UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 26th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
Recently, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has busted a major module of cyber-enabled crimes allegedly coercing foreign nationals for payments and recovered cash amounts of nearly 2.2 crore rupees.
Background:-
- As part of the operation, the CBI conducted searches in an ongoing investigation of a case at around 24 locations across multiple States, including Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Gujarat.
About CBI:-
- Establishment and Early Focus:
- Originally established as the Special Police Establishment in 1941 with the primary objective of investigating corruption cases related to procurement during World War II.
- Formation of the CBI:
- The establishment of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption.
- In response, the CBI was officially formed in 1963 through a resolution of the Union Home Ministry.
- Evolution and Merger:
- The Special Police Establishment, dealing with vigilance cases, established in 1941, was later merged with the CBI.
- Originally under the Union Home Ministry, it was later transferred to the Ministry of Personnel, where it currently functions as an attached office.
- Legal Basis:
- The CBI is not a statutory body; instead, it derives its powers from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act of 1946.
- Scope of Operations:
- The CBI serves as the primary investigating agency of the Central Government.
- It specializes in investigating crimes related to corruption, economic offences, and serious and organized crimes (excluding terrorism).
- Leadership Structure:
- The CBI is headed by a Director, who is assisted by a special/additional director.
- Director's Tenure and Appointment:
- The Director of the CBI is granted a security of two-year tenure by the CVC Act of 2003.
- The appointment process involves a three-member committee consisting of the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India or a Supreme Court Judge nominated by the Chief Justice.
- In the absence of a recognized leader of the opposition, the leader of the single largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha is included in the committee.
- CBI Academy and Training Centers:
- The CBI Academy, established in Ghaziabad, UP, commenced operations in 1996.
- Additionally, there are three regional training centers situated in Kolkata, Mumbai, and Chennai.
- Supervision and Oversight:
- The superintendence of CBI concerning the investigation of offenses under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 is under the purview of the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC).
- Other matters fall under the jurisdiction of the Department of Personnel & Training (DOPT) in the Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Grievances of the Government of India.
Functions:-
- Anti-Corruption Mandate:
- Investigating cases of corruption, bribery, and misconduct involving Union government employees.
- Fiscal and Economic Laws:
- Probing cases related to the violation of fiscal and economic laws.
- National and International Crimes:
- Investigating serious crimes with national and international implications perpetrated by organized criminal groups.
- Coordination and Cooperation:
- Coordinating activities among anticorruption agencies and various state police forces.
- Public Interest Cases:
- Taking up, upon request from a state government, cases of public importance for investigation.
- Authorization by the Central Government for investigating a state crime requires consent from the concerned State Government.
- Conventional Crimes:
- Undertaking the investigation of conventional crimes like murder, kidnapping, rape, etc., either on the referral from state governments or as directed by the Supreme Court/High Courts.
- Crime Statistics Management:
- Maintaining crime statistics and disseminating criminal information.
- Interpol Representation:
- Functioning as the “National Central Bureau” of Interpol in India, facilitating international cooperation in law enforcement.
Source: AIR
Ram Madhav writes: Don’t rewrite the Constitution
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
On Constitution Day, voices are emerging to replace India’s Constitution, a unique document created through extensive discussion and amendments.
Comparative Constitutionalism:
- The comparison with other countries like France, Nepal, Chile, and Uzbekistan highlights India’s distinct process of constitution-making.
- Critics label the present Constitution as “colonial,” citing similarities with the Government of India Act 1935, but historical context and unique influences are acknowledged.
Historical Influences and Unique Drafting Process:
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad asserted that India wasn’t bound to adhere strictly to global constitutional categories, emphasizing the influence of India’s historical realities.
- The Nehru Report’s significance in shaping constitutional ideals, serving as a foundation for future constitutional struggles.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- The challenge lies in addressing criticisms of the Constitution being “colonial” and responding to calls for a rewrite, balancing historical influences with contemporary needs.
