence it is true.
Conclusion 2: Some trees are fruits → As all fruits are trees, some trees will be fruits, hence, it is true.
Hence, both conclusions 1 and 2 follow.
Example 6: Read the given statements and conclusions carefully. Assuming that the information given in the statements is true, even if it appears to be at variance with commonly known facts, decide which of the given conclusion(s) logically follow(s) from the statements.
Statements:
- All jacks are kings.
- All kings are queens.
Conclusions:
(I) Some queens are jacks.
(II) All jacks are queens.
(a) Only conclusion (I) follows.
(b) Only conclusion (II) follows.
(c) Both conclusions (I) and (II) follow.
(d) Neither conclusion (I) nor (II) follow
Sol:
Given Statements:
All jacks are kings.
All kings are queens.
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is:Conclusions:
I. Some queens are jacks - True (Since all jacks are kings and all kings are queens, jacks are a subset of queens, implying some queens are jacks).
II. All jacks are queens - True (The statement "All kings are queens" and "All jacks are kings" directly implies that all jacks are also included within the set of queens).
So, Both conclusions I and II follow.
Hence, the correct answer is "Option 3".
Example 7: Read the given statements and conclusions carefully. Accept the information given in the statements as correct, even if it appears to be different from 'commonly known facts, and decide which of the given conclusions(s) logically follow from the statements.
Statement:
(I) All tablets are medicines.
(II) All prescriptions are tablets.
Conclusions:
(I) All tablets are prescriptions.
(II) Some medicines are prescriptions.
(a) Only conclusion (II) follows.
(b) Both conclusions (I) and (II) follow.
(c) Neither conclusion (I) nor (II) follows.
(d) Only conclusion (I) follows.
Sol:
The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as shown below :Conclusions:
(I) All tablets are prescriptions. → Follow (As no keyboard is key and all keys are rings. So it is possible but not definite.)
(II) Some medicines are prescriptions. → Does not follow (As some mouse are keyboard and no keyboard is key. As whole prescription comes in tablets which whole comes in medicines, therefore it is true.)
∴ Here, Only conclusion (I) follows.
Hence, the correct answer is "Option 1".
Example 8: Read the given statements and conclusions carefully. Assuming that the information given in the statements is true, even if it appears to be at variance with commonly known facts, decide which of the given conclusion(s) logically follow(s) from the statements.
Statements:
(i)All spades are diamonds.
(ii) All diamonds are hearts.
Conclusions:
(I) Some hearts are spades.
(II) Some spades are hearts.
(a) Only conclusion (II) follows.
(b) Only conclusion (I) follows.
(c) Neither conclusion (I) nor (II) follows.
(d) Both conclusions (I) and (II) follow.
Sol: The least possible Venn diagram for the given statements is as shown below :
Conclusions:
(I) Some hearts are spades → Follow (As all spades are diamonds and all diamonds are hearts. As whole spades comes in diamonds which whole comes in hearts, therefore it is true.)
(II) Some spades are hearts → Follow (As all spades are diamonds and all diamonds are hearts. As whole spades comes in diamonds which whole comes in hearts, therefore it is true.)
∴ Here, Both conclusions (I) and (II) follow.
Hence, the correct answer is "Option 4".
Conclusion
Syllogism is a challenging yet rewarding topic in the CAT exam. By understanding the basic concepts, practising regularly, and applying the tips and tricks outlined above, CAT aspirants can enhance their ability to solve syllogism questions accurately and efficiently. The Venn Diagram method is particularly effective for visualising relationships, while memorising key rules can expedite the Analytical method. With consistent effort and strategic preparation, mastering syllogisms can significantly boost your performance in the Logical Reasoning section, paving the way for a higher overall CAT score. Good luck with your CAT preparation!
|
77 videos|180 docs|96 tests
|
FAQs on Tips and Tricks for Syllogism - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What is Syllogism in CAT? |  |
| 2. How important is Syllogism in the CAT exam? |  |
| 3. What are the types of syllogism questions asked in CAT? |  |
| 4. How can I improve my syllogism solving skills for CAT? |  |
| 5. Are there any shortcuts or tricks to solve syllogism questions quickly? |  |