- Achieving political consensus, as witnessed in the unique drafting process, is a monumental task, especially considering the diverse opinions and interests.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Nehru Report: Draft constitution prepared in 1928 as a response to the challenge posed by Lord Birkenhead, emphasizing fundamental rights and democratic principles.
- Government of India Act 1935: Considered by some as a “colonial” precursor to the Indian Constitution, but viewed differently by considering historical context.
Critical Analysis:
- The article navigates the complexities of assessing India’s Constitution, acknowledging historical influences while defending its efficiency in serving the nation.
- The challenges of potential rewriting are highlighted, emphasizing the need for political consensus and the unique historical context.
Way Forward:
- The way forward involves careful consideration of the Constitution’s strengths, historical foundations, and the feasibility of rewriting in the context of contemporary needs.
- Any potential rewriting should uphold the principles of a “fair measure of general agreement” among India’s diverse population, echoing the spirit of the Nehru Report.
Source: Indian Express
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
Background:-Recently, the National Investigation Agency (NIA) conducted simultaneous raids in Kaimur, Gaya and Aurangabad districts following Naxal-related inputs in Bihar.
- During the raids at different locations in Naxal affected Adhaura area in Kaimur three suspected Maoists were arrested.
- NIA is functioning as the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency in India.
- Establishment: 2008.
- It was established by National Investigation Agency Act, enacted on 31-12-08. (NIA)
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a central agency to investigate and prosecute offences:-
- affecting the sovereignty, security and integrity of India, security of the State, and friendly relations with foreign States.
- against atomic and nuclear facilities.
- smuggling in High-Quality Counterfeit Indian Currency.
- It implements international treaties, agreements, conventions and resolutions of the United Nations, its agencies and other international organisations.
- The agency at the Central level was created for t investigation of offences related to terrorism and certain other Acts post-2008 Mumbai terror attacks.
- In-depth professional investigation of scheduled offences using the latest scientific methods.
- Ensuring effective and speedy trials.
- Developing into a thoroughly professional, result-oriented organization.
- Developing a professional workforce through regular training and exposure to the best practices and procedures.
- Maintaining professional and cordial relations with the governments of States and Union Territories and other law enforcement agencies in compliance with the legal provisions of the NIA Act.
- Assist all States and other investigating agencies in the investigation of terrorist cases.
- Build a database on all terrorist-related information.
- Share the database available with the States and other agencies.
- Study and analyse laws relating to terrorism in other countries.
- Evaluate the adequacy of existing laws in India and propose changes as and when necessary.
- To win the confidence of the citizens of India through selfless and fearless endeavours
Source: AIR
GS-III
SURAT Warship
Subject: Defence
Why in News?
Recently, the Crest unveiling ceremony of the Indian Navy’s Warship “SURAT”.
Background:-
- The Crest of Indian Navy’s latest, indigenous under-construction, guided missile destroyer, ‘Surat’, is scheduled to be unveiled by Shri Bhupendra Patel, the Chief Minister of Gujarat in the presence of Adm R Hari Kumar, the Chief of the Naval Staff, at a ceremony to be held in the city of Surat .
About SURAT Warship:-
Builder: The destroyer was constructed by Mazagon Docks Shipbuilders Ltd. in Mumbai.
- Naming Significance: The destroyer is named after the commercial capital of Gujarat - Surat, reflecting its rich maritime and ship-building history.
- Project 15B Destroyer: INS Surat marks the culmination of the Project 15B series, being the fourth and final ship in the Indian Navy's Destroyers.
- Class Designation: These destroyers belong to the Visakhapatnam class, named after the lead vessel INS Visakhapatnam, following the naval tradition of naming Indian Naval Destroyers after cities.
- Historical Context: The lineage of naming Indian Naval Destroyers after cities began with Project 15. The subsequent Project 15A included INS Kolkata, INS Kochi, and INS Chennai. The current Project 15B involves the construction of next-gen stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- Project 15B Overview:
- Vessels: The Project 15B program encompasses the construction of four stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- Commissioning Schedule: INS Visakhapatnam was the first, followed by INS Mormugao, INS Imphal, and finally, INS Surat, which is expected to be commissioned in 2024.
- Construction Methodology: INS Surat was built using the Block construction methodology, involving hull construction in separate locations and subsequent assembly at a central hub.
- Warship Category: INS Surat is a formidable Guided-missile destroyer.
- Geographical Significance: Notably, INS Surat holds the distinction of being the first capital warship named after the city of Gujarat.
- Upcoming Commissions: While INS Mormugao is set to be commissioned in 2022, INS Imphal is scheduled for 2023, and INS Surat is likely to be commissioned in 2024, all following one-year intervals.
Source: PIB
Cashew Crop
Subject: Agriculture

Why in News?
Recently, the chairman of the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority said that APEDA facilitated the exporting of over 30 tonnes of cashew on World Cashew Day.
About the Cashew Crop:
- Geographical Origin and Introduction:
- Native to Brazil in Latin America, the cashew tree was introduced to India by the Portuguese in the 16th century (1570).
- Climatic Conditions:
- Soil and Climate Suitability:
- Well-drained deep sandy loam soils are ideal for cashew cultivation.
- Various soil types, including sandy and laterite, are generally suitable.
- Adaptation to Indian Coastal Areas:
- Cashew trees thrive in Indian coastal regions characterized by hot and humid conditions.
- Temperature Range:
- Optimal growth occurs in temperatures ranging from 20 to 38 °C.
- Humidity Range:
- Relative humidity in the range of 60 to 95% is conducive for cashew cultivation.
- Rainfall Requirements:
- Annual precipitation ranging from 2000 to 3500mm is favorable.
- Extremely low temperatures and frost are not conducive to successful cashew plantations.
- Expansion to Non-Traditional Areas:
- Cashew cultivation is expanding beyond traditional areas, reaching the plains of Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh, and some parts of the North East hill region.
- Global Significance:
- India holds the second-largest share in the world's cashew nut production and exports.
- Top Export Destinations:
- Key export destinations for Indian cashew nuts include the UAE, the Netherlands, Japan, and Saudi Arabia.
- Soil and Climate Suitability:
Key facts about Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)
- Establishment and Legislative Foundation:
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) was established by the Government of India through the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act of 1985.
- Administrative Oversight:
- APEDA operates under the auspices of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Core Objective:
- The primary goal of APEDA is to develop and promote the export of products specified under its jurisdiction.
- Scheduled Products and Registration:
- Products specified under the APEDA ACT are termed scheduled products.
- Exporters dealing with scheduled products are mandated to register under APEDA.
- Supportive Functions:
- APEDA plays a pivotal role in the development of scheduled products by providing:
- Financial Assistance
- Information
- Guidelines for exporters involved in the trade of scheduled products.
- APEDA plays a pivotal role in the development of scheduled products by providing:
Source: The Hindu
Need for climate-smart agriculture in India
Subject: Agriculture

Why in News?
The article underscores the critical challenges of climate change and food insecurity facing humanity. It emphasizes the significance of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) as a holistic approach, promoting sustainable development, resilience to climate change, and greenhouse gas emission reduction.
Key Highlights:
- Global Challenges: Addressing climate change and food insecurity as critical global issues.
- Impact on Agriculture: Discussing the negative effects of climate change on agriculture, leading to increased challenges for farmers.
- Holistic Solution: Introducing climate-smart agriculture (CSA) as a holistic solution to adaptation and mitigation challenges.
- Emphasizing Importance: Highlighting the importance of CSA in enhancing resilience, improving productivity, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Government Initiatives: Citing Indian government initiatives promoting CSA, such as the National Adaptation Fund and Soil Health Mission.
Key Challenges:
- Climate Risks: Analyzing the substantial risks posed by climate change to agricultural productivity, with India potentially facing a 9% decline in crop yield.
- Need for Reforms: Discussing the need for significant reforms in the agriculture industry to adapt traditional farming practices to climate change.
- Transformative Approach: Emphasizing the requirement for a radical transformation of the agriculture sector to achieve sustainable development goals.
Key Terms/Phrases:
- Holistic Approach: Exploring the concept of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) and its three pillars.
- Precision Farming: Highlighting the importance of precision farming in optimizing agricultural methods.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Describing the role of CSA in building resilience against climate change.
- Agroforestry and Carbon Sequestration: Identifying specific CSA measures for environmental benefits.
- Paris Agreement: Linking CSA to global initiatives such as the Paris Agreement on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Key Examples and References:
- Global Efforts: Noting community-supported agriculture efforts worldwide as examples of CSA in action.
- Specific Measures: Citing studies from the northwest Indo-Gangetic Plain showcasing the benefits of CSA for wheat production.
- Government Support: Referring to government initiatives in India, including the Soil Health Card Scheme.
- International Frameworks: Connecting CSA to international frameworks like the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Key Facts/Data:
- Climate Impact: Highlighting the potential 9% decline in crop yield in India due to climate change.
- GHG Emissions: Noting agriculture’s significant share (17%) in greenhouse gas emissions in 2018.
- Economic Autonomy: Pointing out the economic autonomy gained by farmers through CSA implementation.
- Government Initiatives: Providing data on government spending on initiatives like the National Adaptation Fund.
Critical Analysis:
- Urgency of Action: Emphasizing the urgency of addressing climate change’s impact on agriculture and the need for a comprehensive approach like CSA.
- Positive Outcomes: Discussing the positive outcomes of CSA, including economic autonomy for farmers and benefits to biodiversity conservation.
- Localized Responses: Highlighting the importance of localized responses to climate change and the role of CSA in meeting international obligations.
Way Forward:
- Investment in Capacity-Building: Recommending continued investment in capacity-building programs for CSA.
- Knowledge Dissemination: Emphasizing the importance of providing practical tools and knowledge for the adoption of CSA.
- Triple Goals: Stating the role of CSA in ensuring food security, empowering farmers, and protecting ecosystems.
- Unique Juncture in India: Recognizing the unique juncture in India where CSA adoption is essential due to climate vulnerability and agricultural significance.
Source: Indian Express
What is Carbon Dioxide Removal?
Subject: Environment and Ecology
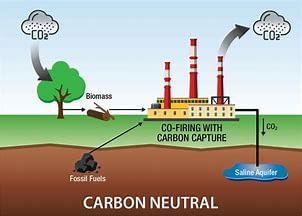
Why in News?
According to the Emissions Gap report, delaying greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction will further increase the future dependence on carbon dioxide removal (CDR) from the atmosphere.
About Carbon Dioxide Removal:
- It is using technologies, practices, and approaches to remove carbon dioxide from our atmosphere through deliberate and intentional human actions.
- This includes traditional methods like afforestation as well as more sophisticated technologies like direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS).
What are the different CDR methods?
- Biochar
- It is the substance produced by burning organic waste from agricultural lands and forests in a controlled process called pyrolysis.
- Although it resembles common charcoal in appearance, the production of biochar reduces contamination and is a method to safely store carbon.
- Pyrolysis involves the burning of wood chips, leaves, dead plants, etc. with very little oxygen, and the process releases a significantly small quantity of fumes.
- Biochar is a stable form of carbon that cannot easily escape into the atmosphere.
- Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS)
- It involves bioenergy production, often through combustion to generate electricity or heat.
- The resulting CO2 emissions from this combustion are captured and stored underground, preventing them from contributing to the greenhouse effect.
- It sequesters photosynthetically fixed carbon as post-combustion CO2.
- Direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS)
- It extracts CO2 directly from the atmosphere at any location.
- This captured CO2 is then permanently stored in deep geological formations or used for other applications.
- It uses electricity to remove CO2 from the air.
- Enhanced rock weathering
- It involves pulverising silicate rocks to bypass the conventionally slow weathering action.
- The resultant product, usually a powder, has a higher reactive surface area, which is then spread on agricultural lands for further chemical reactions.
- Ocean alkalinity enhancement
- It involves adding alkaline substances to seawater to accelerate this natural sink.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|





















